Throughout the 9 months of pregnancy, the fetus keeps on growing in size until it is fully developed as a human: from a zygote to a baby. At the same time, the body of the pregnant woman and the symptoms that accompany her during pregnancy change month after month as fetal development progresses.
It is common to talk about pregnancy in weeks, months or trimesters. In this article, we will summarise what happens month by month in the baby's pregnancy, as well as the changes and symptoms that a woman may notice.
Provided below is an index with the 14 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 11.1.
- 11.2.
- 11.3.
- 11.4.
- 11.5.
- 11.6.
- 11.7.
- 11.8.
- 11.9.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
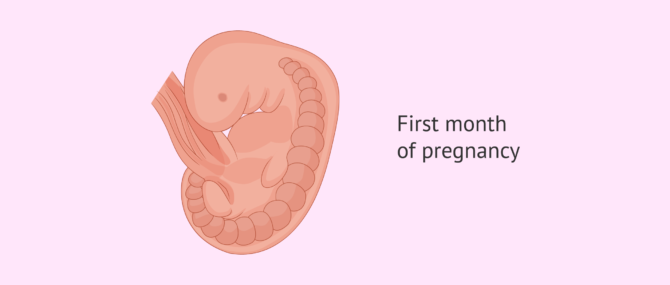
One month pregnant
If several sexual intercourses take place during a woman's fertile days in search of pregnancy, it is common that it is not known exactly when conception occurred and the exact onset of pregnancy. However, it is easier for a woman to know when her last period was. Therefore, this is the date that is usually taken as a reference and, therefore, the first week of gestation, in reality, corresponds to the week in which the woman had her last menstrual period.
Follicle recruitment occurs during the second week, in which a set of pre-selected follicles starts growing. However, at the end, only one of them will continue developing.
At the third week, the process continues. An egg is released from the follicle that contained it. Afterwards, the egg cell will start its journey through the Fallopian tubes, a step known as ovulation. Once in the tube, the goal of the oocyte is to be fertilized by a spermatozoon, and to continue developing as a zygote (one cell) first and then as an embryo.
As Dr. Silvia Jiménez explains, the embryo will continue on its way to the uterus, where it will implant approximately 7-9 days after ovulation. At this time, the embryo takes between 6 and 8 days to develop. Thus begins the release of the hormone beta-hCG, which is the hormone detected by pregnancy tests.
In an in vitro fertilization cycle, on the other hand, the embryo can be transferred on day 2, 3 or 6. When it is transferred on day 6-8 (blastocyst stage), the embryo is more evolved and implantation can occur around one day after transfer.
It is possible that, due to the increase of this hormone, the woman starts to notice some symptoms in this first month, but in a very soft and practically imperceptible way. Until the absence of the next menstruation, she will not be truly aware of the pregnancy.
After embryo implantation, gastrulation takes place. The cells of the epiblast divide until they form three different types of cells, which will become the baby's tissue in the future. The cells of the mesoderm develop at this point too, as well as the notochord, which replaces the role of the vertebral column till its formation.
The size of the embryo is still so small that it cannot even be spotted through an ultrasound yet.
Get more information about this stage here: First month of pregnancy.
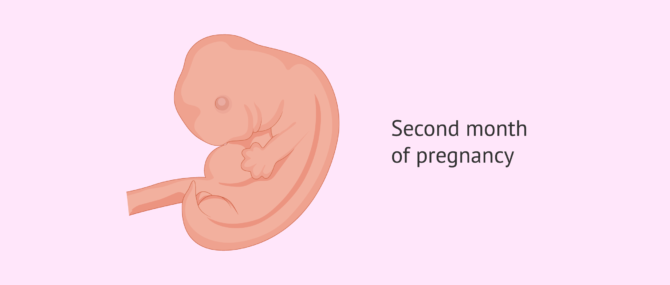
Two months pregnant
During the second month of the pregnancy, the spinal cord, the brain, the heart, the intestine, and the skin are formed. The eyes, ears, nose, and upper lip as well as the limbs begin to develop as well. Many things happen throughout this month, in which the embryo starts resembling a human being.
