Controlled ovarian stimulation (COS) is the first step towards assisted reproductive treatment, either for artificial insemination (AI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF).
In addition, it is also necessary to stimulate the ovaries when a woman wants to vitrify her eggs to preserve fertility, and for women who are going to be egg donors.
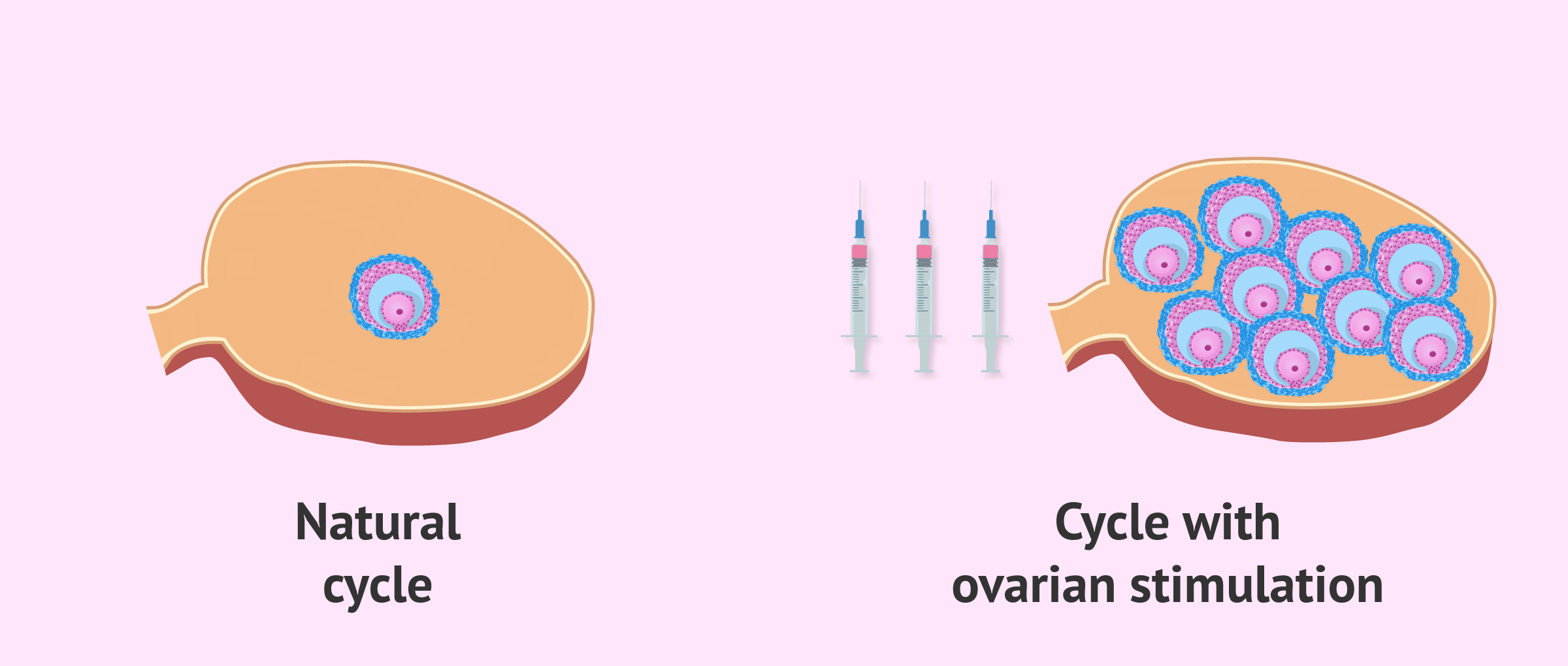
The purpose of ovarian stimulation is to achieve the maturation of several follicles at the same time in the ovaries. With this, the number of oocytes to fertilize is increased and, with it, the number of embryos and the possibility of achieving a pregnancy.
Provided below is an index with the 8 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 2.1.
- 2.2.
- 2.3.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 5.1.
- 5.2.
- 5.3.
- 5.4.
- 5.5.
- 5.6.
- 5.7.
- 5.8.
- 5.9.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
How does the ovary work?
