Tubal ligation in women is considered a permanent contraceptive method, as the possibility of a natural pregnancy after this surgery is practically zero.
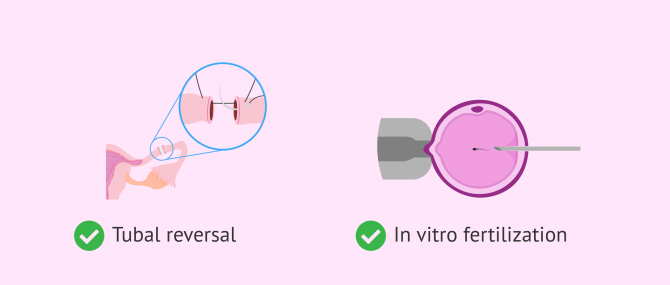
However, a woman who has her tubes tied can become pregnant again these days thanks to these two options:
- in vitro Fertilization (IVF)
- Tubal ligation reversal
The most appropriate option will depend on the particular situation of each woman, although it is true that IVF has a greater guarantee of success. In the case of tubal reversal, it is essential to take into account the time that has elapsed since the tubal ligation was performed and the method used to evaluate the success of the procedure.
Provided below is an index with the 8 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 3.1.
- 4.
- 5.
- 5.1.
- 5.2.
- 5.3.
- 5.4.
- 5.5.
- 5.6.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
What is tubal ligation?
The fallopian tubes are the muscular tubes that connect the ovaries and the uterus. This is where fertilization takes place, that is, the union between the egg and the sperm to give rise to the embryo, which will later descend into the uterus to implant in the endometrium and give rise to pregnancy.
Tubal ligation, also known worldwide as Pomeroy, consists of surgery to block this transport of the egg and sperm and therefore prevents fertilization and subsequent gestation.
During the surgical procedure, the tube can be sectioned, cut, ligated, or cauterized, to ensure that the ends of the tube are not rejoined.
The Pomeroy is the most commonly used technique to do a tubal ligation. It consists of cutting about 3 or 4 cm of the fallopian tube in its middle part. Generally, the Pomeroy allows for posterior tubal reconstruction.
Due to the high efficacy of this contraceptive method, it is recommended to do it in women who have been mothers and decide with total certainty not to have more children.
However, for various reasons in the lives of these women, it is possible to change their minds and desire pregnancy again.
In this case, pregnancy after tubal ligation is possible through assisted reproduction or tubal ligation reversal.
Pregnancy by IVF
As we have said, tubal ligation prevents the encounter between the egg and the sperm and, as a consequence, fertilization. However, this does not imply a blockage of ovulation, that is, the woman would still release an egg from the ovary in each menstrual cycle.
Tubal ligation does not imply menopause, therefore, women sterilized with this method continue with their regular menstrual cycle, producing both ovulation and menstruation.
This opens up the possibility for these women to access assisted reproduction if they wish to become mothers again. Specifically, pregnancy is possible with a treatment of in vitro fertilization.
Tubal ligation does not affect either the ovaries nor the uterus. It is, therefore, possible to administer drugs to the patient to perform an ovarian stimulation and then extract the eggs from the ovary to fertilize them in the laboratory.
The embryos are developed in culture for a few days and then transferred to the mother's uterus, where they will remain waiting to be implanted and lead to a pregnancy.