At one end of the embryo, a round-shaped head, thicker than the torso, will develop, while a kind of tail will grow at the other end.
This month of pregnancy is crucial because the heart develops at this point, which is the vital organ of the baby-to-be per excellence.
Changes in the mother are unnoticeable yet. Her belly is still not visible to the plain eye, but she is likely to start feeling typical pregnancy symptoms, including nausea, sickness, tiredness... In some cases, pregnancy progresses without symptoms, but it should be clear that it's not a negative sign—it just means that symptoms vary from woman to woman.
Continue reading about the second month of pregnancy in the following post: 2 months pregnant.
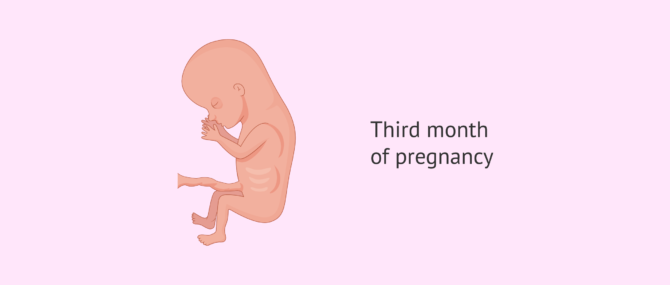
Three months pregnant
After the third month of pregnancy, the embryonic stage is over and the fetal stage begins, so the embryo is now called fetus. The baby-to-be already has all the organs but they are still developing. Further growth is necessary for them to be considered fully developed. During this month, the male or female genitals are formed as well. However, in spite of this, it is not easy to see the baby's gender yet.
Through these 4 weeks, the fetus grows around 7 cm long and can weight up to 15-20 g approximately. It is common for the pregnant woman to start gaining weight from this moment on. During the 3rd month of pregnancy, you will gain about 10% of the total weight you are expected to gain throughout the entire pregnancy.
The baby moves vigorously but you cannot feel him yet. The baby now kicks, rotates the ankles and wrists, opens and closes the fists, and bends the toes. He also frowns, squeezes the lips, and makes other facial movements. You should be aware that this is common in every pregnancy in order not to be concerned when it happens. The fact that the baby starts moving more vigorously is not something to be concerned about, but rather a very positive sign—it indicates that the baby is very much alive, and that everything is working as expected.
By the end of the third months, the uncomfortable symptoms caused by the beta hCG hormone begin to disappear, such as nausea and morning sickness, as hCG levels start to level off.
This month usually gives prospective parents a sense of safety and wellness, given that, from the third month of pregnancy onwards, the risk of miscarriage decreases to a large extent. No remarkable issues or complications are expected to appear in the months to come.
Also at this point, the bond between the mother and the fetus becomes stronger. For this reason, the mother is likely to pay closer attention to her diet and lifestyle, as everything that she does or eats affects the fetus directly.
You can get further information on the symptoms, signs and changes that occur during the third month of pregnancy here: 3 months pregnant.
Four months pregnant
In this month, the fetus is all covered in a downy hair called lanugo. The role of lanugo is to keep the fetus warm, as its body does not produce enough body fat yet.
The vocal cords are formed at this stage but the baby won't be using them until birth. As a matter of fact, this is the reason why children cry right after being delivered, or it is initiated if they do not do it automatically. The purpose of causing them to cry is to ensure that the vocal cords work properly and that the baby responds to stimuli.
The baby's eyes are big, shut, and separated during this phase. Although they are still very separated from each other, the face of your baby is well-defined, and we can now spot a neck, which allows us to differentiate the head from the rest of the body. Teeth begin to show up, although there is still a long process till they are fully out. The outer ear moves upwards.
As your baby's face defines more accurately, its muscles become capable of practicing suckle movements. This is the reason why babies suck their thumb. Thumb-sucking becomes a habit in most children throughout their early years.