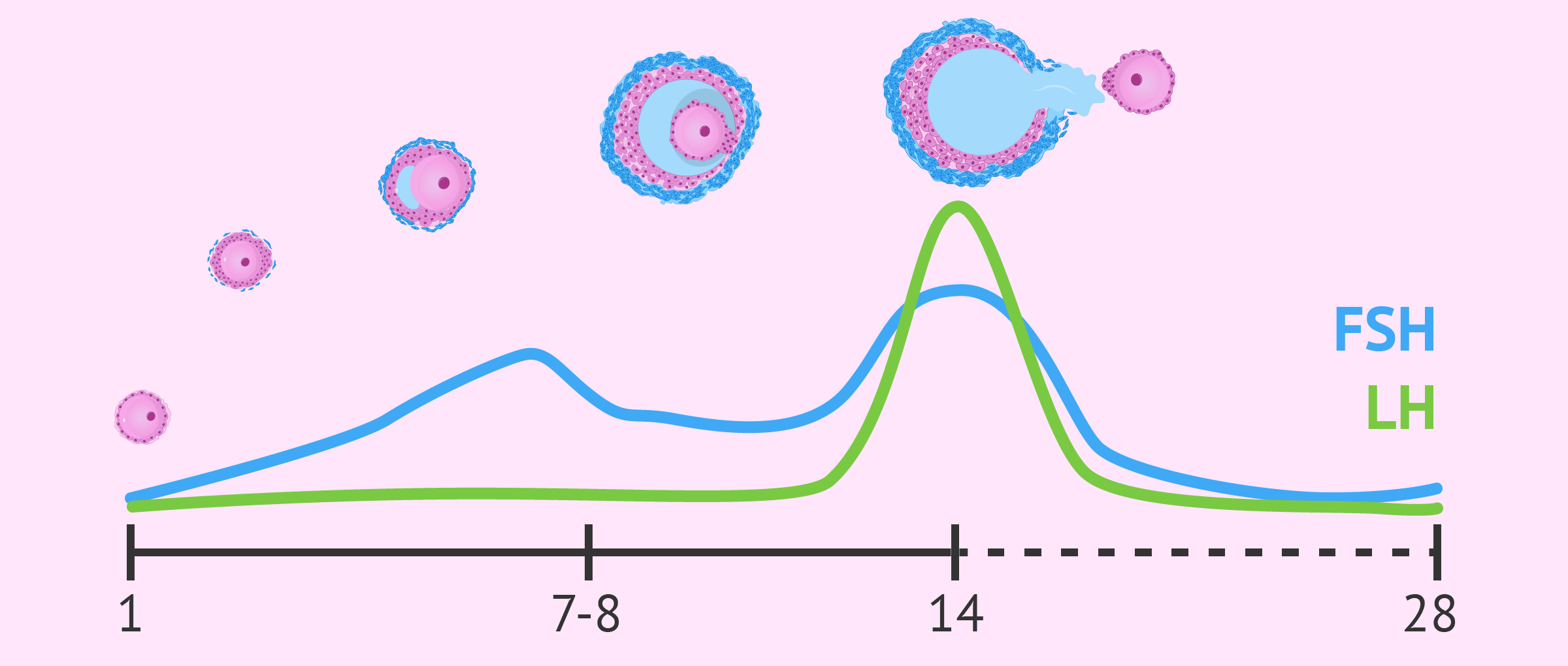
Follicles are small ovarian structures that contain an egg inside. With each menstrual cycle, follicular recruitment takes place depending on the hormonal levels of gonadotropins, especially FSH.
The FSH hormone is responsible for stimulating follicular development. After 7-8 days of follicle growth, the FSH level decreases and only one follicle is able to survive and continue its maturation.
As a result, in each ovarian cycle, only one of the follicles is able to fully develop into a preovulatory follicle. The rest of the follicles that began their development degenerate and, therefore, the eggs that were inside them are lost.
In the middle of the menstrual cycle, around day 14, there is a surge of the hormone LH, known as LH peak which triggers ovulation. Thus, the periovulatory ovarian follicle ruptures, and the egg is expelled into the fallopian tube, where it is susceptible to fertilization.
If you want to learn more about the role of hormones in a woman's menstrual cycle, you can continue reading here: The menstrual cycle: what happens in each of its phases?
