Contraceptive methods are defined as strategies to prevent or significantly reduce the likelihood of fertilization, and thus pregnancy, from occurring during vaginal intercourse.
Their use became widespread in the mid-20th century as a form of family planning and birth control, as they break the association between sexual intercourse and conception.
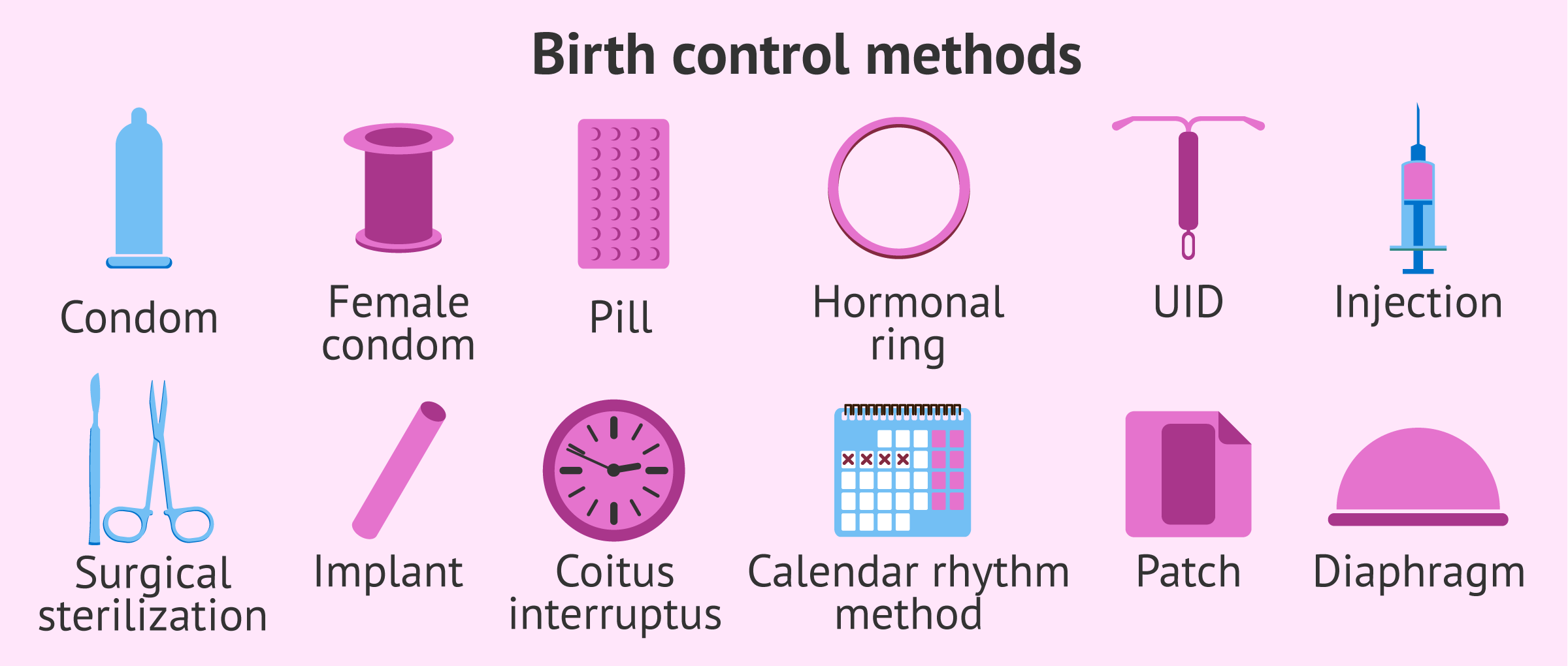
There are several types of contraceptives, which can be classified according to their composition and mechanism of action.
Provided below is an index with the 10 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 4.3.
- 4.4.
- 4.5.
- 4.6.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 7.1.
- 7.2.
- 7.3.
- 7.4.
- 7.5.
- 7.6.
- 7.7.
- 7.8.
- 7.9.
- 7.10.
- 7.11.
- 7.12.
- 7.13.
- 7.14.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
How are contraceptive methods classified?
There are a multitude of ways to classify contraceptive methods. For example, the different parameters discussed below can be taken into account:
- Male or female
- depending on whether it is used by men or women.
