The hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is a glycoprotein released by the embryo after implantation in the maternal uterus. For this reason, hCG is known as the pregnancy hormone the pregnancy hormone the detection of hCG allows the confirmation of pregnancy.
In addition, there are quantitative pregnancy tests performed from a blood sample, which give the exact hCG hormone value as a result. This type of test thus makes it possible to establish reference values according to the weeks of gestation.
Provided below is an index with the 9 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 3.1.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 6.1.
- 6.2.
- 6.3.
- 6.4.
- 6.5.
- 6.6.
- 6.7.
- 6.8.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
Beta-hCG hormone tests
Although it is commonly referred to as beta-hCG, the truth is that the hCG hormone consists of two subunits:
- The alpha fraction
- common with other hormones released by the pituitary gland such as TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone), FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) or LH (luteinizing hormone).
- The beta fraction
- is unique to the hCG hormone and, therefore, is the subunit detected by pregnancy tests.
Pregnancy tests detect the beta subunit of hCG, whether performed in urine or blood. In addition, two ways of analyzing this hormone can be distinguished:
- Quantitative pregnancy tests
- show the exact level of the hormone in maternal blood.
- Qualitative pregnancy tests
- only indicate the presence or absence of beta-hCG hormone in blood or urine, without giving an exact value.
In relation to quantitative tests, there are ranges of normal hCG hormone values that indicate whether the woman is pregnant or not. In addition, these values can give approximate information about the weeks of gestation.
Beta-hCG reference values
The hCG hormone is present in a woman's body throughout pregnancy, but its levels vary as the pregnancy progresses.
During the first trimester of pregnancy, hCG is increasing until it reaches a peak concentration in the 12-14th week of pregnancy. At this time, hCG may exceed 200,000 mIU/ml.
Thus, reference intervals are established for the hCG hormone value in blood according to the weeks of pregnancy (from the date of the last menstrual period or LMP):
- 9-130 mIU/ml: 3-4 weeks pregnant
- 75-2600 mIU/ml: 4-5 weeks pregnant
- 850-20800 mIU/ml: 5-6 weeks pregnant
- 4000-100200 mIU/ml: 6-7 weeks pregnant
- 11500-289000 mIU/ml: 7-12 weeks pregnant
- 18300-137000 mIU/ml: 12-16 weeks pregnant
- 1400-53000 mIU/ml: 16-19 weeks of pregnancy (2nd trimester)
- 940-60000 mIU/ml: 19-41 weeks of pregnancy (3rd trimester)
It is important to keep in mind that these reference values for hCG hormone are guidelines and that there is a great deal of variation among women.
Therefore, the increase in beta as gestation progresses is even more important than its specific value. In general, in an evolving pregnancy, beta-hCG should be doubled approximately every 48-72 hours during the first trimester of gestation.
When is the pregnancy test reliable?
In the natural search for pregnancy, the ideal is to wait to perform the pregnancy test until the first delay of menstruation or 15 days after sexual intercourse.
In the case of assisted reproduction treatments, it is generally recommended to wait about 10-15 days after the embryo transfer or artificial insemination (AI) to do the pregnancy test so that the result is reliable. This period of time is known as beta wait.
Assisted procreation, as any other medical treatment, requires that you rely on the professionalism of the doctors and staff of the clinic you choose. Obviously, each clinic is different. Get now your Fertility Report, which will select several clinics for you out of the pool of clinics that meet our strict quality criteria. Moreover, it will offer you a comparison between the fees and conditions each clinic offers in order for you to make a well informed choice.
If we do the pregnancy test early, it may happen that the hCG hormone value has not increased enough to be detected by the test. This could result in a false-negative result.
