The vaginal ring, also called the intravaginal ring or V-Ring, is a hormonal contraceptive method with a flexible, transparent structure.
This type of contraceptive is placed by the woman herself in her vagina and acts by constistently releasing low amounts of female sex hormones. In addition, the ring is designed to be used for 3 consecutive weeks, after which menstruation will begin.
The effectiveness of this contraceptive method against pregnancy is 98-99%, as is the contraceptive pill.
Provided below is an index with the 9 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 2.1.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 5.
- 6.
- 6.1.
- 6.2.
- 6.3.
- 6.4.
- 6.5.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
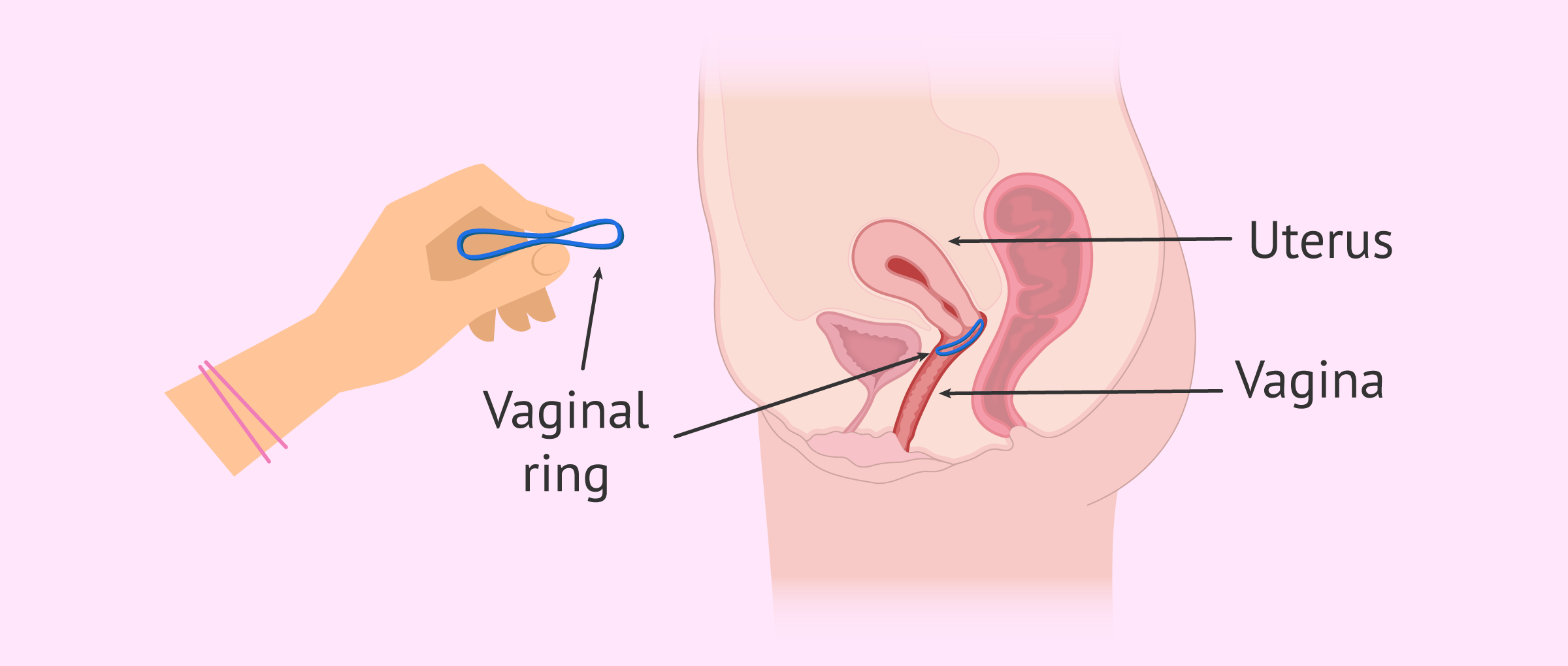
What is the contraceptive ring?
The vaginal ring is a contraceptive device about 5 cm in diameter that a woman puts into her vagina. It is a contraceptive method composed of a transparent and flexible material that acts releasing hormones in a progressive and prolonged manner over time.