- Oral or non-oral
- refers to whether contraceptives are taken in pill form or placed elsewhere in the body.
- Hormonal or non-hormonal
- based on whether they include hormones in their composition.
- Temporary or permanent
- depending on the duration of contraception.
- Reversible or irreversible
- refers to the total sterilization of the man or woman.
The same contraceptive can be included in several of the groups described above. Therefore, for a clearer understanding of how each one works, we will rely on their mechanism of action to describe them throughout this article, as well as the main indications.
Natural contraception
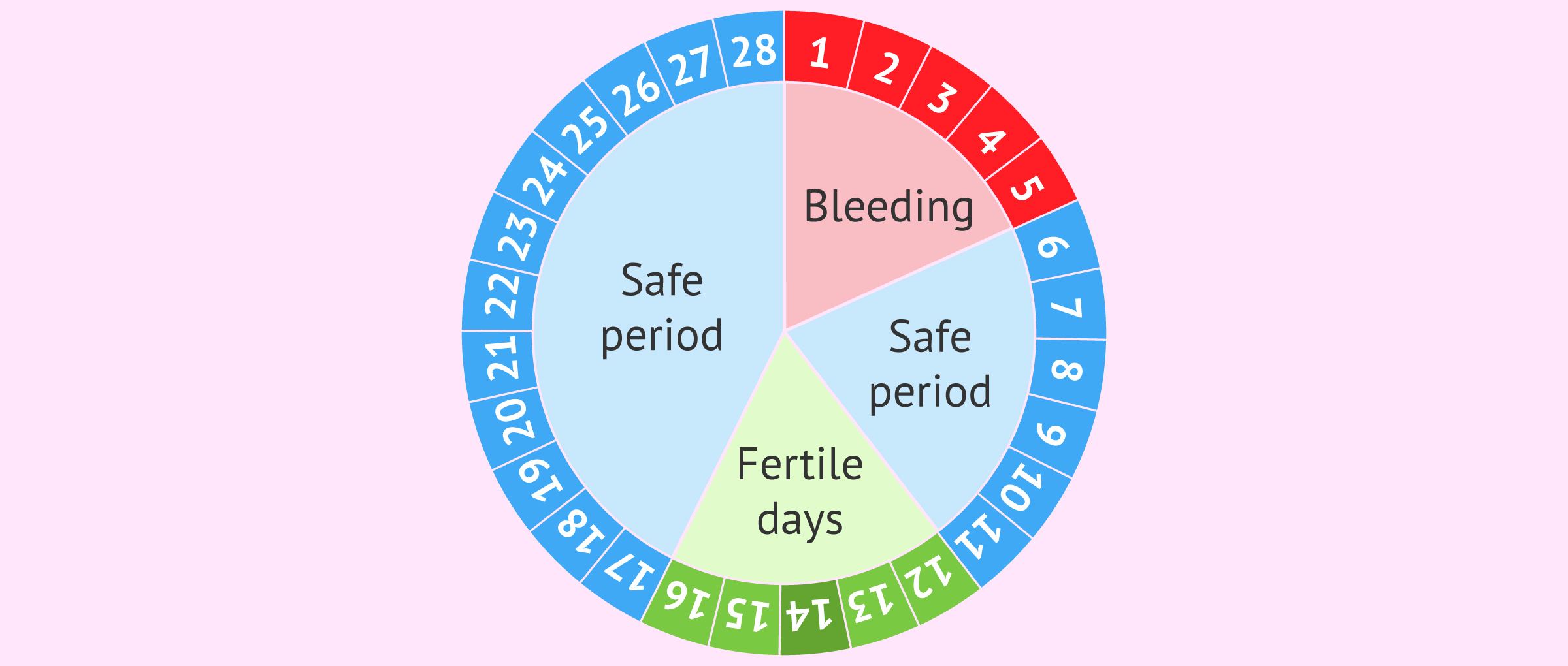
This mechanism of action of contraceptives is based on the control of the menstrual cycle to avoid sexual intercourse on the woman's fertile days, which are those close to the time of ovulation. This natural contraceptive is popularly known as Ogino-knaus.
