The first month of pregnancy is a special one, as it is the moment when the woman finds out that she is expecting. Even though it is not visible yet, she is able to feel the first pregnancy symptoms by the end of this month. It is at this point that a pregnancy test can provide you with an accurate result.
Pregnancy starts when the sperm meets the egg in the Fallopian tube. From this moment on, a zygote starts to form (one-cell embryo), which will grow on a daily basis until it reaches the blastocyst stage.
When the embryo becomes a blastocyst, about 7-8 days after egg fertilization, it is ready to be implanted in the womb of the woman. This extraordinary event is known as embryo implantation and marks the beginning of the pregnancy journey.
Provided below is an index with the 6 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 1.1.
- 1.2.
- 1.3.
- 1.4.
- 2.
- 2.1.
- 2.2.
- 2.3.
- 3.
- 3.1.
- 3.2.
- 3.3.
- 3.4.
- 3.5.
- 3.6.
- 3.7.
- 3.8.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
What happens in the first month of pregnancy?
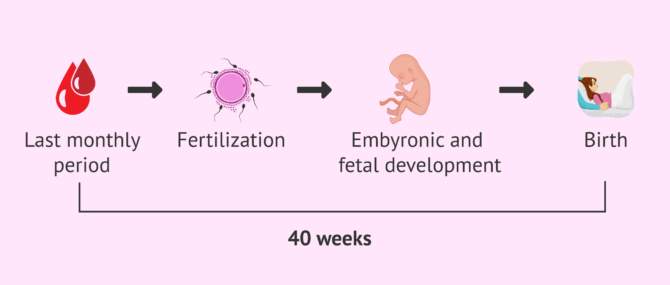
Pregnancy is a long process that lasts about 40 weeks. Throughout the process, both the pregnant woman and the fetus go through a series of major changes.
Before examining the details of the first month of pregnancy week by week, it should be noted that gynecologists and all professionals from the field of assisted human reproduction start counting the weeks of pregnancy with the date of the last menstrual period (LMP).
This is because it is sometimes difficult for a woman to know the exact time of fertilization. However, a woman usually does know when her last menstrual period was. Therefore, the "first day of pregnancy" is considered to coincide with the date of the last menstrual period in a 40-week gestation.
Pregnancy lasts approximately 40 weeks from the beginning of the last menstrual cycle to the time of delivery. However, it is important to note that during weeks 1 and 2, the woman is not actually pregnant yet.
However, it should be noted that some do consider that week 1 of pregnancy begins when the fertilization of the egg occurs after sexual intercourse, and the existence of the embryo.
Throughout this article we will discuss the weeks of pregnancy as it is usually done by specialists in reproduction and obstetrics, considering the first week of pregnancy from the date of the last menstrual period (LMP).
Week 1 of pregnancy
As we have mentioned, the beginning of pregnancy is considered to be the first day of the last menstrual period, so that all gynecologists can have a consensus when counting the weeks of gestation.
Therefore, the first week of pregnancy coincides with the week in which the woman experiences her last menstrual bleeding before becoming pregnant.
Nothing special happens in this first week compared to other menstrual cycles, because conception has not really taken place yet. However, the female reproductive system begins to prepare for it as in every cycle:
- Ovaries
- They respond to the hormones produced by the pituitary gland, i.e. FSH and LH, and start to develop the ovarian follicles that can be found within. Also, sex hormones start to be produced, especially estrogens.
- Endometrium
- Proliferation of the endometrial lining begins one more time. It becomes thicker thanks to the action of estrogens over the uterus.
If you want to know in more detail everything that happens during this first week of pregnancy, you can continue reading in the following post: Week 1 of pregnancy: what are the symptoms in the mother?
Week 2
During the second week of pregnancy, two important events take place before conception of the embryo occurs:
- Follicle recruitment and selection
- Out of all the primordial follicles that started to mature in the ovary, only one of them will continue its development due to its increased response to the effects of FSH.
- Ovulation
- The primordial follicle that has continued developing turns into a Graaf follicle that bursts when the LH surge occurs. As a consequence, a mature egg cells is released from the ovary.
Ovulation can occur either at the end of the second week or at the beginning of the third week of pregnancy, depending on the woman's menstrual cycle. Approximately, ovulation occurs around day 14 of the cycle if the woman is regular. This day and the adjacent days are the so-called fertile days since the probability of achieving pregnancy is higher.
In addition, after ovulation, the remains of the Graafian follicle in the ovary give rise to the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone.