At the beginning of this month, the size of your baby is about 8.5 cm long, and can grow to up to 18 cm. As for the weight, it usually ranges from 150 to 170 grams. Skin folds start to develop on the palm of the hands and the fingers—your baby has now a fingerprint.
Also, this month, the baby begins to expel urine, which is mixed with amniotic fluid. The functions of his sweat and sebaceous glands begin to develop. The intestine begins to fill with a thick substance secreted by the liver called meconium.
The volume of your belly will continue to increase, as will your body weight. To notice the baby is something already habitual in this month, because by his size and development, his movements are frequent.
If you want to learn more about this 4th month, you can read this post: What Happens During the 4th Month of Pregnancy?
Five months pregnant
During the fifth month of pregnancy, the internal organs develop faster. As regards the blood system, the heart chambers are completely delimited and the heart beats strongly. Other relevant changes occur at this stage, such as the development of basic senses, including the sense of taste, along with the taste buds. Also, the baby is now able to notice the first sounds and lights.
By the end of this month, your baby can measure up to 22-25 cm approximately.
Sometimes you will think that the baby is asleep because he is not moving and then, when you lay down, you will feel your baby move. That is because, when you are lying down, the baby can move more easily and when you get up, he gets stuck in the pelvis.
Your baby will develop the second layer of teeth during approximately the last weeks of the 5th month. Baby teeth have now developed within the dental alveoli. Millions of neurons are created in the brain, which is almost as developed as it will be by the time of birth.
Your navel is likely to go flat or, conversely, pop out. In this case, it will come back to normal when you give birth. As for your womb, it will move upwards, to the height of your navel. This process will transform your silhouette completely, as it is time for your waist to thicken.
Nausea, vomiting, and sickness often disappear at this point, but other symptoms can appear now, including heartburn or stuffiness in your nose. This is caused by your digestion process slowing down its rhythm and by the changes that occur in the position of your baby, which press against your body.
Learn more about the changes that occur during this month by clicking the following link: Five months pregnant.
Six months pregnant
In the sixth month, the baby has got hair, eyebrows, and eyelashes. The length of the umbilical cord allows him to move in the amniotic sac he is in. These movements facilitate the development of the muscles.
The baby is now developing specific sleep and activity patterns. You may even feel his reaction to loud noises. If you play music, you will feel his response, particularly to the metal instruments of an orchestra. The baby moves energetically.
Your baby is expected to be between 27cm and 32 cm in length, and from 450 until about 750-1,000 g in weight. You may be able to touch the different parts of his body through your abdominal wall.
The skin of your baby will lose its translucent appearance and become more consistent. Now, he or she can open and close the eyes, in addition to being able to make gestures such as sticking the tongue out. His body becomes more proportioned in comparison with the head. In short, your baby's development is very advanced at this point and he resembles very much the newborn that you will hold in your arms very soon.
The end of the second trimester is coming to its end, and your belly is now more than evident to the plain eye. The weight of the baby has increased a lot, which may cause you to feel exhausted, experience lower back pain, certain positions make you really uncomfortable, or feel bloated.
To delve deeper into this month of pregnancy, visit the following article: 6 months pregnant.
Seven months pregnant
The seventh month of pregnancy marks the start of the third trimester. Fetal development is at an advanced stage now—and delivery is closer. It is totally normal if you feel more tired or even bloated. Likewise, you are likely to experience trouble sleeping, as well as performing basic movements, like lying your shoes, or bending down to pick something from the floor. Moreover, your feet and ankles are likely to swell.
During this month, the baby's lungs are fully developed. The skeleton is more consistent because the ossification of the bone tissues. The fat is stored in his body, which will help the baby regulate the body temperature by itself. This will be very useful following birth.
The amount of hair covering the baby's body is considerably reduced, and lanugo disappears.
Throughout this month, the weight of the fetus increases from 33 cm to 38 cm approximately, and the weight can range from about 1,100 to 1,300 g.