Ovulation takes place approximately in the middle of the menstrual cycle, although not in all women it is so exact, especially in those who have an irregular menstrual cycle. Therefore, it is necessary for women to keep a strict control of their menstruation and ovulation.
Some women use methods to find out if they are in their fertile period, for example, analyzing cervical mucus or measuring the basal temperature, since there is a rise of 0.2 to 0.5 ºC at the time of ovulation.
There is also the natural method of coitus interruptus, colloquially known as backward intercourse. In this case, ejaculation inside the vagina should be avoided, but not previous penetration.
The advantages and disadvantages of natural contraceptive methods are as follows:
- Advantages
- there are no side effects, the cost is zero and they can be used during pregnancy and lactation.
- Disadvantages
- are not safe methods. Its contraceptive efficacy does not exceed 75% and, in addition, it does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
These contraceptive methods should only be used by couples who, although not actively seeking pregnancy, do plan to become parents in the near future and would not have a problem if it were to occur earlier than expected.
Barrier methods
These are contraceptives that physically prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
The best known of all is the male condom. However, other barrier methods of contraception are available:
- Male condom
- also called prophylactic or condom. This contraceptive method is shaped like a sheath and is placed around the penis. Generally, the condom is made of latex and comes lubricated with spermicides. When placed around the penis, semen is trapped inside the penis after ejaculation. Its effectiveness is 97% and the price is usually around 10 euros per box.
- Female condom
- is similar to the male condom, but with a wide rigid ring to prevent it from slipping out of the vaginal opening. It is priced at 2 euros per unit, a little more expensive than the male condom.
- Diaphragm
- is a rubber cap that is placed in the vagina and obstructs the opening of the cervix, thus preventing the passage of sperm. It is 95% effective, costs 50 euros, but can be used several times if well cared for.
- Vaginal sponge
- is like a polyurethane foam that is placed at the entrance of the cervix and absorbs semen and releases spermicide. Its effectiveness varies from 70 to 90%, but it may cause vaginal irritation.
- Intrauterine device (IUD)
- also known as copper T. The IUD is placed inside the uterus by the gynecologist and is 95% effective and permanent. The copper IUD is cheaper than the hormonal IUD, its price is around 100 euros.
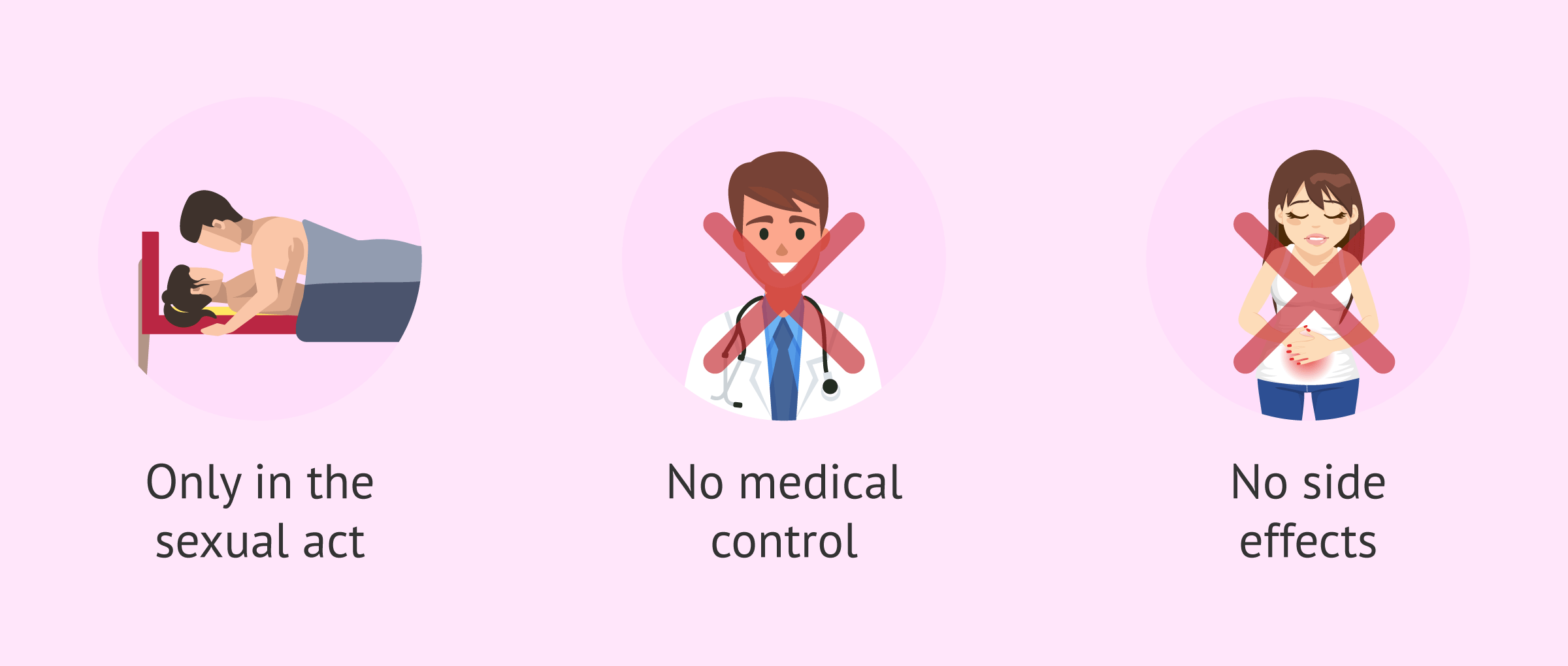
The main advantages of these contraceptives (with the exception of the IUD) are the following: it is only necessary to use them during sexual intercourse, they do not require medical control, they have no side effects and can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. However, of all the barrier contraceptives discussed, they avoid direct contact between mucous membranes and protect against most sexually transmitted diseases. Only male and female condoms would prevent the transmission of STDs.
