GnRH antagonists are drugs used in assisted reproduction treatments to control ovarian function and prevent spontaneous ovulation. They are the most commonly used GnRH agonists in short ovarian stimulation protocols.
We can find them with different chemical compositions and commercial names, but their function is the same, whether they are used in artificial insemination or in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatments.
Provided below is an index with the 7 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 1.1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 4.3.
- 4.4.
- 4.5.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
What are GnRH antagonists?
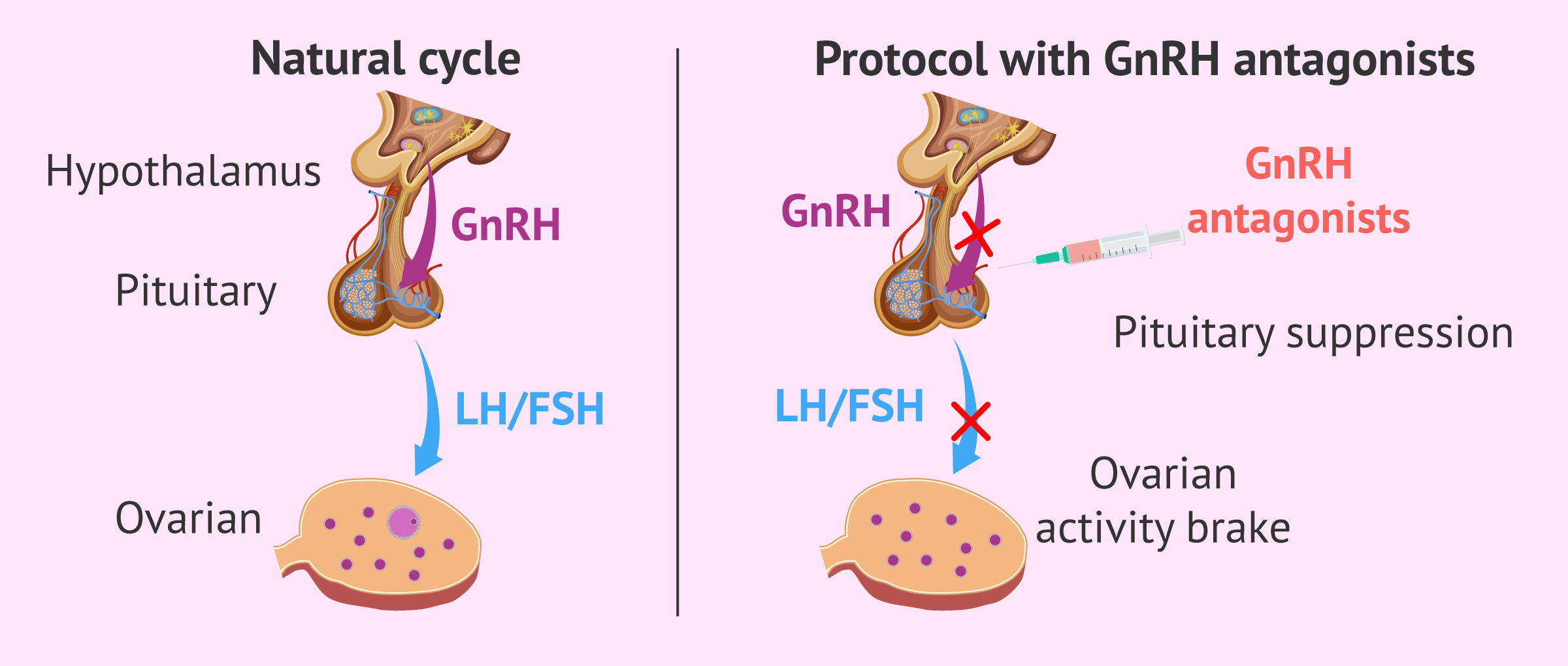
GnRH antagonists are drugs belonging to the group of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs, which are used for ovarian stimulation in assisted reproduction treatments (artificial insemination, in vitro fertilization, and ICSI). Thanks to them, we can control ovarian function.