Due to this significant increase of the length and the weight, the movements of the baby are more limited. Now, he is likely to exert more pressure against your bladder. This might cause you not only to feel more intensely the movements of the fetus, but also a constant urge to urinate.
The skin gets thicker and pigmented. The iris gets pigmented too. Pigmentation occurs thanks to a group of cells called melanocytes, that is, melanin-producing cells.
For more information about the 7th month of pregnancy, click here: Seven months pregnant.
Eight months pregnant
The body hair starts falling off. Also, the baby continues to gain weight, so he takes up all the space in the uterus while at the same time he keeps on putting more and more pressure on your bladder. Throughout this month, he will gain half the total weight that babies gain during the 10 months of pregnancy.
The lungs are almost fully developed and therefore they occupy more room in the uterus, causing you to feel more bloated, especially when lying down on bed. Normal symptoms include trouble sleeping, as it will be more difficult for both you and the baby to move.
In addition to being able to feel the light and hear sounds, the olfactory neurons are formed and the baby can now perceive the strong smells that you might encounter, a sign that the brain is still developing. You will feel that his movements are spasmodic. This is due to the fact that the baby might hiccup because he has swallowed too much amniotic fluid. But that is a good symptom because it puts into motion the alimentary canal.
At this point, pregnancy is likely to give you heartburn or to cause you really bad constipation. These are common pregnancy symptoms at the ninth month and are caused by a rise in progesterone levels. There is no reason to be concerned. We recommend that you each foods that are rich in calcium, iron, folic acid, proteins, and vitamin C. You are in the final stages of pregnancy, so you must take special care of yourself, while continuing with your normal lifestyle as long as possible.
Feeling extremely tired during this stage is a typical symptom as well. It is caused not only by an increase in your body weight, which causes fatigue in most women, but also because your womb has expanded in a way that presses your side and causes rib pain, thereby making it harder for you to breathe.
See how your baby develops during this month of pregnancy with this guide: Eight months pregnant.
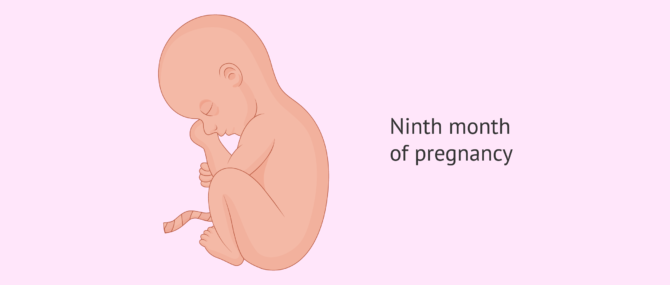
Nine months pregnant
The baby gets the head stuck in the mother's pelvis. Both his stomach and intestine are now working. The skin is no longer wrinkled but softer thanks to the fat cells of the skin; you will notice that your belly is lower. His skin color has turned from reddish to more pinkish, and it is now more similar to the skin color he will have at birth.
As explained earlier, for several weeks now, since the baby is stuck, he moves less and you will probably only feel some kicks and weak movements. In fact, you will feel him every day, which means that everything is going as it should.
By the end of month 9, your baby will measure about 43 centimeters and his weight is expected to increase from 1,980 g to 2,730 g on average.
His kicks can leave you breathless, as if he was kicking you literally, but this just means that he has almost no room for moving. He will turn head down to prepare for labor, and you will be able to distinguish between a foot, back or hand perfectly. The nails are now well formed, reaching the end of the fingers.
The baby is now able to breath and make gestures such as sucking or swallowing at the same time, movements that will allow him to feed from breast milk following birth. He starts producing his own blood cells as well.
Most mothers-to-be perceive this as a very long moth, although at the same time they live it very intensely. The due date is almost there and they cannot wait to see their baby's face.
Want to learn more about the ninth month of pregnancy? Check out our complete guide: 9 months pregnant.
Last month of pregnancy
During the last stages of pregnancy, both his little toenails and fingernails are rather long—beyond the finger tips—so the baby can scratch or even scrape himself.