There are currently three brands of contraceptive rings: Nuvaring, Setlona and Ornibel. The active principle of all of them is etonogestrel and ethinyl estradiol, two hormones that act by preventing ovulation and causing changes in the cervix. Therefore, the only difference is the hormone concentration presented by each contraceptive ring model.
How does the vaginal ring work?
Like other homonal birth control methods (such as patches or pills), the vaginal ring contains two types of hormones: estrogen (ethinyl estradiol) and progestin (etonogestrel). These hormones enter the bloodstream through the wall of the vagina.
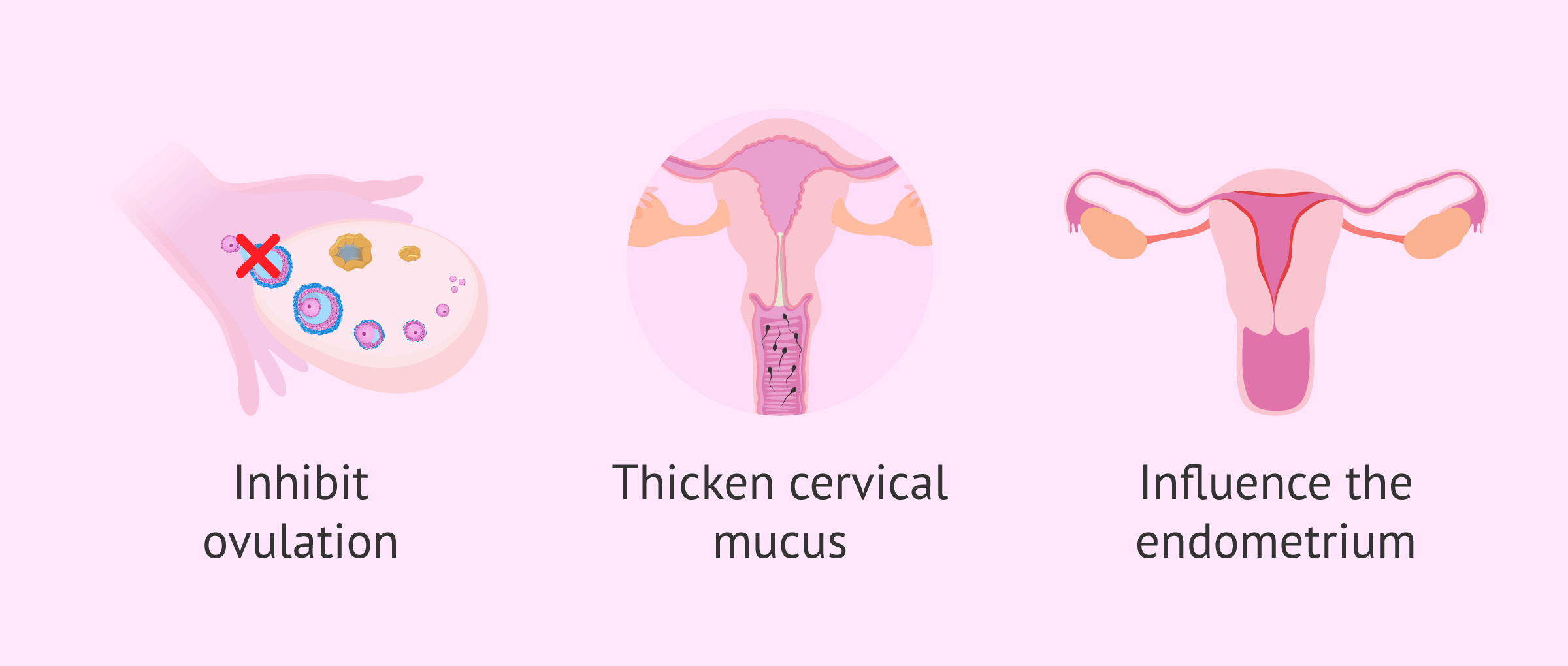
In general, the release of both hormones causes the following effects in women:
- Inhibit ovulation in the ovaries.
- Thickening the cervical mucus to prevent sperm from reaching the egg and making fertilization difficult.
- Influencing the endometrium by preventing it from reaching the thickness necessary for embryo implantation to occur.
On the other hand, the effects of the contraceptive ring are reversible. Thus, it is only necessary to remove the vaginal ring to regain fertility in a short period of time.
