With the ninth month of pregnancy, the final stretch begins, which covers from week 33 till week 36 of pregnancy. These days, the symptoms to expect are quite uncomfortable, as the baby's development is finishing, and the only thing left for him to do is gaining more and more weight.
Labor might start at any time within the next weeks, so we recommend that you avoid traveling or long trips, and try to pay attention to any kind of sign that indicates your baby's birth is imminent.
Provided below is an index with the 8 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 3.1.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 4.3.
- 4.4.
- 5.
- 5.1.
- 5.2.
- 5.3.
- 5.4.
- 5.5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
Baby development
At this stage of pregnancy, it is likely that the baby is stuck in the pelvis, which is to say, with the head placed above the cervix. This position is called cephalic presentation, head presentation or head-first presentation. If the baby is not lying in this position over the next few weeks, your OB/GYN may schedule a C-section, since vaginal delivery would be highly complicated if the baby is inadequately positioned.
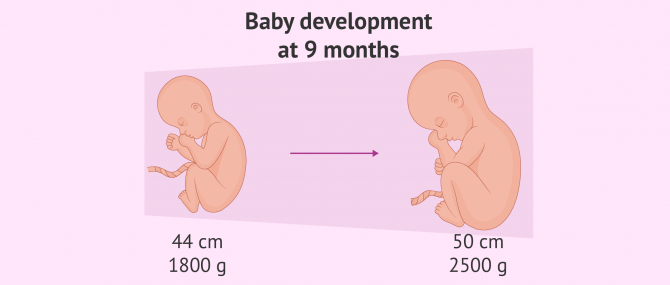
Although each baby develops differently, on average, a fetus of 36 weeks can measure almost 50 cm, and weight between 2200 and 2800 g. He or she can gain up to 30 g daily.
The physical appearance of the fetus at this month of pregnancy is very similar to the one he or she will have at birth, as labor is just a few weeks ahead.
Lanugo has almost disappeared from the skin of the baby. This, along with the accumulation of fat under the skin, which is ready and has a pinkish color, give him or her a totally human appearance. Get more info by clicking the following link: What Is Lanugo?
Almost all vital organs work perfectly, including:
- Lungs
- They are fully developed, and ready to allow the baby to breathe when he or she is born. This is possible thanks to the corticoids produced by the adrenal glands.
- Digestive system
- The unborn baby is now ready to digest amniotic fluid, and his intestines are filled with meconium.
Meconium is a green-colored, viscous substance that fills the colon of the fetus during pregnancy. It is the first fecal material of the newborn.
The maternal organism starts to transfer temporary immunity to the unborn child via the umbilical cord. This gives him or her protection against a number of childhood illnesses.
Changes in the mother
The situation of the mother-to-be when she is nine months pregnant does not vary too much if compared to the previous weeks. However, the discomforts she was already experiencing might get even worse due to the advanced stage of pregnancy.
If the baby is already settled into a head-down position, the mother might feel some relief, as pressure on the stomach decreases. But this position means the baby's feet are located under the breastbone, which makes kicks very annoying and may lead to shortness of breath. Simultaneously, the head adds pressure to the bladder, thereby increasing the urination frequency.
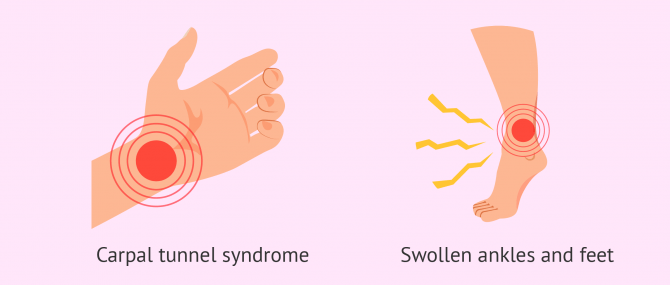
It is very likely that bloating and liquid retention become worse during the hot summer months. It is normal that you feel that your feet and ankles are excessively swollen.
A common affection of pregnant women is the Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), which is caused by the inflammation of the nerves located in the median nerve and accumulation of fluid, causing pain and numbness of the wrists.
It is also normal that the belly button pops out during this month due to the expansion of your abdomen. A few months after birth, skin, muscles, and uterus go back to their normal position, and your belly button will go back in.
When a woman is 9 months pregnant, she is expected to have gained between 10 and 14 kg of weight, which makes back pain, cramping, pelvic pain, and exhaustion more common. These nuisances can be relieved with the following exercises:
- Pilates.
- Yoga.
- Swimming for pregnant women.
- Kegel exercises.
- Spine stretches.
Insomnia is also very common, as women need to get up several times during the night to urinate. In addition, hormonal changes also reduce deep sleep, which is the sleep that allows rest.