The purpose of these hormones is to prevent the LH peak, which would cause premature follicular ovulation and luteinization. In this way, we can control the time at which it occurs so that it does not occur prematurely.
If there were a spontaneous ovulation, it would not be possible to retrieve the eggs in the follicular puncture or to perform artificial insemination on an optimal day for fertilization to occur.
In addition, the LH peak would also affect endometrial receptivity. Therefore, in women who require endometrial preparation, either for frozen embryo transfer or for ovodonation treatments, GnRH analogs are also administered.
It should be noted that their use is not exclusive to assisted reproduction patients: they are also indicated, for example, in the treatment of endometriosis and hormone-dependent tumors, such as breast or prostate cancer.
Effects: how does it work?
Once a GnRH antagonist is administered, it binds to the GnRH receptors and blocksthem. In this way, it prevents GnRH from binding to its receptors by competitive blockade. These receptors are located on the surface of the gonadotroph cells of the pituitary gland.
Blocking GnRH receptors, in turn, inhibits the synthesis of gonadotrophins (FSH and LH) by the pituitary gland. These hormones exert their function in the ovary: they are involved in the regulation of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, GnRH antagonists slow down ovarian activity and inhibit the menstrual cycle.
Unlike GnRH agonists, their action is immediate and they do not produce a flare-up effect, which causes FSH and LH secretion to increase at the beginning of agonist administration.
The immediacy of their action and the absence of flare-up effect mean that, compared to protocols with GnRH agonists, it is necessary to inject fewer doses of antagonists to achieve the same pituitary suppression.
Therefore, it simplifies ovarian stimulation and makes it less uncomfortable for the patient: we go from approximately one month of hormonal treatment to 10-12 days.
Advantages: simplification of treatments
The benefits of using this drug in ovarian stimulation treatments are as follows:
- It produces immediate suppression of serum LH levels and prevents premature ovulation. Because their effect is so rapid, they can be administered at the time when there is an obvious risk of the LH peak occurring, as they take hours to achieve pituitary inhibition. In the case of agonists, they need 7-10 days to achieve this effect.
- The duration of the ovulation stimulation treatment is shorter, thus reducing discomfort for patients: fewer injections are necessary and they have to visit the clinic less often for check-ups during ovarian stimulation.
- It is usually well tolerated by the woman, with few side effects, as the stimulation is not very aggressive because it allows lower doses of FSHto be administered. The fact that fewer hormones are needed also makes the treatment cheaper.
- It decreases the frequency of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) because it allows GnRH agonists to be used to induce ovulation instead of hCG, which increases the risk of OHSS. Therefore, these protocols are especially indicated in patients with an elevated risk of OHSS: young women, such as donors, or with polycystic ovary syndrome.
- It does not cause follicular cysts because it does not have the flare-up effect that occurs after administration of GnRH agonists.
For all these reasons, short protocols with GnRH antagonists are increasingly used among assisted reproduction specialists. The GnRH antagonists most commonly used in these treatments are Cetrotide (cetrorelix) and Orgalutran (ganirelix).
Disadvantages
The use of GnRH antagonists presents few disadvantages since, being a stimulation that is not too aggressive, it is tolerated by most women with practically no contraindications.
The only problem is that, in many studies, the pregnancy rate has been found to be slightly lower (between 3% and 5% lower) than that obtained in ovarian stimulation protocols using GnRH analogs. This is due to the effect that antagonists have on endometrial receptivity.
In addition, if oral contraceptives or estrogens are not administered prior to initiating antagonist therapy, it can make follicular growth asynchronous, which also negatively affects success rates because fewer eggs are retrieved per cycle.
FAQs from users
When is a short IVF protocol with GnRH antagonists indicated?
This type of protocol is used in assisted reproduction treatments, since its objective is to increase the probability of treatment success.
Therefore, the short cycle with gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonists is indicated in patients in whom it is necessary to prevent premature ovulation, in couples with a history of suboptimal ovarian response, etc.
Read more
How do GnRH antagonists affect endometrial receptivity?