Vaginal ring effectiveness rate
The effectiveness of the vaginal ring is approximately 98-99%. Therefore, only a small percentage of couples using this contraceptive method will have an accidental pregnancy.
Of course, a woman's chances of getting pregnant also depend on proper use of the vaginal ring and other factors such as certain diseases or the administration of medications. In addition, the ring loses effectiveness if it is not replaced in time.
It is important to note that the exact position of the ring in the vagina does not influence its contraceptive effectiveness.
The first time the contraceptive ring is used, it must be inserted 5 days after menstruation at the latest. Thus, an immediate effectiveness of the vaginal ring can be granted. If it is not placed in this time, it will be necessary to use another barrier method during the first 7 days.
Placement and removal
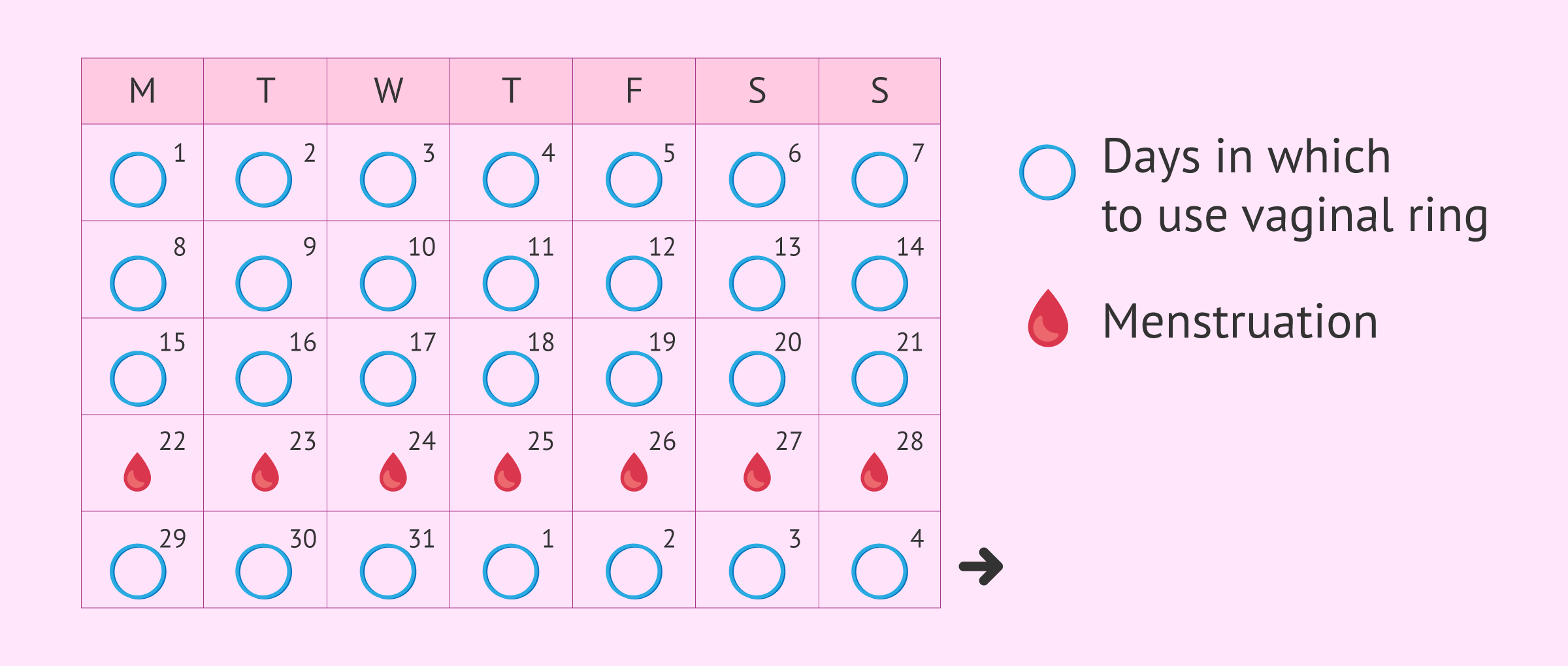
The process of placing the vaginal ring is simple and fast. With clean hands, the woman will hold the ring with her forefinger and thumb, pressing on the ends. When the ring is flat, she inserts it into the vagina until it is not noticeable, where the ring will remain for 3 weeks.
