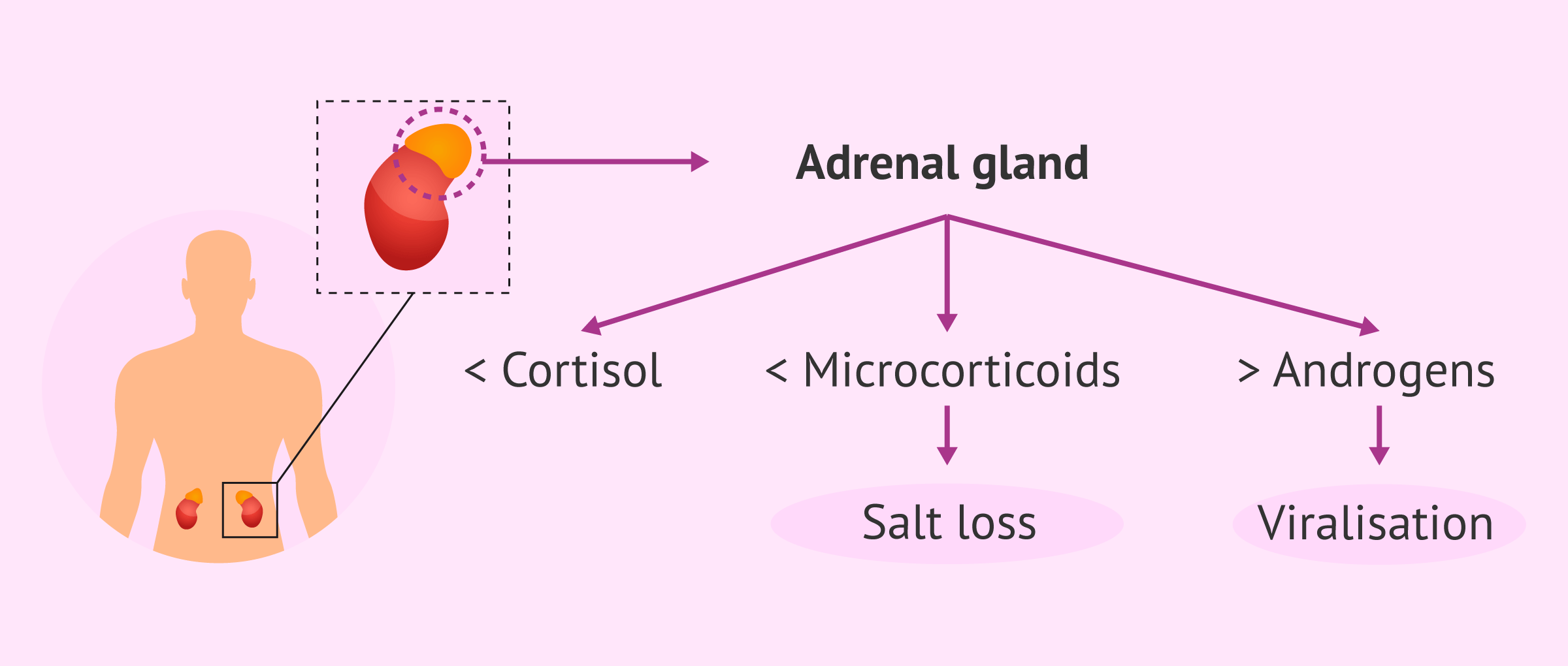
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is an autosomal recessive inherited metabolic disease affecting the adrenal glands, located above the kidneys. The adrenal glands are responsible for the production of cortisol, mineralocorticoids and androgens. When there is a diagnosis of adrenal hyperplasia, there will be a decrease in cortisol and mineralocorticoid levels; while androgen levels will increase.
Neonatal diagnosis can be of vital importance in detecting congenital adrenal hyperplasia. The heel prick test collects a blood sample from the baby in the first two days of life and a second sample after the first four days. This test is also used for the detection of other congenital diseases such as hypothyroidism.
Read the full article on: Congenital adrenal hyperplasia: types, symptoms and treatment ( 47).
By Marta Barranquero Gómez B.Sc., M.Sc. (embryologist) and Neus Ferrando Gilabert B.Sc., M.Sc. (embryologist).
Last Update: 07/05/2023