Hormonal birth control
These are the most commonly used contraceptive methods in women. Hormonal contraceptives are composed of synthetic versions of female sex hormones, usually estrogen and progesterone.
Hormonal contraceptives can be composed of estrogens, which prevent ovulation, and progesterone, which prevents endometrial priming and alters cervical mucus, or progesterone alone.
Their mechanism of action consists of altering the natural hormonal levels in the woman to prevent ovulation from taking place and thus prevent the possibility of fertilization by the sperm. In addition, hormonal contraceptives also alter the endometrium and cervical mucus, and prevent the uterus from preparing for embryo implantation.
The reliability of hormonal contraceptives is very high (98-99%), provided they are used correctly and according to medical indications.
In addition to their contraceptive function, these hormonal methods of contraception have other applications: they help to control vaginal bleeding during menstruation and are used for the treatment of diseases such as endometriosis.
However, hormonal contraceptives also have some drawbacks. Because they work by regulating each woman's own hormonal system, many women who use them experience unwanted side effects. In addition, not all women can use hormonal contraceptives and they do not prevent the spread of STDs.
Depending on the mode of administration, hormonal contraceptives are classified as follows:
Combined oral contraceptive pills
They consist of pills that must be taken on a daily basis by oral route.
Contraceptive pills are composed mainly of estrogens and gestagens. Among their advantages are the following:
- They reduce monthly menstrual flow and help ease period pain.
- They are often prescribed to prevent anemia.
- They help regulate menstrual periods.
- They protect against ovarian and endometrial cancer.
- They diminish the risk of developing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
- They can be prescribed for acne treatment.
On the other hand, the disadvantages of this oral contraceptive are listed below:
- They are for daily use: they require one intake per day in the same time slot, which can lead to forgetfulness.
- They increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- They have side effects: weight changes, breast enlargement and tenderness, appearance of cellulite, heaviness, depression, etc.
- They require medical control.
The price of the contraceptive pill varies depending on the brand name. Generally, each tablet costs approximately 10 euros, which means an annual cost of about 120 euros.
It should be noted that, despite the widespread use of oral contraceptives in women today, male hormonal contraception is still a challenge for researchers.
For more information about this contraceptive method, you can continue reading in the following post: What is the contraceptive pill? - Efficacy, how to take it and risks.
Contraceptive injection
This type of contraceptive consists of an intramuscular injection of hormones. It lasts for one month or three months depending on the hormone dose and has a very high efficacy of 99%.