Ovarian stimulation step by step
In assisted reproduction treatments, the aim is to mimic what occurs in the natural menstrual cycle, but on a larger scale. For this reason, controlled ovarian stimulation is performed, with the aim of maturing several ovarian follicles at the same time. In addition, ovarian stimulation is bilateral: follicles grow in both ovaries.
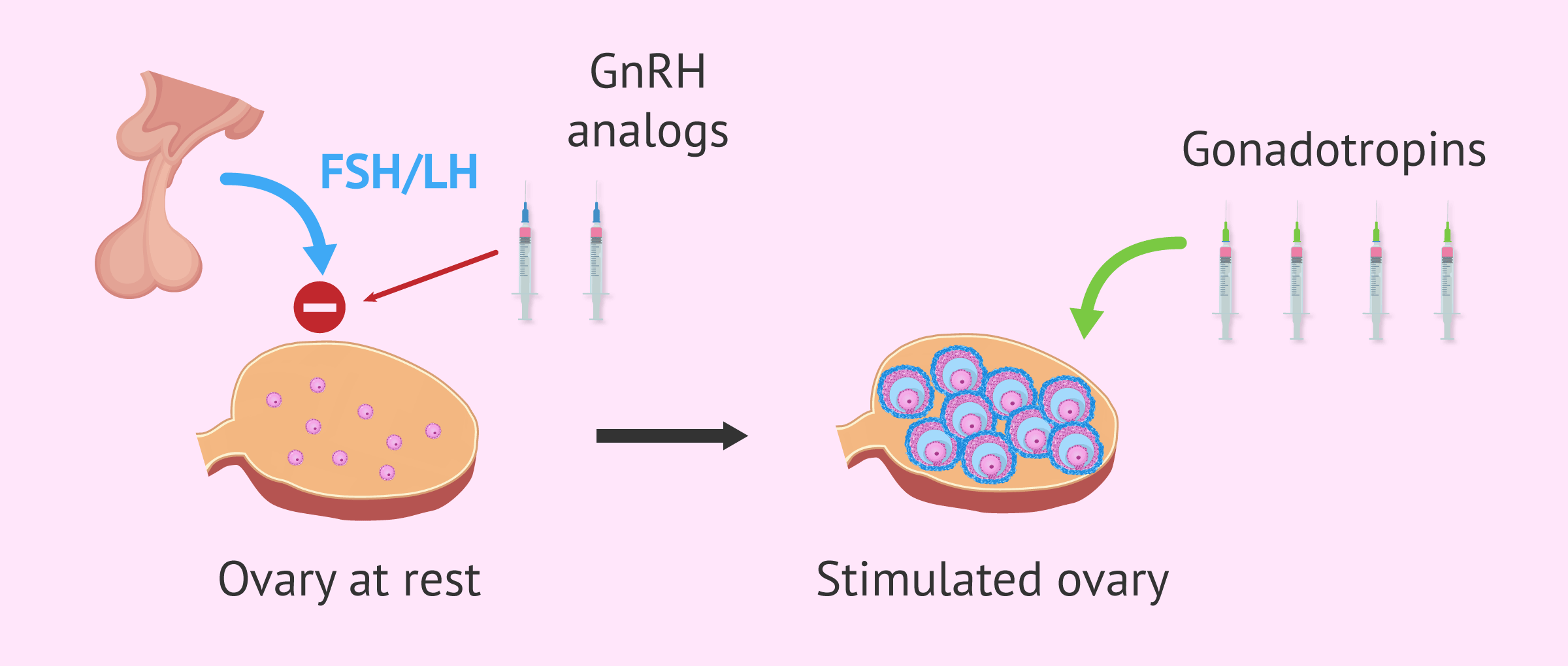
Specifically, controlled ovarian stimulation for IVF consists of three phases characterized by the administration of different drugs:
- Pituitary suppression
- gnRH analogue drugs are administered with the purpose of blocking the internal hormonal flow between the pituitary gland and the ovaries. Thus, there is no endogenous production of gonadotropins (FSH and LH) and the ovaries remain at rest.
- Multiple follicular development
- once the pituitary is blocked, it is necessary to administer exogenous gonadotropins to achieve controlled follicular development. The aim is to synchronize the entire cohort of follicles and have them all grow at the same time, until an adequate size is achieved.
- Final follicular maturation
- this phase consists of a final injection of a drug containing the hCG hormone so that the eggs inside the follicles complete their maturation.