In response, the endometrium continues to increase in thickness and prepares for future embryo implantation.
You can continue reading about all the events that happen in the second week of pregnancy in the following article: Week 2 of pregnancy: symptoms and recommendations for the mother.
Week 3
During this third week of gestation, conception actually occurs. The egg, which is in the fallopian tube after ovulation, is fertilized by a sperm.
At this moment, the fusion of the maternal and paternal genetic material takes place, giving rise to the zygote, and embryonic development begins.
The zygote divides with each passing day and the number of cells increases. Furthermore, although fertilization takes place in the fallopian tubes at the beginning of week 3, the embryo must move towards the uterus during its first days in order to adhere to the endometrium and implant.
By the end of third week, the embryo reaches the blastocyst stage. Blastocyst embryos are composed of the following layers:
- Trophoblast or trophectoderm, which will develop into a large part of the placenta.
- Inner Cell Mass (ICM) or embryoblast, which will give raise to the organs and tissues of the fetus.
If you are interested in going into more detail on the first days of embryonic development, you can continue reading in the following article: Week 3 of pregnancy: the beginning of embryo development.
Week 4
Once the embryo has reached the uterus, it must implant. Implantation consists of the attachment and invasion of the embryo into the endometrium (the layer that lines the inside of the uterine cavity) about 7-9 days after ovulation.
After implantation, the trophectoderm begins to release the pregnancy hormone hCG. This hormone is mainly responsible for the first symptoms of pregnancy such as nausea, abdominal swelling, pain in the abdomen, swollen breasts, etc.
In addition, hCG is the hormone detected by pregnancy tests to confirm pregnancy. To do this, hCG levels must reach a minimum level detectable by the test. For this reason, the woman must wait until she has a delay in menstruation to be able to take a pregnancy test reliably.
Normally, a woman does not suspect that she is pregnant before week 4, since the menstrual delay has not yet occurred. Precisely, the absence of menstruation, as well as other small symptoms that we have already mentioned, will be the ones that make you suspect pregnancy.
To continue reading about this topic and to know when it is reliable to take a pregnancy test, we recommend you to click on the following link: Week 4 of pregnancy: implantation of the embryo in the uterus.
Care in the first month of pregnancy
Both women seeking pregnancy and those who have just received the news that they are expecting a baby need to start taking care of their bodies and their lifestyles.
We now discuss some advice to help maintain a healthy pregnancy and favor the birth of a healthy child with the right weight.
Healthy, balanced diet
Pregnant women need to have a very complete diet that covers all the vitamin and mineral requirements, since the nutrition of the fetus will depend entirely on them, as well as the supply of oxygen.
In particular, pregnant women should start paying attention to the following foods and nutritional intake:
- Folic acid
- is essential for the formation of the baby, as it helps prevent neural tube defects. Green leafy vegetables and legumes provide folic acid to the body.
- Calcium
- A greater supply of calcium is necessary for the correct development of the baby's bones and teeth, among other things. Calcium is also important to prevent preeclampsia in pregnant women. It is advisable to drink milk and yogurt, as well as sesame seeds and almonds.
- Iron
- This mineral is important to prevent anemia in pregnant women. Meat, legumes and nuts are sources of iron.
- Fiber
- fruit, vegetables and cereals should be consumed daily.
In addition, it will be important for the pregnant woman to control the consumption of carbohydrates and fats and to avoid caloric foods, as well as alcohol and coffee.
On the other hand, for the prevention of toxoplasmosis and listeriosis, it will be necessary to wash fruits and vegetables before eating them, not to eat raw meat, fish, and seafood, to avoid undercooked eggs, unpasteurized cheese, etc.
At the beginning of pregnancy, it may be a little difficult to adapt to this new lifestyle. Therefore, it may be advisable for pregnant women to join support groups where they can ask questions and talk to other women in the same situation.
Good lifestyle habits
Another very important recommendation for pregnant women is to quit smoking immediately.
If it is necessary to take medication for any condition such as, for example, a urinary tract infection or the flu, it is important to consult with the doctor about which drugs are appropriate during pregnancy.
In general, substances that may be harmful to the fetus should be avoided. In the event of working in an environment that involves the handling of toxic products or tasks that pose a risk to the pregnancy, the woman will have to consult the possibility of taking time off work during the entire pregnancy.
Sport
If the woman practices high-intensity sports, at this time she should start to moderate physical exercise. Sports such as pilates, yoga or swimming are a good option both for women who like to keep their bodies in shape and for those who do not usually do sports.