The main advantage of injectable contraceptives is that they eliminate the risk of forgetfulness compared to daily contraceptive pills. In addition, the contraceptive injection reduces acne, menstrual cramps, period bleeding, etc.
Despite this, this contraceptive method can have several side effects: irregular bleeding, headaches, nausea, skin spots, weight gain or breast tenderness.
In addition, the contraceptive injection does not prevent STDs, it requires medical control and, in case of abandonment due to desire of pregnancy, ovulation may take some time to be restored.
The cost of the contraceptive injection may vary depending on the type. Approximately, each monthly ampoule costs about 3 euros.
For more information related to this contraceptive method, you can continue reading in the following post: What is the contraceptive injection and how is it used?
Birth control patch
It is a small patch applied to the skin that releases hormones on an ongoing basis. It is changed once a week and, even though it is usually highly accurate, it may be less effective in women who are overweight. The birth control patch can be attached to your skin on different areas of your body: buttocks, abdomen, upper torso, or upper/outer arm.
It presents the same pros and cons as birth control pills. Even so, we would add the following downsides:
- No protection against STIs.
- Bleeding or spotting when you first start using it.
- Sore or irritated skin.
- Possibility that it becomes detached.
- They are not indicated for women aged above 35 years.
- Its effectiveness diminishes in women whose weight is 90 kg or more.
- It is expensive, if compared to other birth control methods.
Since the contraceptive patch is transdermal application, vomiting and diarrhea do not affect the hormonal release, which is the case with the oral pill.
The price of the contraceptive patches is 14.50 euros for a box and each box contains 3 patches. Therefore, the woman would have enough for 3 weeks.
Contraceptive implant
It is a small flexible tube that is inserted under the skin of a woman's upper arm and works by releasing hormones into her body in order to prevent ovulation.
The main advantage of the implant is that it may last one, three, or even five years.Therefore, it is a permanent contraceptive with high contraceptive efficacy.
The advantages and disadvantages of the contraceptive implant are discussed below:
- Advantages: regulates menstruation, reduces bleeding and prevents pain.
Disadvantages - Disadvantages: requires minor surgery for placement, may leave a small scar, and hormones may cause side effects.
The price of the contraceptive implant in Spain is around 150 euros, but it is financed by the Social Security. Therefore, the woman will only pay 40% of its cost, about 60 euros.
For more information on this contraceptive method, we recommend reading the following article: Birth Control Implant: Advantages and Disadvantages.
Hormonal IUD
The intrauterine device, known by its acronym IUD, is a “T” shaped device that is placed in the uterus and releases hormones. This hormonal release prevents the implantation of the embryo in the uterus in the event that fertilization occurs.
The duration of the IUD is 5 years and it is inserted by the doctor. Its advantage is its permanent nature, which allows the woman to forget about contraception for a few years. For this reason, it is recommended for use only in women who have previously given birth.
However, some of the disadvantages that women with IUDs may suffer are detailed below:
- Insertion is often painful.
- May cause cramping and back pain.
- May cause irregular and painful periods.
- Risk of pelvic inflammation and inflammation of the cervix.
- Risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- May be spontaneously expelled by the body.
- High cost.
- Does not prevent the transmission of STDs.
The price of the hormonal IUD is approximately 200 euros. In addition, the cost of the gynecologist's consultation for its insertion must be added to this price. However, as it lasts for 5 years, the cost would be compensated.
There is another version of the IUD that releases ions to inhibit sperm motility instead of releasing hormones. You can review both types of IUDs in the following post: How Does the IUD Work and What are the Pros & Cons?