It is very important to schedule the follicular puncture for oocyte retrieval about 32-34 hours after the hCG injection. If more time passes, ovulation would occur and the mature eggs would be expelled from the ovaries into the fallopian tubes.
How many days does it last?
The duration of ovarian stimulation depends on many factors, mainly on how the woman responds to the hormonal medication and whether the follicles are growing properly.
In general, the multiple follicular development phase lasts approximately 10 days. However, the total duration of the cycle will depend on the type of protocol indicated by the gynecologist:
- Short protocol
- gnRH antagonists are used for pituitary suppression, which have an immediate effect after administration. Therefore, the number of injections required is lower.
- Long protocol
- gnRH agonists are used, which should be started in the woman's previous menstrual cycle (around day 21 of the cycle), as they take longer to achieve complete pituitary blockade.
Types of drugs
In order to clarify the types of medications used during ovarian stimulation, we will summarize them below, as well as name some of the most commonly used brand names:
- GnRH agonists
- are used to slow the pituitary in long EOC protocols. Some examples are Decapeptyl, Procrin and Synarel.
- GnRH antagonists
- are used to restrain the pituitary in short EOC protocols. The most commonly used drugs are Cetrotide and Orgalutran.
- Gonadotropins
- these drugs contain FSH and/or LH hormone as active ingredients. These include Gonal-f, Puregon, Menopur, Pergoveris, Ovaleap, Bemfola, Fostipur, Rekovelle and Elonva.
- Ovulation inducers
- are drugs that serve to achieve final follicular maturation and induce ovulation. The most famous in IVF is Ovitrelle, which contains the hCG hormone.
You can find more detailed information on this topic in the following article: What drugs are used for ovarian stimulation in AI and IVF?
Medical control
Hormonal medication to stimulate the ovaries, i.e. gonadotropins, should be started on the first days of menstruation (between days 1-3 of the cycle). Previously, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed on the woman to verify that the ovaries are at rest and, if so, stimulation can begin.
The medication is usually administered by daily subcutaneous injections in the abdominal area. After several days with the application of these drugs, the patient should visit the clinic to check how the follicles are developing. In addition, this control should be repeated approximately every two days.
During these controls, the follicles that are growing and their size are counted by ultrasound. If necessary, the gynecologist would adjust the dose of medication in order to obtain an optimal ovarian response.
The appropriate size that the follicles should reach is approximately 18 mm. In addition, it is also necessary to monitor the estradiol level through blood tests, which is usually 200-300 pg/ml per mature follicle.
At this time, in the case of IVF, the follicular puncture is scheduled for the recovery of mature eggs, and the woman is informed of the exact moment when the hCG injection is to be given.
In the case of AI, ovulation and intrauterine insemination are programmed.
Assisted procreation, as any other medical treatment, requires that you rely on the professionalism of the doctors and staff of the clinic you choose. Obviously, each clinic is different. Get now your Fertility Report, which will select several clinics for you out of the pool of clinics that meet our strict quality criteria. Moreover, it will offer you a comparison between the fees and conditions each clinic offers in order for you to make a well informed choice.
Ovarian response to medication
Each woman may respond differently to the hormonal medication used for EOC, so it is common to obtain different results in different women who have undergone the same stimulation protocol.
On the one hand, there are cases of low response on the one hand, there are cases of ovarian puncture, in which the number of follicles developed is low and few oocytes are recovered in the ovarian puncture (3 or less).
A low-responder may also have a failed stimulation and no oocytes are retrieved, either because the follicles are empty, because they do not reach the appropriate diameter, or because no maturation is achieved.
This tends to happen, above all, in women over 35 years of age who have a low ovarian reserve. However, there are also cases of young women with a low response due to premature ovarian failure or other disorders.
On the other hand, there is the high response cases where just the opposite is true. The ovaries have an excessive response and develop a large number of follicles.
As a consequence, a woman is at risk of suffering from ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) after hCG administration, in which her ovaries are enlarged and she feels a lot of abdominal pain.
In case of suspected OHSS, it is necessary to cancel the fresh embryo transfer to avoid further risk. The OHSS disappears with menstruation, so the solution is to vitrify the embryos and transfer them in a later cycle when the OHSS has disappeared.