The baby's organs can work autonomously and even the lungs are fully developed—he is ready to leave the placenta and the mother's stomach. The uterus will be responsible for exerting all the necessary help as to induce labor naturally.
The baby now measures about 45 to 55 cm, and can weight from 2,520 to 3,670 grams.
You are likely to notice the so-called Braxton Hicks contractions, which occur right before real labor. The amniotic fluid will renew itself every 3 hours. The intestine of your child is full of olive green to black meconium, composed of materials secreted by the digestive glands, along with bile pigment, lanugo, and intestinal epithelial cells.
Water breaking, and therefore labor, can start at any moment. You should be prepared to get to the hospital as soon as possible.
If, after week 42, the baby is not born, labor might be induced, as your baby is more than ready to be born. In fact, going past your due date can be risky for both of you.
Find out what happens during the last month of pregnancy here: 10 months pregnant.
FAQs from users
How soon can you find out the gender of your baby?
Most pregnant women can find out the sex of their baby-to-be, if they choose so, usually between weeks 16th and 20th, that is, during mid-pregnancy. Your doctor may not be able to tell for sure if he or she cannot get a clear view of the genitalia, though.
What should I eat during pregnancy?
In general, your body needs extra nutrients, minerals, and vitamins when you are pregnant. As a matter of fact, you may need to add 350-500 extra calories each day, especially during the second and third trimester of pregnancy.
Keep in mind that key nutrients are essential for the baby's development, and poor eating habits may increase the risk of gestational diabetes and birth complications.
How does the pregnancy trimester system work?
A normal pregnancy, that is, a full-term pregnancy, is divided into three trimesters. In total, a full-term human pregnancy is expected to last 40 weeks, although it can cary from 37 to 42. Each trimester lasts 12-14 weeks approximately.
How does X-ray affect pregnancy?
It is commonly said that getting an X-ray during pregnancy can harm your baby and while it might be true, actually not getting one can harm you. So, in short, this statement can be considered partially true.
According to the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), X-rays are considered safe during pregnancy, but it is true that they should only be done when absolutely necessary.
Moreover, the American College of Radiology (ACR) states that there is no diagnostic X-ray with a radiation dose so significant as to cause negative side effects in a developing embryo/fetus.
What is the longest human pregnancy on record?
Currently, the record belongs to Beulah Hunter, a woman from Los Angeles, California, who had her daughter when she was 25 years old. She carried her daughter in the womb for three extra months, considering that a normal pregnancy lasts 280 days and hers lasted 375.
How does a baby stop growing in the womb?
When a baby stops growing inside the womb before birth, we refer to this situation as intrauterine growth restriction or IUGR. However, not all small fetuses have IUGR—they are just smaller than normal.
In this situation, the baby is smaller than normal during pregnancy. In other words, he or she is not growing at the normal rate and subsequently will have low birth at birth.
The causes behind IUGR are varied, but most commonly it is due to a problem in the placenta. Also, genetic disorders, birth defects, infections in the mother, high blood pressure, smoking or drinking too much, drug abuse, certain prescribed medicines, etc. can lead to IUGR.
Can you tell if it is a boy or a girl in the fourth month of pregnancy?
It is most common to wait until 18-22 weeks of pregnancy to find out the sex of the baby. However, it is sometimes possible to know if it is a boy or a girl earlier by ultrasound.
How does pregnancy affect the skeletal system?
Pregnancy can change a woman's physical appearance in many ways. Let us explain the most evident ones below:
- The uterus can expand up to 1,000 times
- Realignment of the spinal curvatures
- These changes cause the woman to change her way of walking (commonly known as waddling gait)
- The center of gravity is shifted back over the pelvis
- The mobility of the pelvic joints increases
- All this allows stretching at the time of delivery
How do babies grow hair in the womb?
It should be noted that the layer of soft, fine hair that starts growing on the fetus at the 30th week of pregnancy is not hair as we know it, but lanugo. It starts to fall of prior to delivery, when actual hair starts to grow, beginning with the eyebrows and eyelashes.