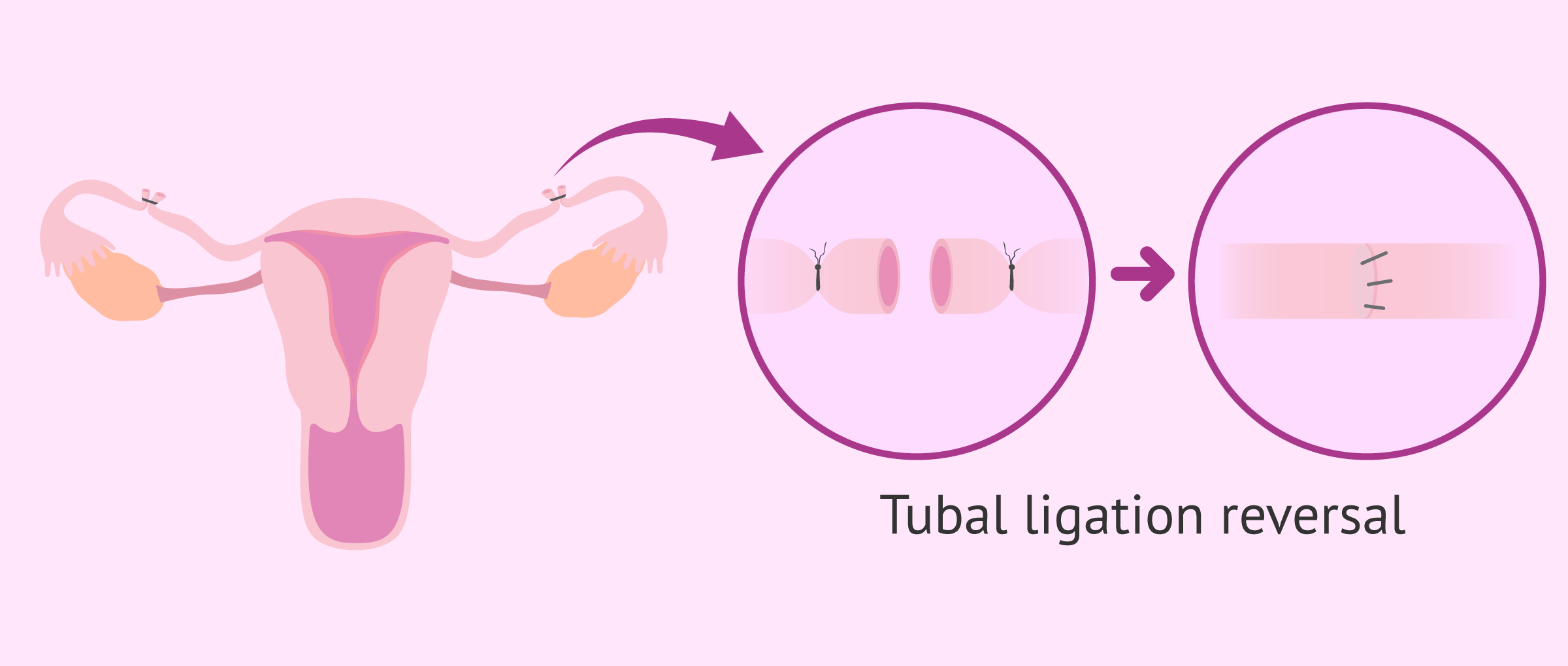
Tubal ligation reversal
This is the alternative method to IVF for achieving pregnancy in women with cut tubes. Tubal ligation reversal is a surgical procedure in which the ends of the tubes that were cut are joined back together.
Reconstruction of the fallopian tubes is technically possible but less effective than IVF because the tubes must regain both permeability and motility after the operation.
Thus, it should be kept in mind that rechannelling of the tubes does not imply 100% recovery of fertility since it is possible that tubal functionality may not be recovered.
Tubal ligation reversal is advised for young women, under 38, who want more than one pregnancy in the future.