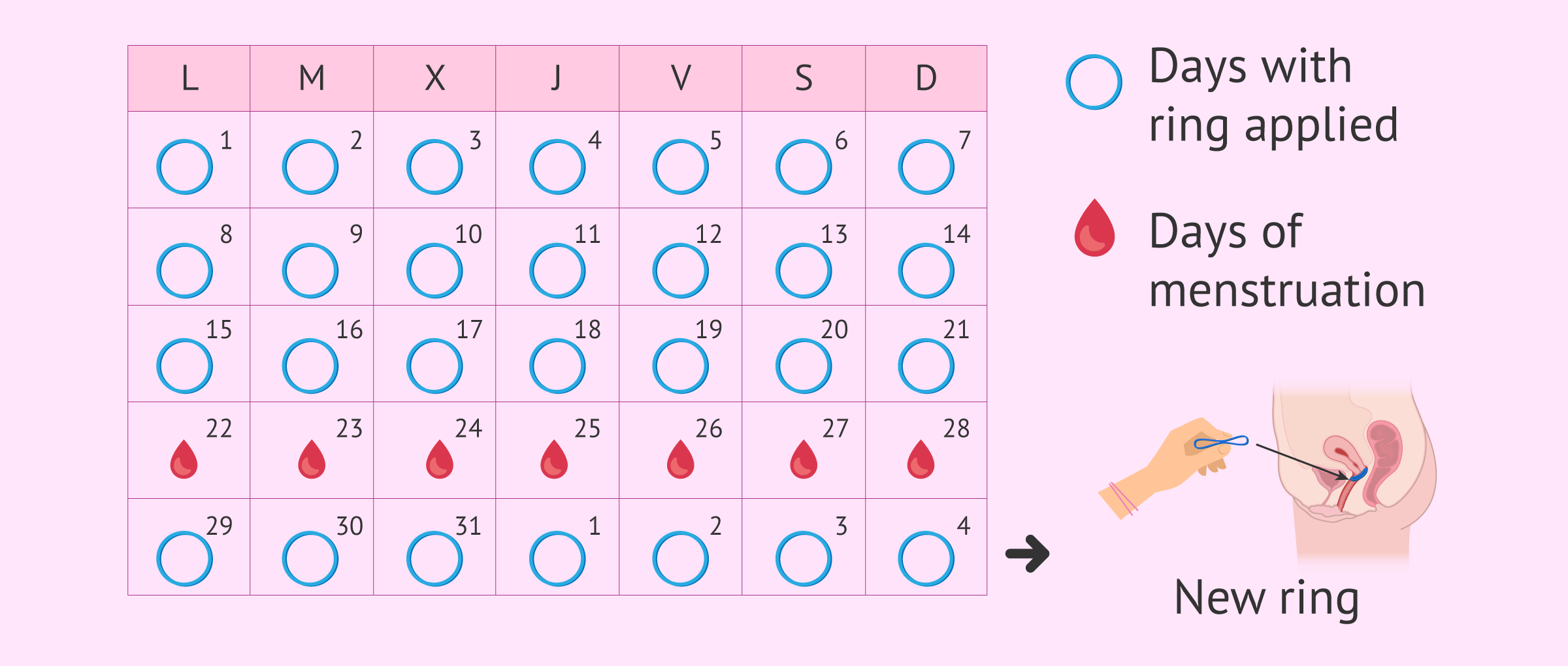
Vaginal ring
It consists of a flexible ring that is placed in the cervix and keeps on releasing hormones. The woman herself has to replace it once a month after three weeks.
In the fourth week, the woman will have her period and, the following week, a new ring is put in place. However, it is not necessary to go to the doctor for the change, but it is the woman herself who does the replacement.
It works more or less the same way as birth control pills, with the additional advantage that it does not have to be taken daily, but just be removed every three weeks. Then, a new ring will be replaced after the period week.
The approximate cost of the contraceptive ring is between 15-20 euros per unit.
Permanent & semi-permanent methods
Male and female sterilization methods are permanent surgical procedures to prevent pregnancy. Despite they were considered irreversible when they first began to be used, today both males and females have the chance to revert them, even though the fertilization potential is not absolutely guaranteed.
- Vasectomy: it prevents the exit of spermatozoa from the testis, thereby eliminating their presence in the ejaculate.
- Tubal ligation: it blocks the passage of the egg through the Fallopian tubes; this way, sperm won't ever be capable of reaching it.
Patients who decide to undergo male or female sterilization are asked to be completely sure that they won't wish to have a baby in the future.
Emergency contraception (EC)
When contraceptive methods fail or are not properly administered, there is the possibility of using an emergency contraceptive method. This is the morning-after pill, also known as postday. It is an oral hormonal method with a high hormonal dose that inhibits ovulation and fertilization.