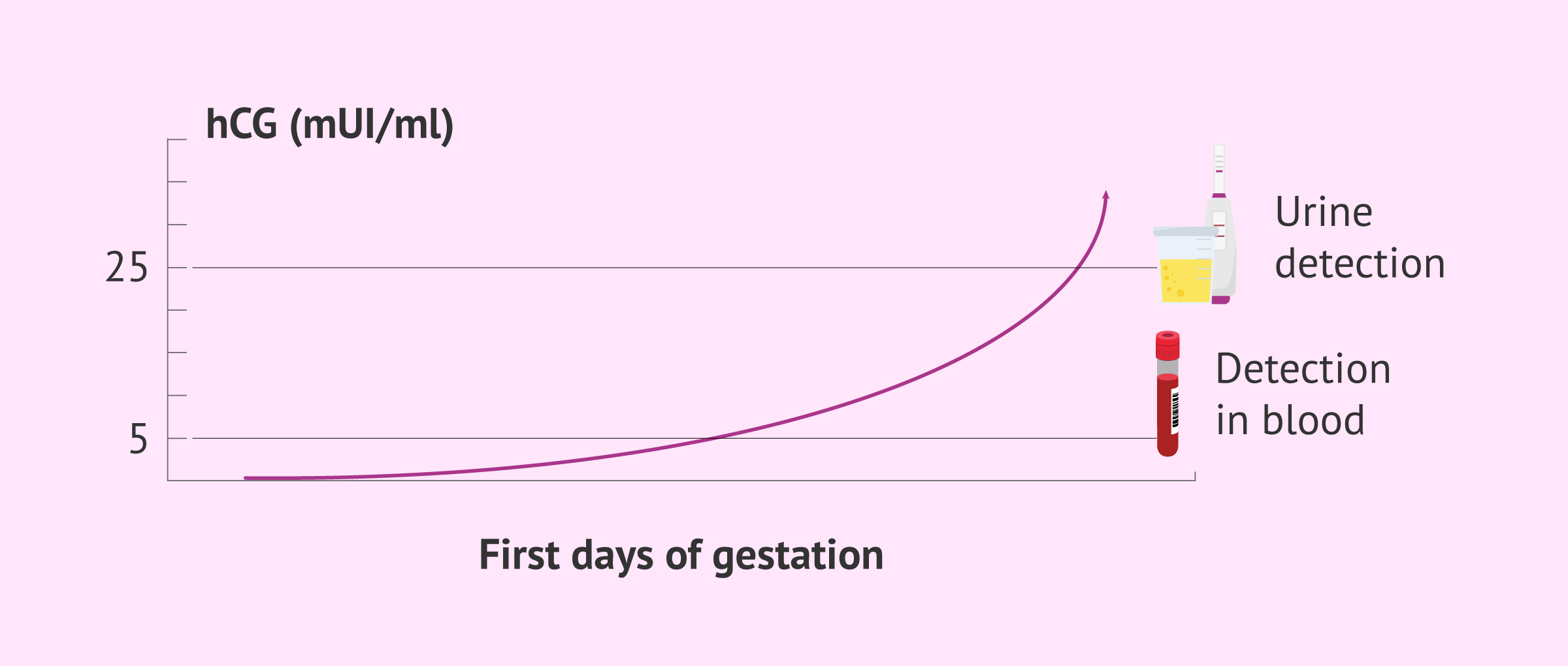
Beta is considered positive when more than 5 mIU/ml is found in the blood test, but this value is very low. As a general rule, after 13 days from implantation, a beta of about 50 mIU/ml should be expected.
In the case of the urine test, the sensitivity of the test is much lower. This means that it will only give a positive result with concentrations of more than 25 or 50 mIU/ml of hCG, depending on the test purchased from the pharmacy. However, there are now ultrasensitive urine tests capable of detecting smaller amounts of the hormone.
Ultimately, it will always be better to test for beta-hCG in the blood, as it gives a specific value of the hormone and detects lower concentrations.
Doubtful results
When a urine pregnancy test is performed, it is possible to obtain a negative result, but the woman may show symptoms of pregnancy. On the other hand, it may also be the case that the value of a quantitative test is positive but low with respect to normal levels.
As mentioned above, the hCG hormone doubles about every 48-72 hours until the end of the first trimester. For this reason, in these doubtful situations, it is advisable to repeat the test after 2-3 days.
In the case of blood pregnancy tests, a repeat test can check for a doubling of the hCG value to ensure that pregnancy is indeed present and is progressing properly.