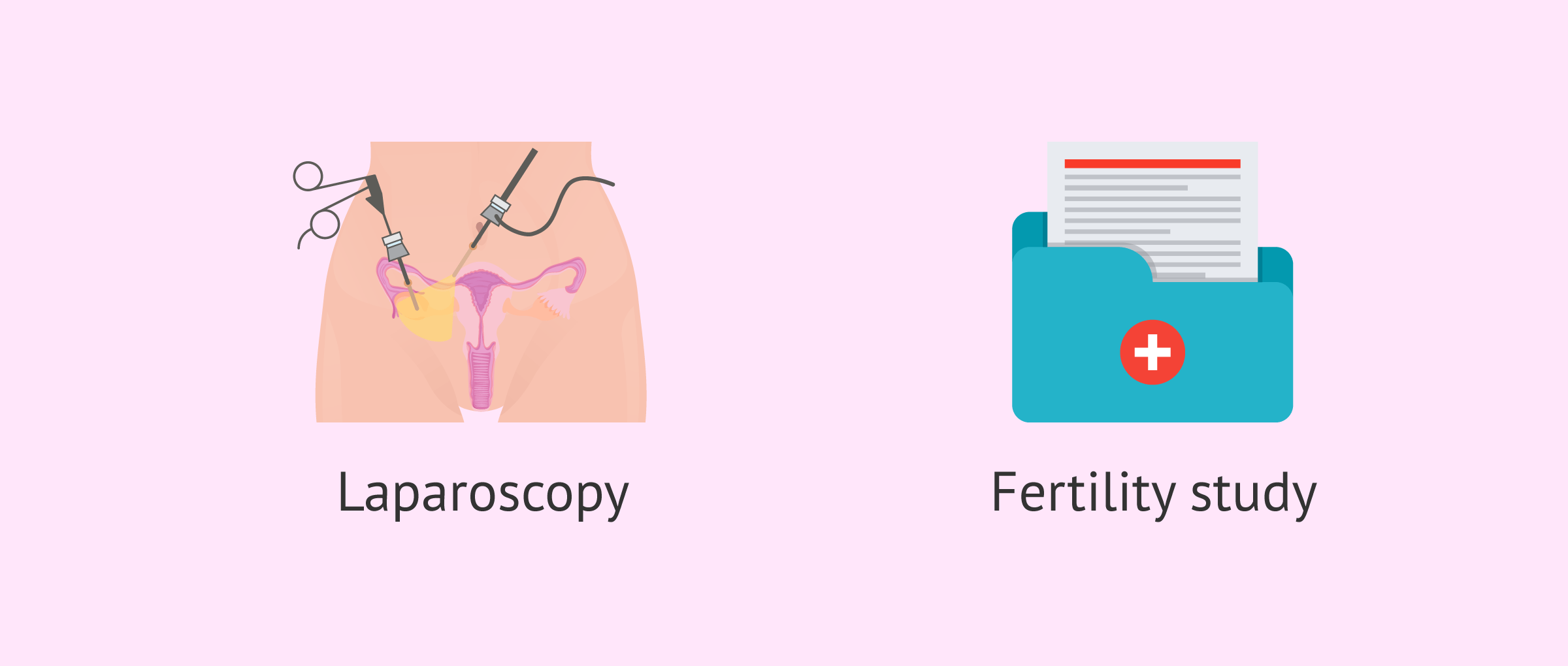
Before doing the reversal surgery, it is necessary to perform some diagnostic tests on the patient:
- Laparoscopy
- exploration of the abdominal cavity to see if the tubes can be recanalized since the ends of the tubes must measure more than 6 cm for this purpose.
- Partner fertility testing
- the goal is to rule out other pathologies that would prevent natural pregnancy. It would not make sense to reverse the tubes if there is another cause of infertility in both men and women.
The success of tubal ligation reversal is usually 70%, although it will depend on the type of ligation performed previously.
It should be noted that surgeries related to the fallopian tubes, including tubal recanalization, increase the risk of extra-uterine pregnancy. For this reason, in addition to the complexity of the operation, most experts recommend considering IVF as the first option for achieving pregnancy after tubal ligation.
Risks of tubal ligation reversal
As we have already mentioned, tubal ligation reversal is a surgical procedure, and as such, it carries risks despite being infrequent.
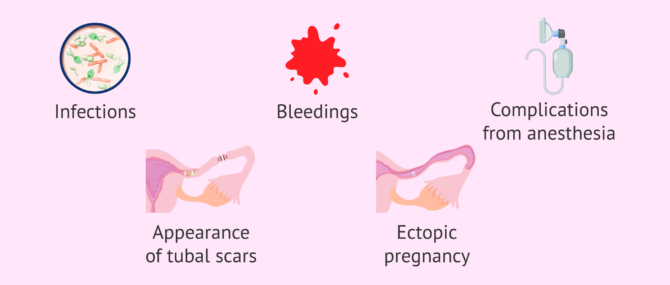
However, it is important that women who are thinking about having a tubal reversal be aware of the possible consequences that the procedure may generate. Some of these are listed below:
- Infections.