Lanugo starts to cover the body of babies in the womb as a way to regulate their own body temperature, given that they still do not have enough fat. When lanugo falls off, babies literally eat it and expel it with their first "poop", which is known as meconium.
Suggested for you
Before a woman falls pregnant, sperms must begin a race towards the egg. However, only of them will be the winner and manage to hit the egg inside the Fallopian tube and fertilize it. Want to learn about the obstacles that sperms must overcome throughout this journey? Click here: The sperm's journey to the egg.
Likewise, woman who get pregnant or suspect that they may have fallen so often worry about the signs and symptoms that accompany it, especially at the earliest stages. The following is a guide where you will find the most common pregnancy symptoms, both physical and emotional: Common signs of pregnancy.
If you have just found out that you are expecting, you should take special care of yourself now more than ever. Following a balanced diet, avoiding habits and practices that may be detrimental for both you and the baby-to-be is a key factor toward a healthy pregnancy. Visit the following post to get more info about basic care: Staying healthy during pregnancy.
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Fileva N, Severino M, Tortora D, Ramaglia A, Paladini D, Rossi A. Second trimester fetal MRI of the brain: Through the ground glass. J Clin Ultrasound. 2023 Feb;51(2):283-299. doi: 10.1002/jcu.23423. PMID: 36785503. (View)
Fleming N, O'Driscoll T, Becker G, Spitzer RF; CANPAGO COMMITTEE. Adolescent Pregnancy Guidelines. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2015 Aug;37(8):740-756. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(15)30180-8. PMID: 26474231. (View)
Hicks JB. Contractions of the Uterus Throughout Pregnancy. Buffalo Med Surg J. 1887 Oct;27(3):97-99. PMID: 36668326; PMCID: PMC9474068. (View)
Lacasse A, Rey E, Ferreira E, Morin C, Bérard A. Validity of a modified Pregnancy-Unique Quantification of Emesis and Nausea (PUQE) scoring index to assess severity of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jan;198(1):71.e1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.05.051. PMID: 18166311. (View)
Sangram Singh B, Joshi K, Pajai S. Intra-cervical Foley Balloon Catheter Versus Prostaglandins for the Induction of Labour: A Literature Review. Cureus. 2023 Jan 17;15(1):e33855. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33855. PMID: 36819352; PMCID: PMC9932625. (View)
Vasciaveo L, Zanzarelli E, D'Antonio F. Fetal cardiac function evaluation: A review. J Clin Ultrasound. 2023 Feb;51(2):215-224. doi: 10.1002/jcu.23421. PMID: 36785505. (View)
Zhang Y, Xu X, Xie Z, Li Y, Zhao D, Lv G, Li P. Identifying symptom clusters among pregnant women during early and late pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2023 Feb 2. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.14712. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36728592. (View)
Zhu S, Zhao A, Lan H, Li P, Mao S, Szeto IM, Jiang H, Zhang Y. Nausea and Vomiting during Early Pregnancy among Chinese Women and Its Association with Nutritional Intakes. Nutrients. 2023 Feb 13;15(4):933. doi: 10.3390/nu15040933. PMID: 36839295; PMCID: PMC9962185. (View)
FAQs from users: 'How soon can you find out the gender of your baby?', 'What should I eat during pregnancy?', 'How does the pregnancy trimester system work?', 'How does X-ray affect pregnancy?', 'What is the longest human pregnancy on record?', 'How does a baby stop growing in the womb?', 'Can you tell if it is a boy or a girl in the fourth month of pregnancy?', 'How does pregnancy affect the skeletal system?' and 'How do babies grow hair in the womb?'.
Authors and contributors












Can you get pregnant with your tubes tied? I wonder because I actually don’t know…
Hey PattyFirth,
No, that is precisely the purpose of tubal ligation… The only way you can get pregnant with your tubes tied is my means of IVF because fertilization occurs outside your body in the lab.