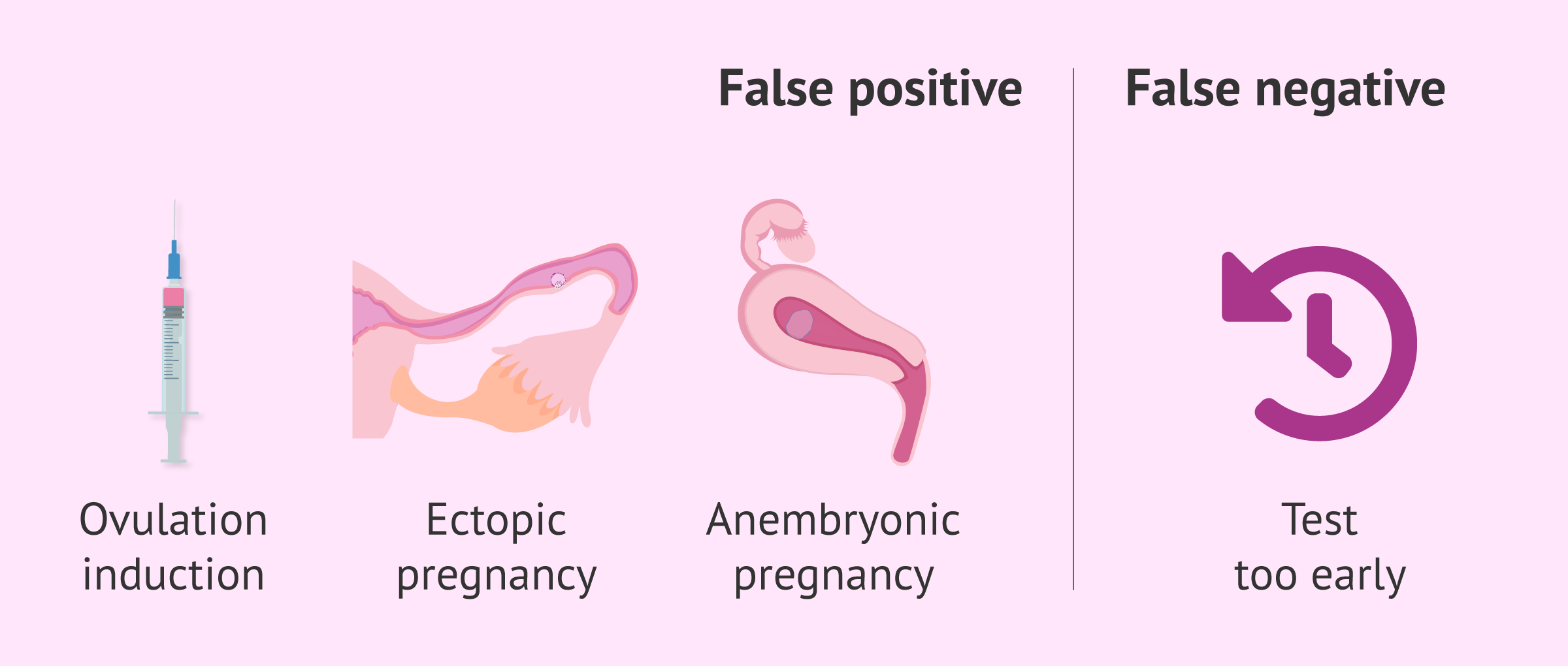
False positives and false negatives
In some cases, the result of the pregnancy test may be erroneous. This is known as false negative and false positiveresults:
- False negative
- in both natural pregnancy and in cases of assisted reproduction, if the test is done too early, the hormone may not be detected because it is still at very low levels. Therefore, it will be necessary to wait for the appropriate day to obtain a reliable result.
- False positive
- in an assisted reproduction treatment, it is common for the patient to be administered hCG to induce ovulation. This hormone can remain in the blood for a few days and confuse the pregnancy test. Thus, the woman would get a positive result even though there may not actually be a pregnancy. On the other hand, it is possible to obtain a positive result and that the woman is not pregnant or the pregnancy is not evolutive, as in ectopic pregnancy, anembryonic pregnancy...
You can learn more about these erroneous pregnancy test results in the following article: Can pregnancy tests fail? False positives and negatives
What happens if hCG values are abnormal?
When performing the quantitative beta-hCG test, a woman may be found to have a result above or below the reference value for the gestational period she is in. If the deviation (more or less) is small, there is no need to be overly alarmed: beta values can vary greatly among women.
