Ovulation is the process whereby a mature egg cell is released after developing in the woman's ovary. It is a crucial phase of the menstrual cycle, which is triggered thanks to the action of female sex hormones.
During ovulation, the woman is on her most fertile days (fertile window). In other words, it is at this point when unprotected sexual intercourse is most likely to result a pregnancy.
Normally, the ovulation phase occurs between day 13 and 15 of the menstrual cycle, although there may be differences in each cycle or even no ovulation at all.
Provided below is an index with the 7 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 2.1.
- 2.2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 4.3.
- 4.4.
- 4.5.
- 4.6.
- 4.7.
- 4.8.
- 4.9.
- 4.10.
- 4.11.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
Definition
Ovulation translates into the most fertile days of a woman. The ovary releases a mature egg cell to the Fallopian tube, where it will stay until a sperm cell reaches and fertilizes, thereby creating an embryo.
To this end, an ovarian follicle containing an egg cell has to grow during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. When the follicle reaches the adequate size, the action of LH causes it to burst and release an egg.
Ovulation takes place thanks to the luteinizing hormone (LH), which increases in levels in order to trigger the process. It is known as LH surge.
After ovulation, the mature egg cell releases has an average lifespan of 24 hours. If fertilization doesn't occur during this timeframe, the egg cell will degenerate eventually. The woman's fertile days come to their end after this, and the couple would have to wait until the next cycle to try to conceive again.
On the other hand, in case fertilization takes place and results in an embryo, it will continue its journey toward the uterus, where it will attach and mark the beginning of a new pregnancy.
In the second phase of the menstrual cycle, the ruptured ovarian follicle turns into the corpus luteum, which is responsible for estrogen and progesterone production.
You may also enjoy some further information reading this: The Four Phases of the Menstrual Cycle.
Date of ovulation
In women with regular menstrual cycles, ovulation is expected to occur at some point halfway through the menstrual cycle. Simply put, in 28-day cycles, ovulation happens on day 14.
As explained above, the menstrual cycle is regulated by sex hormones. FSH and LH, produced by the pituitary gland, are the most important ones. They reach their peak level during ovulation, and for this reason are good indicators of the most fertile days, especially LH.
Alterations in the levels of FSH and LH could lead to anovulation or other menstural irregularities.
Women who are trying to conceive and also those who want to prevent pregnancy are interested in learning when their fertile days are. This allows them to get the timing right.
The following are the most commonly used methods to predict the day of ovulation:
Ovulation calculator & calendar
First of all, it is necessary that you know the average length of your menstrual cycles, keeping in mind that they start at the beginning of your period and end with the start of the next period.
As mentioned above, ovulation occurs on day 14 approximately in women with 28-day menstrual cycles. The fertile window covers from day 12 until day 16 (periovulatory phase).
In women with shorter or longer cycles, the best way to calculate the ovulation day would be by subtracting 15 days to the expected date for the next period. The days prior to and after ovulation should be taken into account as well.
The fertile window covers five days because sperms are expected to be able to survive inside the female reproductive system for about 72 hours. So, even if sexual intercourse took place before ovulation, there would be chances of getting pregnant, too.
Read more: How Do Online Fertility Calculators Work?
Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs)
This method is more accurate than ovulation calculator. For this reason, it is commonly used by women who are trying to get pregnant actively.
OPKs work by measuring the levels of LH in urine and can be purchased at a pharmacy or ordered online.
LH levels start rising exponentially between 36 to 24 hours before ovulation, when they reach their peak (LH surge), and start diminishing again.
Getting a positive result on an OPK means that you are on your fertile days. The main advantage in comparison with the calendar method is that OPKs are able to predict ovulation even in women with irregular cycles.
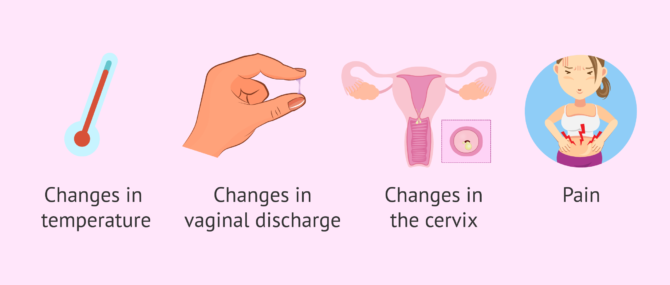
Signs & symptoms
Certain signs and symptoms in the woman's body may indicate that ovulation is taking place. The following are the most common ones:
- BBT stays high
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT) increases from 0.2 to 0.5 °C during ovulation, due to the increase in the levels of progesterone after releasing an egg.
- Increased vaginal discharge
- It changes its consistency and increases its amount. It becomes more elastic and jelly-like to allow the passage of the sperm through the cervix. It is due to an increase in the levels of estrogens.
- Cervix changes
- It will rise and its texture become softer. Also, it relax to allow the cervical opening to open up enough as to allow the passage of sperm.
- Pain
- Cramps or discomfort in the lower abdomen due to a ruptured ovarian follicle.
More often than not, these changes go unnoticed by women, but could be detected by paying attention to your body signs. Also, no two women are exactly alike, so not all will have the same ovulation symptoms.
FAQs from users
What are the causes of anovulation?
There are several causes that can cause us not to ovulate. One of the most common is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, a benign condition that affects many young women. It consists of an endocrine disorder that does not allow correct ovulation.