Contrary to other contraceptive methods, postday contraception is taken after sexual intercourse in case there is a risk of unwanted pregnancy, supposedly due to breakage or failure of another contraceptive method previously used.
In general, the morning-after pill prevents pregnancy if taken within 72 hours after unprotected sex. It is especially effective if taken within 12 hours after sexual intercourse.
Postday can produce more side effects than other contraceptives, such as nausea, vomiting, headache or alterations in subsequent menstruation.
It is important to note that it is an emergency method and should not be used on a regular basis. In addition, the morning-after pill does not protect against the transmission of STDs.
For more information about postday, you can continue reading the following article: Morning-after pill: what are its effects and cost?
FAQs from users
Which contraceptive is best for women with high blood pressure?
The mini-pill or progestogen-only pill, as well as the contraceptive injection, are the safest birth control methods in these cases. Even though the mini-pill is not as reliable as the combined pill, if used carefully the failure rate is low. The combined pill is unadvisable because it can increase the risk for arterial disease.
Can the contraceptive implant affect fertility?
The implant is a long-lasting but reversible method of contraception. It has a contraceptive efficacy of 99.95% and a single implant can last up to 5 years.
It is a small metallic device, which is placed under the skin of the arm. It works thanks to the hormonal release of gestagens that will inhibit ovulation. It is true that women may experience changes in the amount and duration of their periods, there are even women who will not have menstruation while it is present.
Once it is withdrawn, the contraceptive effect disappears quickly and ovulatory cycles will resume normally, so it does not affect fertility at all.
Can female sterilization be reversed?
Yes, through a procedure called tubal ligation reversal. However, untying the tubes is not always possible and depends on the type of tubectomy the woman underwent for having her tubes tied. More information on the following post: Tubal ligation or tubectomy: How does female sterilization work?
Can birth control cause female infertility?
Women who have been using hormonal contraception for a long period of time can take several month to recover normal menstrual cycles, and therefore their fertility. So the answer is yes, hormonal contraceptives can cause temporary infertility in females.
Which methods of contraception are available on the NHS?
The NHS has created a contraception guide on their website where you can find the contraceptive that best suits you. There are 15 methods available on the NHS. You can find information about all of them here: Contraception guide - NHS Choices.
How appropriate are contraceptive methods for women over 40?
In principle, women in their 40s or 50s have access to all available methods, so long as there is no health risk involved. Barrier methods are, however, the most advisable in these cases, as they help prevent sexually transmitted infections.
The combined pill is not indicated for women who smoke, and/or suffer from obesity or high blood pressure, as they may lead to heart, stroke or blood clotting problems. On the other hand, the pill has many advantages for women in this age group, as it regulates periods and helps maintain bone mineral density.
Are there contraceptive methods that don't make you gain weight?
This side effect can only be experienced if you take a hormonal birth control method. Barrier methods and natural family planning do not interact with your hormones, and therefore there is no way this symptom can appear.
Anyway, there is no conclusive proof that hormonal birth control methods can make women gain weight. Some women have even reported experiencing a weight loss after starting using the pill or the vaginal ring, for example.
Are there birth control methods that don't lower libido?
First of all, it should be clear that not all women taking the pill or using NuvaRing will experience this side effect. Some studies have linked this side effect to a diminished level of testosterone (the hormone linked to desire, sex drive, and lubrication), as a consequence of the ovaries being shut down by birth control pills.
How could oral contraceptives increase breast cancer risk?
A woman's risk of developing breast cancer depends on several factors. While some are related to her natural hormones, others are linked to reproductive history factors. Beginning menstruation at an early age, not having children, or experiencing menopause at a late age are factors that may increase the risk of breast cancer.
Several studies have shown that women who use or have ever used the pill have a slightly higher risk of developing breast cancer than those who have never used it. The risk is a bit higher if the woman started using it as a teenager.
Can hormonal imbalances be treated with birth control pills?
Yes, in some cases adolescent girls and women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, primary ovarian insufficiency (POI), irregular menstrual periods, amenhorrhea, acne, menstrual cramps or premenstrual syndrome (PMS) are prescribed birth control pills to lower their hormone levels, and therefore regulare their menstrual periods.
Can birth control methods be used for the treatment of migraine with aura?