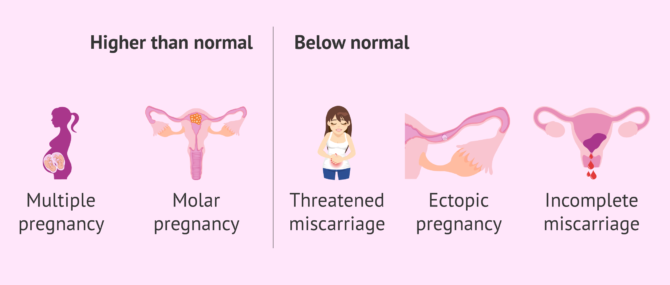
However, if the deviation is very large, it is possible that the woman is facing one of the following cases:
- Above normal values
- may indicate twin or multiple pregnancy, choriocarcinoma, hydatidiform mole or some type of cancer or abnormal cell development.
- Lower than usual values
- may appear in cases of incomplete miscarriage, threatened miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, etc.
Thus, if the beta result is adequate, the first transvaginal ultrasound is scheduled to confirm the number of embryo sacs and their location in the uterus. On the other hand, if the beta is less than 50 mIU/ml, it is usual to perform serial analyses and control the hormone level every few days, to confirm that the hCG value is evolving correctly.
FAQs from users
What does a positive beta, but low hCG levels mean? Am I going to have an abortion?
HCG is a hormone that is produced specifically in the trophoblast (the structure that will later give rise to the placenta) and that maintains the corpus luteum so that it continues to produce hormones that, in turn, will maintain gestation. It is made up of two subunits, the alpha subunit which is common to other hormones produced by the pituitary gland and the beta subunit which is specific to HCG.
As gestation progresses, the levels of this hormone increase. Although there are large variations from one week to the next, and even from one day to the next, there are approximate values for each period of pregnancy. Therefore, in early pregnancy, a low Beta HCG may be indicative of a pregnancy that is not progressing properly.
However, as mentioned above, given the high variability in the concentrations of this hormone and its daily changes, the determination of a single value is not predictive of the evolution of the pregnancy. If there are doubts as to the normality of its values, we usually determine it serially (approximately every 48 hours) to see if the HCG levels increase adequately.
Are beta-hCG values equal in a multiple pregnancy?
No, when there is a multiple pregnancy, beta hCG values are higher. Therefore, there may also be greater symptomatology (nausea, malaise, or drowsiness) during the first trimester of pregnancy.
While a value of 200 mIU/ml would be normal at 2-3 weeks in a singleton pregnancy, in a multiple pregnancy we can find values of around 600 mIU/ml or more in the 14 days after embryo transfer.
Is it possible to have a negative urine pregnancy test and a positive beta?
As we discussed in the article, the urine pregnancy test has a lower sensitivity. Its detection limit is higher, so a low hormone value is more likely to result in a false negative compared to the beta blood test result.
For example, if the sensitivity of the urine test is 30 mIU/ml, the blood test is 5 mIU/ml and the hormone value is about 20 mIU/ml, the urine test will give a negative result, while the blood test will give a positive result.
For this reason, it is essential to wait the time established by the specialist to do the pregnancy test. In this way, we allow time for the hormone to increase its level in the mother's body.
Do beta-hCG values allow detection of ectopic pregnancy because they are higher or lower than those of a normal pregnancy?
No, in principle the initial values do not vary. The embryo, once implanted, initiates the release of the beta-hCG hormone, regardless of the site of implantation.
However, the evolution of the hormone value may vary, since in an ectopic pregnancy there will come a time when the embryo stops its development and this blocks the release of the beta-hCG hormone, which will progressively decrease its level in the maternal blood.
Therefore, although initially, the beta-hCG test would not be helpful in detecting ectopic pregnancy, at a more advanced stage, it can be important.
Are beta-hCG values after IVF different from natural pregnancy?
No, regardless of how embryo implantation is achieved, the release and, therefore, the increase of beta-hCG in the maternal body will be the same.
Should a fasting beta-hCG test be done?
No, it is not necessary to be fasting to take a pregnancy test. However, if the test is to be done in urine, it is recommended to do it with the first urine of the morning so that it is more concentrated and the result is more reliable.
What are the normal beta hCG values at 5 weeks gestation?
In general, at 5 weeks gestation the range of normal values for hCG hormone is between 850-20800 mIU/ml.