- Bleedings.
- Scars on the fallopian tubes.
- Complications resulting from anesthesia.
In addition, the possibility of suffering an ectopic pregnancy, that is to say, that it is more likely for the embryo to implant in a different place from the uterus when a tubal reversal is carried out.
If you would like more in-depth information about this option for achieving pregnancy, you can visit the following article: Is It Possible to Reverse Tubal Ligation?
Costs
Both techniques cost approximately up to $6,000 depending on the center where they are performed. However, as already mentioned, tubal reversal is not a 100% effective technique and does not ensure that pregnancy can be achieved. For this reason, most women prefer to resort to IVF rather than spend the money on something they don't know will work.
As far as IVF is concerned, it should be noted that medication is usually not included in the initial treatment budget. About $2500 and 3000 are charged extra for the stimulation treatment.
If you need to undergo IVF to become a mother, we recommend that you generate your Fertility Report now. In 3 simple steps, it will show you a list of clinics that fit your preferences and meet our strict quality criteria. Moreover, you will receive a report via email with useful tips to visit a fertility clinic for the first time.
If it is necessary to resort to egg donation to achieve pregnancy with eggs from an anonymous donor, the price of IVF rises to $25,000.
There is a cheaper option which is embryo adoption. These come from the donation of a couple who have had surplus embryos in their IVF treatment. The cost is usually around $3000.
In any case, it is advisable to go to a fertility clinic where specialists can advise on the best alternative to have children depending on the possibilities of the woman or the couple.
FAQs from users
Is tubal ligation reversal effective when it comes to getting pregnant?
Tubal ligation consists of preventing the passage of sperm into the tubes, thus preventing fertilization.
The reversal of tubal ligation is not always satisfactory, the factors that may influence are age, time since surgery, and the technique used. In women under 34 years can reach 70% of pregnancies.
Another important factor is the length of the tube after surgery, which must be more than 4 cm.
We can consider reversing a tubal ligation in women under 34 years old and with a residual tube longer than 4 cm.
Is an ectopic pregnancy likely if I have tubal ligation?
Ectopic pregnancy if I have tubal ligation is a rare entity.
Heterotopic pregnancy is a rare form of multiple gestation where an intrauterine pregnancy coexists with an ectopic one. The incidence of heterotopic pregnancy is 1 in every 10,000 to 50,000 spontaneous pregnancies. However, with the increased use of assisted reproductive technologies, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and embryo transfer, the incidence has increased to 0.5 - 1%.
Pregnancies that occur after an embryo transfer resulting from in vitro fertilization occur mainly in the interstitial area of the uterus or in the isthmus of the uterine tube.
Is it possible to do artificial insemination after tubal ligation?
No. In order to perform artificial insemination, it is essential that the fallopian tubes are permeable to allow the passage of sperm to the egg and then the transport of the embryo to the uterus. The assisted reproduction technique that allows pregnancy with the tubes tied is IVF.
Is natural pregnancy possible with a tubal ligation?
Yes. Although this method of contraception is highly effective, there is a 1% chance that recanalization will occur and that the tubes will be rejoined. This chance increases over the years, and there is also an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy with tubal ligation.
For more information on this pregnancy complication, we recommend reading the following article: ectopic pregnancy.
What are the symptoms of tubal ligation pregnancy?
If pregnancy occurs with the Pomeroy or another tubal ligation method, the signs and symptoms that would be noticed would be the same as in women without tied tubes because female hormones influence pregnancy in the same way. Therefore, during the first months of pregnancy, the woman will feel nausea, tiredness, absence of periods, breast discomfort, etc.
It is important to pay special attention to the symptoms that could occur in ectopic pregnancy: abnormal bleeding, very strong abdominal pain on one side, weakness, low back pain, low blood pressure, etc.
Is artificial insemination after tubal ligation possible?
No, because the sperm is unable to travel through the Fallopian tubes and reach the egg. If the ability of your eggs is confirmed, pregnancy can be achieved through IVF, as fertilization does not take place inside the female reproductive system, but in the laboratory.