Once this period is over, i.e. after 21 days, the woman must remove the ring and pause for one week. For this purpose, she attaches a finger to the vaginal ring and gently pulls it outward. If withdrawal is not possible, the woman should see a doctor.
Normally, after the contraceptive ring is removed, menstruation takes two or three days to appear and usually lasts about a week.
In case of forgetfulness, the contraceptive ring can remain a maximum of 4 weeks inside the vagina, although the woman should remove it as soon as she realizes her mishap. However, after this time the possibility of pregnancy cannot be excluded because the contraceptive ring stops releasing hormones.
Use of the contraceptive ring
As we have already mentioned, the effectiveness of the contraceptive ring is 98-99%, but it has both advantages and disadvantages for the women who use it. It is therefore necessary to be well informed about all aspects of the vaginal ring.
Advantages
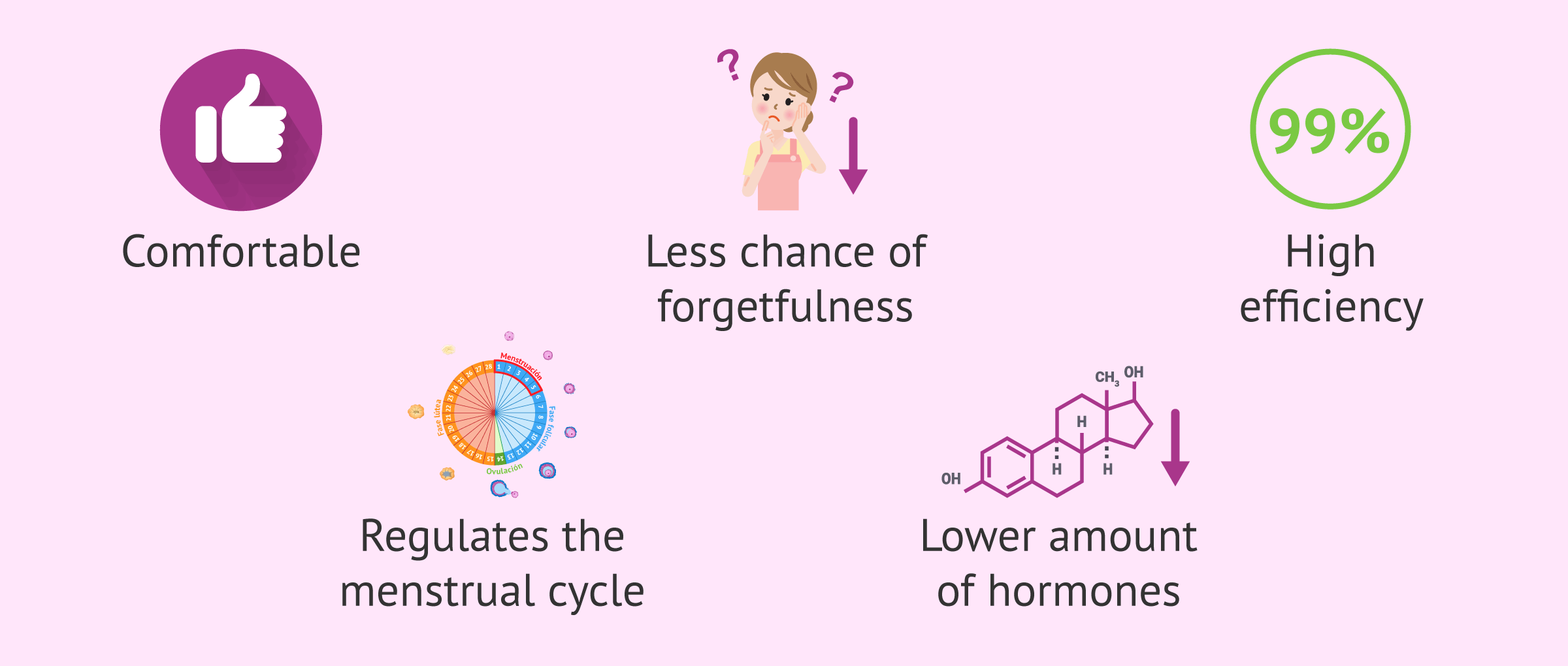
Thanks to the low amount of hormones released, the contraceptive ring has numerous advantages as a pregancy preventing method. We’ll show some of them below:
- Comfortable to insert and remove.
- Less chance of forgetting.