Prenatal visits & recommendations
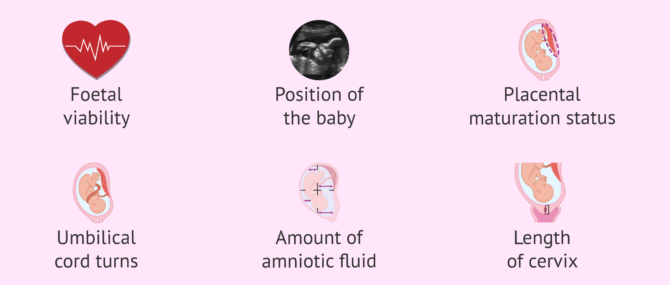
If the third trimester ultrasound scan has not been offered to you yet, it is likely to be performed to you in the next weeks. This imaging test is typically done vaginally, and provides us with the following information:
- Fetal viability
- Detecting and monitoring the fetal heart rate and its frequency is essential to dismiss potential complications.
- Position of your baby
- At this point, it is normal that your baby has settled into a head-down position. Examining the position of your baby is crucial to create a birth plan.
- Maturity of the placenta
- Aging of the placenta can lead to oxygenation or nourishing problems for the fetus.
- Umbilical cord wraps
- The presence of wraps in the umbilical cord should be assessed, particularly around the neck. If wrapping is detected, special attention should be paid during dilation. One should note that this occurs more often than expected, and it is not a concerning issue in most cases as long as it is medically supervised.
- Amniotic fluid volume
- The quantity of this liquid diminishes as the baby grows. However, an excessive decrease may indicate fetal-growth disorders or preterm birth. For this reason, regular amniotic fluid volume assessments are crucial.
- Cervical length
- Monitoring the length of the cervix is key during the final weeks of pregnancy, since it gets shorter (a process called effacement) during the early stages of labor.
In the ninth month of pregnancy, prenatal visits are more frequent, especially during weeks 35 and 36. Again, your OB/GYN may ask you to perform a urine and blood test. Also, he may measure your weight and size.
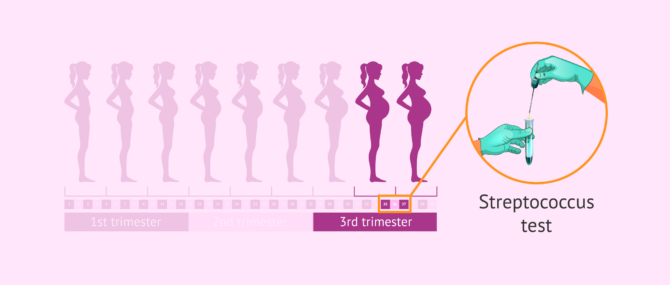
Detection test for streptococcus
One of the most important tests run between weeks 35 and 37 is the one based on the detection of infections caused by group B streptococcus. This bacteria, which typically colonizes the gastrointestinal tract of adults without causing problems, may reach the vagina and cause infections in the baby during labor.
This is the reason why the majority of physicians recommend routine vaginal and anal cultures in order for the pregnant woman to be tested for the presence of this bacteria.
The main risk factors that can lead to the development of this pathology are:
- Previous infections caused by group B streptococcus during the ongoing pregnancy
- Previous urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by this bacteria during the ongoing pregnancy
- Detection of this bacteria in previous childbirth(s)
In case any of the cultures is positive, your doctor will prescribe you antibiotics before labor to prevent contagion to the baby.
The 9th month by week
The changes to be noticed during the weeks that cover the ninth month are key, since any abnormal symptom may be an early sign of labor. What follows are the main events typically experienced by pregnant women at this stage:
Week 33
The baby usually gets stuck in the pelvis during this week. When he or she is placed in this position, his/her anatomy is easily distinguishable.
The fact that the feet are located under the breastbone causes a sharp rib pain as a consequence of the baby physically kicking you in the ribs, due to the reduced room for the baby to grow.
Studies have shown that the baby has rapid eye movement (REM) sleep from this week on.
According to experts, rapid eye movement (REM) sleep can be a sign of the baby dreaming, which is key to newborn stimulation and brain development.
We recommend you to continue reading in the following link: Changes in the baby and common discomforts in the 33rd week of pregnancy.
Week 34
This week, the baby can measure up to 46 cm long, and weight about 2 kg. The bones of your unborn baby are almost totally developed, except for the ones at the top of your baby's head, where the skull bones have not yet grown together to ease the passage of the baby through the birth canal.
Also, the vernix, a waxy white substance that covers the skin of newborn human babies, becomes denser. The reason for this is, again, to reduce friction as your baby passes through the birth canal during delivery.
If birth occurred this week, the baby would need to stay at a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) for a few days. The good news is that the chances for him to survive without long-term health problems is very high.
Week 35
Fetal bone marrow starts producing its own blood cells during a process called hematopoiesis.