The reason for such a wide range for normal hCG levels is that the hormone values are highly variable in each pregnancy. This also makes the particular value less important compared to the levels increasing at the expected rate (in an evolving pregnancy, hCG doubles every 2-3 days in the first trimester of pregnancy).
What is the difference between beta hCG and pregnancy tests?
Pregnancy tests can be determined at both the blood and urine levels.
Both tests can diagnose pregnancy by testing for a chemical called hCG, but with different sensitivity and specificity. This hormone has a specific value depending on the days or weeks of pregnancy and generally doubles in value every two days.
Blood tests measure the quantitative levels of the hormone beta-hCG (human gonocorionic hormone) that appears in the early stages of embryo implantation. The result is sensitive at blood level already with the presence of 1 to 5 mIU/ml of hCG, while at urine level it must be higher than 50 mIU/ml of HCG, which delays its positivity in the latter by a few days.

One thing to note about these tests is that the blood test will give us an absolute value, i.e. a clear number, which at a medical level and depending on the situation of each woman, we can not only diagnose pregnancy but also serious pathologies of the trophoblast.
In recent years, the pharmaceutical industry has improved the sensitivity of urine tests or home tests. Nowadays, urine flow measurement tests are available on the market in both strips and digital formats that can detect hCG levels above 10-15 mUL/ML. It is important when performing these tests to follow the correct indications, as there can be many failures or false negatives due to poor collection technique or the concomitant use of certain medicines that are also eliminated via the kidneys.
Approximately 10 days after an embryo transfer at the blastocyst stage and 15 days after an artificial insemination, hCG levels should be measured in the blood, if implantation has occurred, while urine tests should wait a few more days depending on the type of home test.
Recommended readings
If you are interested in reading more about the hCG hormone, we recommend you to visit this link: What is hCG hormone or Human Chorionic Gonadotropin?
On the other hand, if you wish to obtain more detailed information about when to take a pregnancy test, you can read the following article: When to take a pregnancy test to be reliable?
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Butch AW, Ahrens BD, Avliyakulov NK. Urine reference intervals for human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) isoforms by immunoextraction-tandem mass spectrometry to detect hCG use. Drug Test Anal. 2018 Jun;10(6):956-960. (See)
Cole LA, Butler S. Detection of hCG in trophoblastic disease. The USA hCG reference service experience. J Reprod Med. 2002 Jun;47(6):433-44. (See)
Jou HJ, Shyu MK, Shih JC, Chang MY, Lim CC, Tzeng CY, Chen SM, Hsieh FJ. Second trimester maternal serum hCG level in an Asian population: normal reference values by ultrasound dating. J Matern Fetal Med. 2000 Mar-Apr;9(2):118-21. (See)
Kohorn EI. What we know about low-level hCG: definition, classification and management. J Reprod Med. 2004 Jun;49(6):433-7. (See)
Korevaar TI, Steegers EA, de Rijke YB, Schalekamp-Timmermans S, Visser WE, Hofman A, Jaddoe VW, Tiemeier H, Visser TJ, Medici M, Peeters RP. Reference ranges and determinants of total hCG levels during pregnancy: the Generation R Study. Eur J Epidemiol. 2015 Sep;30(9):1057-66. (See)
Seeber BE. What serial hCG can tell you, and cannot tell you, about an early pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 2012 Nov;98(5):1074-7. (See)
Sirikunalai P, Wanapirak C, Sirichotiyakul S, Tongprasert F, Srisupundit K, Luewan S, Traisrisilp K, Tongsong T. Associations between maternal serum free beta human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2016;36(2):178-82. (See)
Wang Z, Gao Y, Zhang D, Li Y, Luo L, Xu Y. Predictive value of serum β-human chorionic gonadotropin for early pregnancy outcomes. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2020 Jan;301(1):295-302. (See)
FAQs from users: 'What does a positive beta, but low hCG levels mean? Am I going to have an abortion?', 'When is hCG produced after conception?', 'Are beta-hCG values equal in a multiple pregnancy?', 'When do hCG levels stop doubling?', 'Is it possible to have a negative urine pregnancy test and a positive beta?', 'How do pregnancy tests detect hCG?', 'Do beta-hCG values allow detection of ectopic pregnancy because they are higher or lower than those of a normal pregnancy?', 'Are hCG levels higher with twins?', 'Are beta-hCG values after IVF different from natural pregnancy?', 'Can hCG levels go up and down?', 'Should a fasting beta-hCG test be done?', 'When does hCG show in urine?', 'What are the normal beta hCG values at 5 weeks gestation?', 'What is the difference between beta hCG and pregnancy tests?', 'When do hCG levels drop after miscarriage?', 'Can you have normal hCG levels and still have twins?', 'Can hCG levels go up with a blighted ovum?', 'When do hCG levels drop after giving birth?', 'Can hCG determine gender?' and 'Can high hCG levels mean Down syndrome?'.