Symptoms and side effects
The hormonal medication used in EOC produces very characteristic symptoms that almost all women usually present:
- Bruising at the injection site.
- Abdominal swelling.
- Temporary weight gain.
- Heaviness in the legs.
- Mood swings
- Sensation of pressure on the ovaries.
- Vaginal dryness.
These are symptoms and slight discomfort very similar to those usually experienced in premenstrual syndrome, but it is important for the woman to be clear that they are due to medication.
However, the woman can go through ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) as we have already mentioned, which can become very serious if the necessary measures are not taken.
You have much more information about this in the following post: Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: What is it and how is it cured?
FAQs from users
Approximately how many injections does ovarian stimulation require?
It will depend on the ovarian stimulation protocol to be followed and on the characteristics of each patient. Generally speaking, in a long ovarian stimulation protocol, 27-29 injections will have to be administered.
On the other hand, if a short ovarian stimulation protocol is carried out, the number of injections will be approximately 20-22.
Read more
Can I go to the gym and lift weights during assisted reproduction treatment?
In general, during an assisted reproduction treatment, you can lead a normal life unless otherwise indicated by the gynecologist. Weight training is usually discouraged during the final phase of ovarian stimulation and after an embryo transfer.
In the case of ovarian stimulation, when the ovaries begin to increase in size the patient usually feels more swollen and may have abdominal discomfort or pain. If she has this discomfort, it is better not to do intense physical exercise. In any case, regardless of the clinical manifestations that you may notice, if the ovaries have increased in size, it is advisable to avoid physical exercise (such as weight lifting) because of the risk of ovarian torsion (the ovary can rotate on its own axis and the blood supply is blocked). This is a serious complication that has to be treated in the operating room to recover the ovarian vascularization.
After an embryo transfer, it is also recommended to avoid exertion, especially during the following 3 days, to avoid any type of uterine contraction that could decrease the chances of the embryo implanting.
How is it possible to improve the stimulation process and along what lines are you working in this direction?
Ovarian stimulation generates, in addition to some minor discomfort such as swelling or fluid retention, but not in an exaggerated way, some anxiety for two reasons: first, because of the fact of having to take an injection (or two) every day, and second, because of the fear of doing it right (there are many errors in the administration of the medication by the patient, which sometimes the patient is not aware of or is aware of but does not tell the doctor because of "embarrassment").
Advances in this sense are in the search for oral drugs but, for the moment, there has already been a great advance in this sense, and that is the administration of an injection whose effect lasts 7 days (Elonva) instead of the usual 24h; this reduces the number of injections and avoids the aforementioned errors.
How many controls are performed during ovarian stimulation?
The number of controls to be performed is variable, although the most usual is to perform between two and three controls throughout the stimulation. The first control is usually performed after 4-5 days of medication and from then on the controls are scheduled every 48-72 hours until we have follicles between 18-20 mm, which would be the optimal time to make the ovulation discharge and schedule the puncture.
Are there natural products to make ovarian stimulation more natural?
No, only hormonal stimulation of ovulation and through injections is possible. There is no more natural method. The administration, although it is through a needle prick, is simple and painless.
What response is expected in ovarian stimulation at age 45?
It is common for women over 40 years of age to have a low ovarian reserve, so it is expected that the ovary will have a low response. Many women who want to have a child at this age need oocyte donation because they cannot use their own eggs.
Does ovarian stimulation advance menopause?
No, what the hormonal medication does is to "rescue" those follicles that begin maturation but were going to degenerate and die. In a natural cycle only one egg matures completely, but with the medication the objective is that all those that begin maturation finish it.
What happens if I start ovarian stimulation and have a natural pregnancy?
This is not possible, since before starting the ovarian stimulation the woman will undergo a transvaginal ultrasound to check the state of the ovaries. In the case of having become pregnant naturally in the previous cycle, the gynecologist would see it in this ultrasound and the whole IVF process would be interrupted.
In addition, since in many IVF cycles it is necessary to take birth control pills and/or GnRH agonist drugs beforehand, it would not be possible to get pregnant naturally during this period.
Is it possible to perform ovarian stimulation with a single tube?