It is important not to completely abandon physical activity during pregnancy, as long as it has not been contraindicated by the specialist. One option is to take daily walks to exercise and help relax the body.
In addition, it is advisable to rest for as long as the woman needs, maintain good sleeping habits, go to bed and get up at the same time every day, etc. In general, everything that helps the woman to feel well throughout her pregnancy.
FAQs from users
What are the symptoms of pregnancy in the first month?
Pregnancy is a process of constant physiological changes in a woman's body. These changes are a consequence of the adaptation that the body must make to successfully achieve the growth and development of the intrauterine fetus.
These changes begin shortly after implantation and can manifest themselves even before the positive Beta HCG.
Read more
What happens if I drink alcohol before I know I am pregnant?
During the first few days of pregnancy (before the absence of menstruation), the embryo undergoes rapid changes in its development until it forms a blastocyst. This is the name given to embryos that manage to develop up to day 5-6 of development and form a specific structure. It is at this stage that it should implant in the uterus. When this happens, the gastrulation process begins, in which the cells of the embryo have to differentiate into three layers (endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm) and begin to form rudimentary organs.
This period is particularly sensitive to any type of toxicant, including exposure to alcohol. Any aggression could alter this evolutionary process of the embryo and produce problems in the embryo.
Most of the studies carried out on the effect of alcohol in these early stages have been carried out in mice, and have shown that alcohol intake is clearly detrimental. Placental volume and proper functioning of the placenta in exposed mice was found to be much lower than in mice that did not ingest alcohol.
In addition, one study showed that a single dose of alcohol at this stage could cause craniofacial malformations similar to those of fetal alcohol syndrome.
Therefore, total abstinence from all alcoholic beverages is recommended to all pregnant women or women who are trying to become pregnant.
How old is the embryo in the first month of pregnancy?
It may be 2 weeks old.
What is the point of talking about week 1 of pregnancy if fertilization has not yet occurred? Why is it counted from the last menstrual period?
It is counted from the last menstrual period to be able to determine more accurately the time of pregnancy, because the woman knows exactly when she gets her period but there is no way of knowing when fertilization actually occurs.
The truth is that it is somewhat strange to talk about weeks of pregnancy when fertilization has not occurred. Therefore, there are those who start counting from the moment they sense that fertilization has taken place, based on the fact that in a regular cycle, fertilization takes place about two weeks after the menstrual period starts.
These variations are the reason why sometimes 9 months of pregnancy and sometimes 10 months of pregnancy are referred to. However, pregnancy is usually considered to be 40 weeks from the date of the last menstrual period.
Is it normal to have a small amount of vaginal bleeding during the first month of pregnancy?
During the first month of pregnancy, there may be occasional spotting that need not be worrisome. In many women, bleeding occurs as a result of implantation. Others have light spotting simply due to embryonic development and the hormonal changes inherent to gestation.
Only if the bleeding is intense and continuous will it be a reason to consult a specialist.
Is it true that the first month is when miscarriage is most likely to occur?
Yes, miscarriages occur more frequently in the first months of gestation. If the embryo is able to evolve in the first months, it can usually continue to develop. However, there can also be a gestational loss in advanced stages.
Should I be concerned about bloating and abdominal pain in the first month of pregnancy?
No, in principle, feeling slight discomfort in the belly does not have to be a sign of alarm, since the hormonal changes that your body is having due to fertilization and embryo implantation can cause symptoms such as nausea, ovarian pain, abdominal pain, bloating, etc.
Is the belly noticeable in the first month of pregnancy?
No, the pregnant belly does not start to become evident until later in pregnancy, around the 17th week of pregnancy.
However, there may be symptoms late in the first month of pregnancy such as abdominal bloating and nausea, due to the hCG hormone released by the embryo after implantation.
Recommended Reading
When a woman is one month pregnant, she may notice various symptoms that are typically associated with pregnancy. However, they may unnoticed up until she takes a pregnancy test that confirms that she isindeed expecting. Get more information by clicking the following link: What Are the Earliest Symptoms of Pregnancy Before Missed Period?
As early as the first month of pregnancy, the pregnant woman should dedicate some time to learn about prenatal care and the changes her body is going to go through. We invite you to read this article: Maternal health and pregnancy
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Ashary N, Tiwari A, Modi D. Embryo Implantation: War in Times of Love. Endocrinology. 2018 Feb 1;159(2):1188-1198.