- High efficiency.
- Regulates the the menstrual cycle.
- Reduces uterine cancer.
- Contains less hormones.
In addition, the use of the contraceptive ring may have other benefits for each woman in particular.
Disadvantages and/or side effects
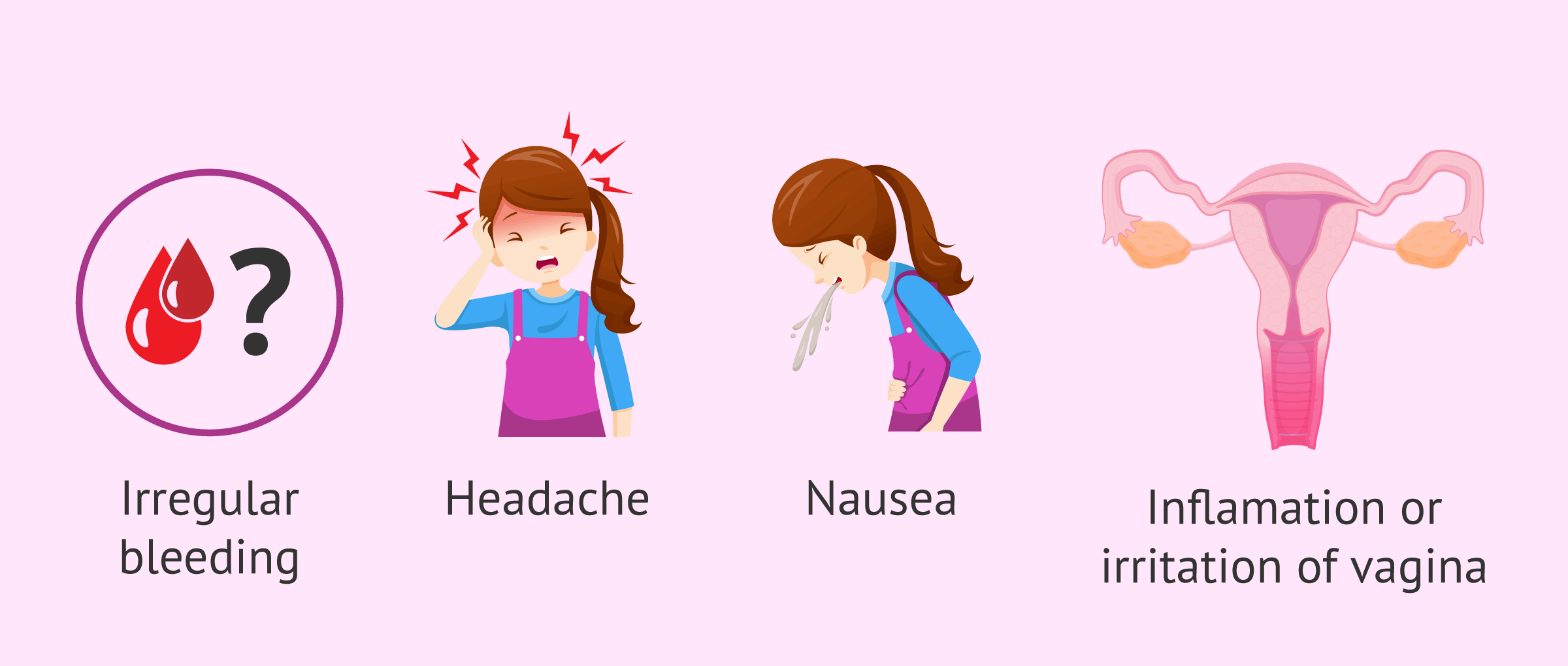
As the body adapts to the hormonal changes produced by the vaginal ring, some women may experience symptoms such as those discussed here:
- Leucorrhea or increased vaginal discharge.
- Irregular bleeding or no monthly bleeding.
- Headache.
- Nausea.
- Inflammation and irritation of the vagina.
Most of these symptoms are usually temporary and go away when a woman has been using the birth control ring for three months.
However, it should be noted that the vaginal ring does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), so the use of an additional contraceptive method is recommended.
If you want to know more about the existing types of contraceptive methods, have a look into the following article: Contraceptive methods: types, effectiveness, risks and prices.
Indications and contraindications
The vaginal ring is a good option for those women who want comfort and don't want to think about taking the pill every day or who have trouble swallowing it.