The fetus reaches the maximum level of development. He or she is a human being now, and the only thing left to do is gaining more and more weight. In fact, on average, unborn babies can gain between 250 and 350 g per week at this point. As a result, back pain gets more intense.
You can visit the following article for more information about this week of pregnancy: 35 Weeks Pregnant.
Week 36
You are likely to go into labor at any time during the next days. For this reason, it is likely that your gynecologist recommends a weekly follow-up of the baby's heartbeats and the contractions you may have.
In case of doubt, we recommend that you solve it as soon as possible, especially on how to react or whom you should call in case your water breaks.
Here you can read more in depth about this week of gestation: 36th week of pregnancy: changes in the baby and symptoms in the mother.
FAQs from users
Is abundant white discharge normal during the 9th month of pregnancy?
In the final weeks of pregnancy, it is normal that you experience an increase in the amount of vaginal discharge due to pressure of the fetus over the vaginal tract. However, if the discharge expelled is too thick and abundant, it might be the mucus plug. In such case, we recommend that you ask your doctor as soon as possible.
Can you go into labor without baby dropping?
Yes. Normally, when a woman is nine months pregnant, the most likely is that the baby is already stuck in the pelvis. However, if that is not the case, it is convenient to schedule a C-section before the sac breaks and labor contractions start.
What if the baby is not moving during the 9th month of pregnancy?
The movements of the unborn baby tend to slow down as the pregnancy progresses due to insufficient room in the uterus. However, if fetal activity stops totally, we recommend that you visit your doctor at once.
What should I eat during the ninth month of pregnancy?
Keeping in mind that your baby is almost complete, at this stage he or she will be accumulating baby fat. For this reason, you should eat foods that are high in fiber, calcium, iron, vitamin C and A, and folic acid. Since your baby needs to add on weight during these days, it is recommended that you make your meals a little bigger in quantity.
Is it normal to have yellow discharge in the ninth month of pregnancy?
No. Yellowish discharge during pregnancy may be caused by a yeast infection. In these cases, abnormal vaginal discharge is often accompanied by a foul odour as well. In any case, it is best to consult a specialist.
Suggested for you
When the ninth month of pregnancy starts, labor is very close, so it is not uncommon that contractions and symptoms become more noticeable. Get more information: 33 Weeks Pregnant.
We have explained that one of the main symptoms of pregnancy at this stage are cramps. Want to learn more about what causes them? Read: Cramps When Pregnant.
Finally, one of the most important aspects to have under control during the nine months of pregnancy, and especially during these final weeks, is the risk of preterm birth. In this sense, being familiar with its early signs is strongly recommended. Read this next: What Is Preterm Delivery?
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
ACOG. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2002) Exercise during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Committe Opinion Nº 267 . Washington, DC. January. Obstet Gynecol; 99:171-3 (View)
Artal, R. O'Toole, M. and White, S. (2003) Guidelines of the American College of Obstetrician and Gynecologists for exercise during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Br J Sports Med; 37: 6-12 (View)
Best Start Resource Centre (2016). A Healthy Start for Baby and Me. Ontario’s easy-to-read guide about pregnancy and birth. Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Copyright 2010, 2012, 2016 Health Nexus (View)
Daskalakis G, Pergialiotis V, Domellöf M, Ehrhardt H, Di Renzo GC, Koç E, Malamitsi-Puchner A, Kacerovsky M, Modi N, Shennan A, Ayres-de-Campos D, Gliozheni E, Rull K, Braun T, Beke A, Kosińska-Kaczyńska K, Areia AL, Vladareanu S, Sršen TP, Schmitz T, Jacobsson B. European guidelines on perinatal care: corticosteroids for women at risk of preterm birth. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023 Dec;36(1):2160628. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2022.2160628. PMID: 36689999. (View)
Goncu Ayhan S, Ayhan E, Çaglar AT, Sahin D. Ultrasonography for carpal tunnel syndrome in pregnancy: a prospective cross-sectional study. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2022 Aug;42(6):1769-1774. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2022.2036970. Epub 2022 Mar 9. PMID: 35260035. (View)
Khalil MR, Thorsen PB, Møller JK, Uldbjerg N. Number of colony forming units in urine at 35-37 weeks' gestation as predictor of the vaginal load of Group B Streptococci at birth. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2018 Apr;223:68-71. (View)
Poojari Y, Annapureddy PR, Vijayan S, Kalidoss VK, Mf Y, Pk S. A comparative study on third trimester fetal biometric parameters with maternal age. PeerJ. 2023 Jan 19;11:e14528. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14528. PMID: 36694822; PMCID: PMC9867875. (View)
FAQs from users: 'Is abundant white discharge normal during the 9th month of pregnancy?', 'Can you go into labor without baby dropping?', 'What if the baby is not moving during the 9th month of pregnancy?', 'What should I eat during the ninth month of pregnancy?' and 'Is it normal to have yellow discharge in the ninth month of pregnancy?'.
Authors and contributors