Authors and contributors

More information about Cristina Algarra Goosman
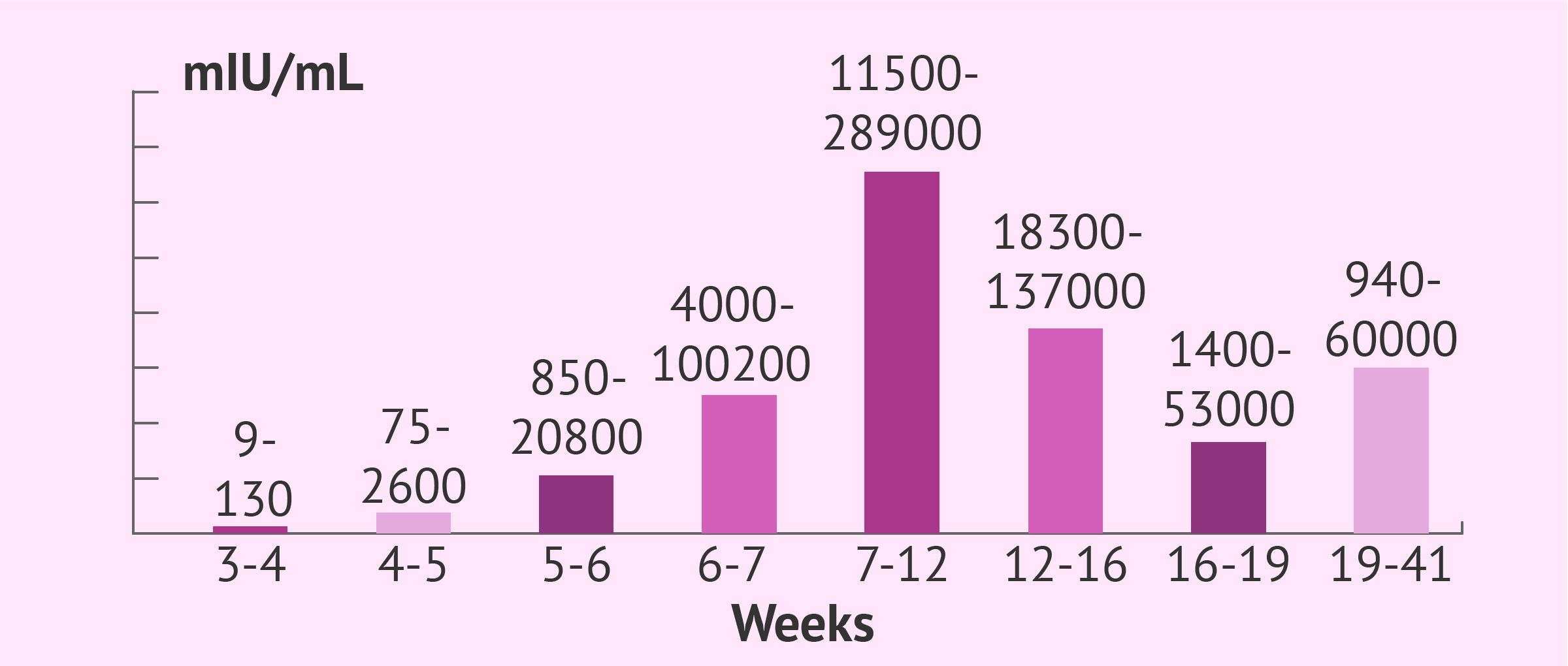




Hello… My hCG level is 12 mIU per ml, does it mean I’m pregnant or no? Pls, help!
Dear Eloïse,
even though beta hCG results are considered to be positive for values from 5 upwards, the truth is values above 50 are the best indicators. Since 5 is a confusing value, my advice is that you repeat the test after 2-3 days to check whether it’s increasing.