Combined oral contraceptives and progestogen-only pills can help improve a woman's headaches and migraines but also worsen them. It depends on each woman and the type of hormone in the pill. Studies, however, suggest that the lowest dose pills (those containing 20 micrograms of estrogen) are the most suitable for women who suffer from migraine regularly.
What's the best birth control for diabetics?
Diabetics should remember that birth control pills alter a woman's hormonal levels. In this sense, high doses of hormones can have a negative impact on blood sugar levels, which can make it harder for them to control their diabetes.
Moreover, there is an increased risk for heart attack or stroke among women who use the pill, a risk that is higher in the case of diabetics. This applies to other types of hormonal contraception such as Depo-Provera, the contraceptive implant, the patch and the vaginal ring.
Intrauterine devices are neither indicated for diabetics because they increase the risk of developing infections in the uterus, a risk which is already higher among women with type 2 diabetes.
Female sterilization by means of tubal ligation is, outside of abstinence, perhaps the most secure method for diabetics, as it does not affect a woman's blood sugar levels. However, surgery is not without risk, and women should keep in mind that it is a permanent method of birth control, which in many cases cannot be reversed.
Can birth control cause permanent hair loss?
There is no scientific proof that contraception can cause permanent hair loss. However, hair loss is included as a side effect caused by the pill, although the loss is commonly minimal. It may not occur until after the woman has stopped taking it. Those whose family histories include hair loss are not recommended to use a method other than the pill.
Can hormonal contraceptives lead to breast tissue growth?
Yes, it may happen, although the extent to which breast size increases depends on the woman and the birth control method used. Estrogen and progestin can cause you to experience an increase in breast size, but it generally reverses after a few cycles or when the woman stops using them. This side effect is often accompanied by breast tenderness (i.e. mastalgia).
Suggested reading (EC)
Nowadays, contraceptives are an important method when it comes to planning the number of children a family wants to have and when. If you are interested in reading more about this topic, we recommend you to access the following post: What Are Family Planning Methods? - Your Reproductive Health Options.
Hormonal contraceptives have other applications besides preventing pregnancy. For example, they are used as a treatment for women with endometriosis. If you want to know in detail what this disease consists of, you can continue reading in the following article: What Is Endometriosis? - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is another pathology that can be treated with hormonal contraceptives. For more information about this, you can enter the following article: What Is PCOS or Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
FAQs from users: 'Which contraceptive is best for women with high blood pressure?', 'Can the contraceptive implant affect fertility?', 'Can female sterilization be reversed?', 'Can birth control cause female infertility?', 'Which methods of contraception are available on the NHS?', 'How appropriate are contraceptive methods for women over 40?', 'Are there contraceptive methods that don't make you gain weight?', 'Are there birth control methods that don't lower libido?', 'How could oral contraceptives increase breast cancer risk?', 'Can hormonal imbalances be treated with birth control pills?', 'Can birth control methods be used for the treatment of migraine with aura?', 'What's the best birth control for diabetics?', 'Can birth control cause permanent hair loss?' and 'Can hormonal contraceptives lead to breast tissue growth?'.
Authors and contributors












I had a girlfriend in the ’80s that used a diaphragm. I got her pregnant three times in one year while she had it in. The problem is that my penis is 9″ long and her vagina is shallower than most women. I was actually bumping into her cervix with my penis during sex and dislodging the diaphragm.
Thanks for this guide to contraception! I didn’t know about the ring, to be honest. I find it very attractive, any opinions out there?
Hello, I have implanon and I have unprotected sex ever since… Before implanon, IUD was my contraceptive method of choice, so I had unsafe sex also. The week I had the IUD removed, I had unsafe sex (I had no birth control method on me). By the end of that week, my doctor told me to use the contraceptive patch up until I had Implanon inserted. When I told doc I had had sex without condom or contraception, he said I should take the morning-after pill. I did it as he said, but now I’m worried that pregnancy has happened. Now I have the implant, but I’m worried I’m pregnant… I haven’t tested for pregnancy but I’m feeling something inside my stomach. I’ve gained weight and I can’t stop craving food…. Besides I’m totally exhausted from morning to midnight… What is happening to my body?