There could also be anovulation of hypothalamic or pituitary cause, such as intense physical exercise, low weight, etcetera. Other hormonal alterations such as alterations in thyroid hormone (TSH) or prolactin, can cause ovulation not to occur properly.
Advanced age would also be a cause why, in spite of having periods, in many cycles ovulation does not occur regularly.
Do high prolactin values affect ovulation?
Elevated prolactin levels can influence the production of other hormones or their regulation, especially FSH and LH, hormones involved in follicular genesis and ovulation. Therefore, when there are high levels of prolactin, could lead to a lack of ovulation and often cycles without menstruation in women
Can alterations in the cervical mucus lead to female infertility?
Yes, alterations in the cervical mucus can are a common cause of female infertility. The cervical mucus is a secretion produced before ovulation and it disappears after the woman ovulates. It has a sticky texture, and its mission is to pave the way for sperm. It is, in fact, a good indicator of female fertility.
Does fever affect ovulation?
No, it doesn't. However, in women who use the basal body temperature method to track their ovulation, a fever will make the temperature readings inaccurate, thereby making it harder to determine her most fertile days. But fever won't screw up any progress you and your partner have already made.
How reliable is the Clearblue Ovulation Test?
Ovulation tests can detect the LH hormone surge with 99% accuracy. It is therefore one of the most reliable indicators of ovulation.
Is it possible to menstruate without ovulation?
Women with anovulatory cycles may have menstruation as well. However, these women are very likely to have menstrual disorders.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is one of the pathologies that can be treated with anovulation. If you'd like to know more about the pathology which affects women in reproductive age, click here: What is the polycystic ovary syndrome?
Can you release an egg during your period?
Yes, it is possible in women with shorter cycles or highly irregular cycles. In such cases, unprotected sex during your period could lead to pregnancy.
Do you release an egg every time you ovulate?
Yes. If the body doesn't release an egg during a woman's cycle, it is known as anovulatory cycle. In other words, that ovulation is not occurring. If a woman doesn't ovulate or release an egg, she should not have any bleeding at all.
Do you release an egg on birth control?
It depends on the type of birth control method used. If you use a hormonal type of contraceptive, then the answer is no: they work by inhibiting ovulation. Birth control pills and other hormonal methods contain synthetic forms of estrogen and progestin, which are used to alter the normal functioning of the cycle in order to prevent ovulation.
Other forms of birth control, such as the copper IUD and condoms, don't contain hormones, hence their name barrier methods. They work by blocking the pathway of sperm toward the egg.
Is the date of ovulation the date of conception?
No. Conception can occur as early as within 24 hours of ovulation. Also, and keeping in mind that sperm can live inside a woman's body for up to three days, conception can happen 3 days after sexual intercourse, depending on the date of ovulation.
Is it possible to ovulate from both ovaries?
Normally, the ovaries take alternate turns in releasing an egg, but sometimes both ovaries can release an egg at the same time. If fertilization occurs in both, the woman will get pregnant with non-identical twins.
Recommended reading
Often, when a woman has shorter or irregular menstrual cycles, her fertile days take place very close to her menstruation. For information on this try the following page: Is It Actually Possible for You to Get Pregnant While on your Period?
As explained above, hormonal alterations can lead to alterations in the menstrual cycle and affect ovulation. Get more information by clicking the following link: Female Infertility Due to Ovarian Endocrine Factor.
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Chiazze L Jr Brayer F T Macisco J J Jr Parker M P Duffy B J 1968 The Length and Variability of the Human Menstrual Cycle JAMA, 203 (6) pp 377-380.
Fluhmann C F 1934 The Length of the human menstrual cycle. Department of obstetrics and gynecology American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2 (1) pp 73-78.
Haroun HSW. Reproductive cycles in females. MOJ Women’s Health. 2016;2(2):62‒64.
Hummel, T., Gollisch, R., Wildt, G., and Kobal, G. (1991). Changes in olfactory perception during the menstrual cycle. Experentia, 47, 712-715.
Vollman R F 1956 The Degree of Variability of the Length of the Menstrual Cycle in Correlation with Age of Woman Gynaecologia 142 (5): 310–314.
Wilcox AJ, Weinberg CR, Baird DB. Timing of intercourse in relation to ovulation: effects on the probability of conception, survival of the pregnancy and sex of the baby. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1517– 1521.
FAQs from users: 'Do high prolactin values affect ovulation?', 'What are the causes of anovulation?', 'Can alterations in the cervical mucus lead to female infertility?', 'Does fever affect ovulation?', 'How reliable is the Clearblue Ovulation Test?', 'Can ovulation day vary each month?', 'When do you ovulate after an abortion?', 'Can you get pregnant not during ovulation?', 'Is it possible to menstruate without ovulation?', 'Can you release an egg during your period?', 'Do you release an egg every time you ovulate?', 'Do you release an egg on birth control?', 'Is the date of ovulation the date of conception?', 'Is it possible to ovulate from both ovaries?', 'Does ovulation make you more attractive?', 'Is it possible to ovulate twice in a month?' and 'What is the best day of ovulation to conceive a boy?'.
Authors and contributors

More information about Michelle Lorraine Embleton







Hello there. I get terrible pain at around day 14 of my cycle. I´ve always wondered what it was. Could this be ovulation pain?