Yes, of course. The fallopian tubes have no influence whatsoever on an in vitro fertilization treatment. As long as the woman has ovaries, it is possible to perform ovarian stimulation with both tubes, with only 1 or with none. In follicular puncture, the gynecologist will extract the oocytes directly from the ovaries.
In the case of artificial insemination this is different, since the tubes are necessary. Therefore, if the woman has only one tube, the stimulation will be done on both ovaries, but only the follicles from the ovary where the healthy tube is located will be used.
Recommended readings
Controlled ovarian stimulation is the first step in IVF. It will then be necessary to extract the eggs by follicular puncture. To learn more about this process, we recommend you to read the following article: What does the follicular puncture of an IVF process consist of?
Finally, the last step of IVF will be to transfer the embryos that have managed to develop in culture to try to achieve pregnancy. You have all this information here: Embryo transfer: when and how is it done?
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Coroleu B, Devesa M, y Alvarez M. Guía 18. Estimulación ovárica para FIV-ICSI en los ciclos con presunción de baja respuesta. Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Departamento de Obstetricia, Ginecología y Reproducción Hospital Universitario Quirón Dexeus, Barcelona. Sociedad Española de Fertilidad (SEF) y Sociedad Española de Ginecología y Obstetricia (SEGO)
Ferraretti AP et al. (2011). ESHRE consensus on definition of poor response to ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization: the Bologna criteria. Hum Reprod; 26: 1616-24.
Griesinger G. y col. (2006). GnRH-antagonists in ovarian stimulation for IVF in patients with poor response to gonadotropins, polycystic ovary syndrome, and risk of ovarian hyperstimulation: a meta-analysis. Reproductive BioMedicine Online; 13: 628-638.
Hamdine O. et al. (2015). Ovarian response prediction in GnRH antagonist treatment for IVF using anti-Müllerian hormone. Hum. Reprod.; 39: 170-8.
Lehert P, Kolibianakis EM, Venetis CA. y col. (2014). Recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone (r-FSH) plus recombinant luteinizing hormone versus r-FSH alone for ovarian stimulation during assisted reproductive technology: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology; 12: article 17.
Rodríguez Gálvez, I., Tocino Díaz, A., Fernández Sánchez, M. Fármacos en la estimulación ovárica: clomifeno, gonadotropinas, análogos GnRH, hCG. En: Unidad 06, Bloque I: Esterilidad femenina. Máster en Reproducción Humana de la Universidad Rey Juan Carlos y el Instituto Valenciano de Infertilidad (IVI).
FAQs from users: 'Approximately how many injections does ovarian stimulation require?', 'What does IVF ovarian stimulation entail?', 'How many controls are performed during ovarian stimulation?', 'Can I go to the gym and lift weights during assisted reproduction treatment?', 'How is it possible to improve the stimulation process and along what lines are you working in this direction?', 'What are the most common side effects of Puregon?', 'Are there natural products to make ovarian stimulation more natural?', 'What response is expected in ovarian stimulation at age 45?', 'Does ovarian stimulation advance menopause?', 'What happens if I start ovarian stimulation and have a natural pregnancy?' and 'Is it possible to perform ovarian stimulation with a single tube?'.
Authors and contributors


More information about Cristina Algarra Goosman

More information about Michelle Lorraine Embleton










Hello, I am going to undergo ovarian stimulation in a few weeks, is it necessary to take any special care? I am afraid that the procedure will hurt or that I will not be able to continue with my normal life after it, thank you.
Hello Linsdey,
Ovarian stimulation itself should not be a painful process, the associated symptoms can be bothersome and treated by medication. Such as abdominal bloating or the feeling of pressure on the ovaries.
I imagine you mean by intervention the removal of the stimulated eggs. This is done under anesthesia and requires some aftercare, but not to the level of incapacitating you to lead a normal life.
I hope I have helped you,
Best regards.
Does having ovarian stimulation ensure a response? I think I’ve been told I have a low response but I don’t know if that affects it.
Hello zoe,
Ovarian stimulation does not ensure follicles, that is why there are different medications and concentrations of them.
They do not all work the same way or have the same effect on different women.
Women with a low ovarian response may be more susceptible to low production of viable eggs for IVF or fertility preservation. This is best avoided with hormone medication management.
I recommend that you read the following article: Low response to ovarian stimulation.
I hope I have helped you,
Best regards