Not all women can (or should) use the birth control ring, though. There are some medical conditions that make using the ring less effective or more risky for a woman's health (for example, high blood pressure and some types of cancer).
Other cases in which it is not convenient to use the vaginal ring are the following:
- Severe Obesity.
- Being a woman over 35 years.
- Having a familiy background of breast or uterus cancer.
- Diabetics.
- Vaginal bleeding with no known cause.
- Pregnant women.
In addition, women who use hormonal contraceptive methods (vaginal ring, patches, or pills) should not smoke, as this increases the risk of serious side effects.
FAQs from users
Can I have sex on the birth control ring?
The contraceptive ring has a soft and comfortable texture, so it does not need to be removed to have sex. However, if you prefer, you can remove the ring without problem. In this case, you only have to remember to insert the ring back into the vagina in no more than 3 hours.
How much is the vaginal ring?
In the US, the vaginal ring costs between $30-35. However, they are covered by most health insurance plans.
Is it common to use the contraceptive ring before fertility treatment instead of pills?
Before the first step in IVF or ICSI (hormone therapy) cycles, a pre-treatment with a contraceptive can be administered, most often an oral contraceptive.
A COC (combined oral contraceptive) contains both progestogen and oestrogen, as does the vaginal ring which could also be used prior to fertility treatment.
A pre-treatment with a progestogen or oestrogen alone could also be implemented before hormone therapy. These pre-treatments suppress the production of hormones by the patient. Therefore, they may improve the woman's response to hormone therapy in IVF/ICSI cycles. In this way, adverse events such as cyst formation (fluid-filled sac that develops in the ovary) and the number of pregnancy losses could be reduced, and pregnancy outcomes could be improved.
Does the birth control ring interact with any medications?
Yes. Antibiotics from the rifampicin group interact with the effects of the vaginal ring.
However, analgesics, anti-inflammatories or common antibiotics such as amoxicillin do not decrease the effectiveness of the contraceptive ring.
What should I do if the birth control ring falls out by accident?
When this happens, the woman should wash the birth control ring with water and put it back in her vagina.
If the vaginal ring has spent more than three hours outside the woman's body, an additional contraceptive method must be used for the next 7 days.
Suggested for you
If you have just had a baby and are breastfeeding, an IUD is a recommended contraceptive. You can learn more in the following article: How Does the IUD Work and What are the Pros & Cons?
If you, on the other hand, want a permanent method of birth control, you can opt for a tubal ligation (in women) or a vasectomy (in men).
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Lete I, Doval JL, Pérez-Campos E y cols. Self-described impact of noncompliance among users of a combined hormonal contraceptive method. Contraception. 2008; 77(4):276-82 (View)
Milsom I, Lete I, Bjertnaes A, et al. Effects on cycle control and body weight of the combined contraceptive ring, NuvaRing, versus an oral contraceptive containing 30 µg ethinyl estradiol and 3 mg drospirenone. Hum Reprod 2006;21:2304-11 (View)
Nelson AL. Comprehensive overview of the recently FDA-approved contraceptive vaginal ring releasing segesterone acetate and ethinylestradiol: A new year-long, patient controlled, reversible birth control method. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Oct;12(10):953-963. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2019.1669448 (View)
Paton DM. Contraceptive vaginal ring containing segesterone acetate and ethinyl estradiol: long-acting, patient-controlled, procedure-free, reversible prescription birth control.Drugs Today (Barc). 2019 Jul;55(7):449-457. doi: 10.1358/dot.2019.55.7.2965363 (View)
Temmerman M. A new woman-controlled contraceptive vaginal ring: a global step forward. Lancet Glob Health. 2019 Aug;7(8):e986-e987. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30289-X (View)
Vargas SE, Midoun MM, Guillen M, Getz ML, Underhill K, Kuo C, Guthrie KM. A Qualitative Systematic Review of Women's Experiences Using Contraceptive Vaginal Rings: Implications for New Technologies.Int Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2019 Oct 4;45:25-34. doi: 10.1363/45e7619 (View)
FAQs from users: 'Can I have sex on the birth control ring?', 'How much is the vaginal ring?', 'Is it common to use the contraceptive ring before fertility treatment instead of pills?', 'Does the birth control ring interact with any medications?' and 'What should I do if the birth control ring falls out by accident?'.