The comparison of protocols with GnRH agonists and antagonists and their relationship to the impact on endometrial receptivity remain controversial. However, some studies have provided evidence that both GnRH agonists and antagonists slightly affect endometrial receptivity compared to natural cycles.
In contrast, other studies have suggested that antagonist protocols have a strong impact on the expression of related genes in human endometrial receptivity, as well as that agonists cause delay in this process.
For ovarian stimulation, is it sufficient to inject GnRH antagonists?
No. GnRH antagonists only serve to control endogenous hormone levels. It is necessary to stimulate follicular growth by administration of gonadotropins and induce ovulation by hCG or GnRH agonists.
Is luteal phase support chosen in cycles with agonists?
Dr. Carolina Arboleya answers the question:
Normally, when we do cycles with agonists, we do opt for luteal phase support, to put intravaginal progesterone to give that luteal phase support ras the puncture to the patient.
How many days does ovarian stimulation with GnRH antagonists last?
With the use of GnRH antagonists, the duration of ovarian stimulation is approximately 10-12 days. It will depend on the exact protocol used and the woman's response to hormonal treatment.
Recommended readings
If you want to know more about the drugs used in ovarian stimulation treatments, you will find more information in this article: Medications used in controlled ovarian stimulation.
On the other hand, if you wish to know the price of these drugs, we recommend that you access the following link: The cost of hormonal medication in assisted reproduction treatments.
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Alan B Copperman, Claudio Benadiva. Optimal usage of the GnRH antagonists: a review of the literature. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2013 Mar 15;11:20. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-11-20 (View)
Hesham G Al-Inany, Mohamed A Youssef, Reuben Olugbenga Ayeleke, Julie Brown, Wai Sun Lam, Frank J Broekmans. Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone antagonists for assisted reproductive technology. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 29;4(4):CD001750 (View)
Jacques Donnez, Marie-Madeleine Dolmans. GnRH Antagonists with or without Add-Back Therapy: A New Alternative in the Management of Endometriosis? Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 20;22(21):11342. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111342 (View)
P Devroey. GnRH antagonists. Fertil Steril. 2000 Jan;73(1):15-7. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(99)00448-3 (View)
R Marci, A Graziano, G Lo Monte, I Piva, I Soave, E Marra, F Lisi, M Moscarini, D Caserta. GnRH antagonists in assisted reproductive techniques: a review on the Italian experience. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Apr;17(7):853-73 (View)
Samantha Sperduti, Silvia Limoncella, Clara Lazzaretti, Elia Paradiso, Laura Riccetti, Sara Turchi, Ilaria Ferrigno, Jessika Bertacchini, Carla Palumbo, Francesco Potì, Salvatore Longobardi, Robert P Millar, Manuela Simoni, Claire L Newton, Livio Casarini. GnRH Antagonists Produce Differential Modulation of the Signaling Pathways Mediated by GnRH Receptors (View)
Vito S Cardone. GnRH antagonists for treatment of polycystic ovarian syndrome. Fertil Steril. 2003 Jul;80 Suppl 1:S25-31; discussion S32-4 (View)
FAQs from users: 'When is a short IVF protocol with GnRH antagonists indicated?', 'How do GnRH antagonists affect endometrial receptivity?', 'For ovarian stimulation, is it sufficient to inject GnRH antagonists?', 'Is luteal phase support chosen in cycles with agonists?' and 'How many days does ovarian stimulation with GnRH antagonists last?'.
Authors and contributors

More information about Cristina Algarra Goosman








Hello, I have had in the past cycles problems with the endometrium, I have had it very thick and had to do a curettage, I do not know if you can put me this type of GnRH to improve that.
Hi AnnaJohns,
The effects of GnRH both agonists and antagonists are not scientifically proven. However, the endometrial receptivity of cycles in which GnRH is used has been affected compared to natural cycles.
If you have had problems with your endometrium, it is important that your doctors take this into account when preparing the necessary interventions throughout your reproductive process. With your medical history and knowledge, they will be able to establish the hormonal action guidelines that best suit your situation.
I hope I have helped you,
Best regards