Suggested for you
In vitro fertilization is the appropriate assisted reproduction technique to achieve pregnancy if the woman has a tubal ligation. If you need more information about this treatment, you can continue reading on the following link: What is in vitro fertilization (IVF)?
To learn more about tubal ligation reversal surgery, you can continue reading the following article: Is it possible to reverse tubal Ligation?
In case you are looking for an effective contraceptive method, we encourage you to consider other options like the ones you can find in the following post: Which contraceptives work?
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Boeckxstaens A, Devroey P, Collins J, Tournaye H. Getting pregnant after tubal sterilization: surgical reversal or IVF?. Hum Reprod. 2007 Oct;22(10):2660-4 (View)
Gomel V. The place of reconstructive tubal surgery in the era of assisted reproductive techniques. Reprod Biomed Online. 2015 Dec;31(6):722-31 (View)
Van Seeters JAH, Chua SJ, Mol BWJ, Koks CAM. Tubal anastomosis after previous sterilization: a systematic review. Hum Reprod Update. 2017 May 1;23(3):358-370 (View)
Messinger LB, Alford CE, Csokmay JM, Henne MB, Mumford S5, Segars JH, Armstrong AY. Cost and efficacy comparison of in vitro fertilization and tubal anastomosis for women after tubal ligation. Fertil Steril. 2015 Jul;104(1):32-8.e4 (View)
Berger GS, Thorp JM Jr, Weaver MA. Effectiveness of bilateral tubotubal anastomosis in a large outpatient population. Hum Reprod. 2016 May;31(5):1120-5 (View)
Monteith CW, Berger G, Zerden ML. Pregnancy success after hysteroscopic sterilization reversal. Format: AbstractSend to Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Dec;124(6):1183-9 (View)
Jayakrishnan K, Baheti SN. Laparoscopic tubal sterilization reversal and fertility outcomes. J Hum Reprod Sci. 2011 Sep;4(3):125-9 (View)
FAQs from users: 'Is tubal ligation reversal effective when it comes to getting pregnant?', 'Is an ectopic pregnancy likely if I have tubal ligation?', 'Is it possible to do artificial insemination after tubal ligation?', 'Is natural pregnancy possible with a tubal ligation?', 'What are the symptoms of tubal ligation pregnancy?' and 'Is artificial insemination after tubal ligation possible?'.
Authors and contributors








Hi!
I’ 38 years old and would like to become a mother again. I had my tubes tied 15 years ago and would like to know my pregnancy chances.
Hi Tricia
To achieve a pregnancy after a tubal ligation there are two options: reversal of the ligation or resorting to assisted reproduction techniques. Tubal reversal is one possible technique, although the possibility of achieving a pregnancy afterwards is not high. In addition, it is important to know how long the tubes have been tied.
The other alternative is In Vitro Fertilization (IVF). In this way, fertilization occurs in the laboratory and the embryos generated are transferred directly to the uterus, without the need to go through the fallopian tubes. Artificial Insemination (AI) would not be possible, since the encounter between the egg and the sperm would not occur.
On the other hand, the criteria for access to a Social Security assisted reproduction treatment will depend on each Autonomous Community, but most public centers do not contemplate reproductive treatments for those patients who have undergone a voluntary sterilization method, as is the case with tubal ligation.
Therefore, if you need to visit a private assisted reproduction center, I recommend you access the Fertility Report. This is a free tool with which you will receive a personalized list of the clinics in your area of interest that meet our quality criteria. You will also get quotes, services included, detailed explanation of the treatment, etc.
I hope I have helped you.
Best regards
How much is a tubal ligation reversal in the U.K., please?
Hi Linda,
generally speaking, the costs range from £3,000 to £5,000 depending on the fertility center you are going to perform the procedure. Also, keep in mind that the NHS does not cover a tubal ligation reversal. Consequently, you need to have it done at a private clinic at your own cost.
If you want to read more about how this process works, I recommend you this post: Is It Possible to Reverse Tubal Ligation?
Hope this helps you
All the best