Belle M, Godefroy D, Couly G, Malone SA, Collier F, Giacobini P, Chédotal A. Tridimensional Visualization and Analysis of Early Human Development. Cell. 2017 Mar 23;169(1):161-173.e12.
Bhakta HH, Refai FH, Avella MA. The molecular mechanisms mediating mammalian fertilization. Development. 2019 Aug 2;146(15):dev176966.
Eisenber, A. (1991) What to Expect When You’re Expecting, New York, NY: Workman Publishing Company, Inc.
Georgadaki K, Khoury N, Spandidos DA, Zoumpourlis V. The molecular basis of fertilization (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2016 Oct;38(4):979-86.
LaGrew DC, Wilson EA (1983). Determination of gestational age by serum concentrations of human chorionic gonadotropin. Obstet Gynecol;62:37-40
Li S, Winuthayanon W. Oviduct: roles in fertilization and early embryo development. J Endocrinol. 2017 Jan;232(1):R1-R26.
MayoClinic.com, Pregnancy Center.(2008, February). Pregnancy. Retrieved April 11, 2008
National Health Service (NHS) (UK) (2009). The Pregnancy Book. Your complete guide to: A healthy pregnancy, Labour and childbirth, The first weeks with your new baby. Crown copyright 2009. Produced by COI for the Department of Health.
Norman RJ, Menabawey M (1987). Relationship between blood and urine concentrations of intact human chorionic gonadotropin and its free subunits in early pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol; 69: 590-593
Okabe M. Sperm-egg interaction and fertilization: past, present, and future. Biol Reprod. 2018 Jul 1;99(1):134-146.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2005). Your Pregnancy and Birth (4th ed.). Washington, DC: Meredith Books.
The American Dietetic Association. (2008) Position of the American Dietetic Association: Nutrition and Lifestyle for a Healthy Pregnancy Outcome. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. 108:553-561.
The National Women’s Health Information Center, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Women’s Health (2006, April). Prenatal Care. Retrieved November 9, 2007
Wilcox AJ, Weinberg CR, Baird DB. Timing of intercourse in relation to ovulation: effects on the probability of conception, survival of the pregnancy and sex of the baby. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1517– 1521.
FAQs from users: 'What are the symptoms of pregnancy in the first month?', 'What happens if I drink alcohol before I know I am pregnant?', 'How does pregnancy look like at 4 weeks?', 'How old is the embryo in the first month of pregnancy?', 'Can I sleep on my stomach if I am one month pregnant?', 'What is the point of talking about week 1 of pregnancy if fertilization has not yet occurred? Why is it counted from the last menstrual period?', 'How many weeks is one month of pregnancy?', 'Is it normal to have a small amount of vaginal bleeding during the first month of pregnancy?', 'Can I ride roller coasters if I am one month pregnant?', 'Is it true that the first month is when miscarriage is most likely to occur?', 'Should I be concerned about bloating and abdominal pain in the first month of pregnancy?' and 'Is the belly noticeable in the first month of pregnancy?'.
Authors and contributors

More information about Michelle Lorraine Embleton
More information about Cristina Algarra Goosman












I´m currently in my 2 week beta wait and I can´t stop reading all these articles on early pregnancy. I’m loving all the info – thanks!
Hi Taraboomday
Thanks for the feedback and wishing all the best for the BFP.
Best regards
Hi, I am 8DPO and I have some pregnancy symptoms, my breasts hurt and I feel nauseous sometimes. Could I take a pregnancy test now?
Hi Karen,
Generally, a reliable result on a home pregnancy test is given after the missed period, i.e. about 14 days after ovulation.
There are some pregnancy tests that detect lower levels of the hCG hormone that identifies pregnancy, but we recommend waiting until two weeks have passed since ovulation and you have missed your period. This will avoid false negatives.
Another option is to go to the doctor so that they can do a blood test that can give a more specific and earlier result on the presence of pregnancy.
I hope I have helped you.
Best regards
Hi, I am a little worried, I have been trying to get pregnant for four months, the first cycles did not work and I had a normal period. Now in this last month after ovulating I am noticing discomfort and pain in the belly, can this be because the baby is implanting? Can I take a pregnancy test?
Hello Cayton,
The discomfort towards the middle of the cycle may be due to ovulation itself since there are women in which the release of the egg from the follicle may even present discomfort.
It may also be that you have ovulated early and you are indeed noticing the discomfort of implantation. I recommend that you wait two weeks after ovulation to get tested, as this will be the time when you can find more reliably the result of the cycle.
Best of luck.