Estrogens are steroid sex hormones (derived from cholesterol) found mainly in women.
Its multiple functions include the development of female sexual organs, the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics and the regulation of the menstrual cycle. For this reason, estrogens are known as the female sex hormones.
In addition, estrogens are the active ingredient of many oral contraceptives as well as medications used in assisted reproductive treatments.
Provided below is an index with the 8 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 3.1.
- 3.2.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 5.
- 5.1.
- 5.2.
- 5.3.
- 5.4.
- 5.5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
Types
Estrogens are the main female sex hormones formed in a woman's adrenal glands and ovaries.
From cholesterol takes place the production of androgens (male sex hormones) and, from these, estrogens are synthesized by the action of the enzyme aromatase.
These are the following 3 types of estrogens that can be found naturally in the human body:
- Estradiol (E2)
- its synthesis takes place from testosterone. This is the largest amount of estrogen found in a woman's body throughout her reproductive life.
- Estrone (E1)
- is derived from the hormone progesterone and is the lowest amount of estrogen found in the body.
- Estriol (E3)
- the enzyme aromatase is obtained from androsterone. It has special relevance during pregnancy, as its measurement provides information on the state of the fetus and placenta.
In addition to these, there are also semisynthetic or synthetic estrogens, such as ethinyl estradiol and mestranol, which can be found in oral contraceptives.
Finally, non-steroidal estrogens, such as stilbenes, isoflavones or other phytoestrogens, have a plant origin.
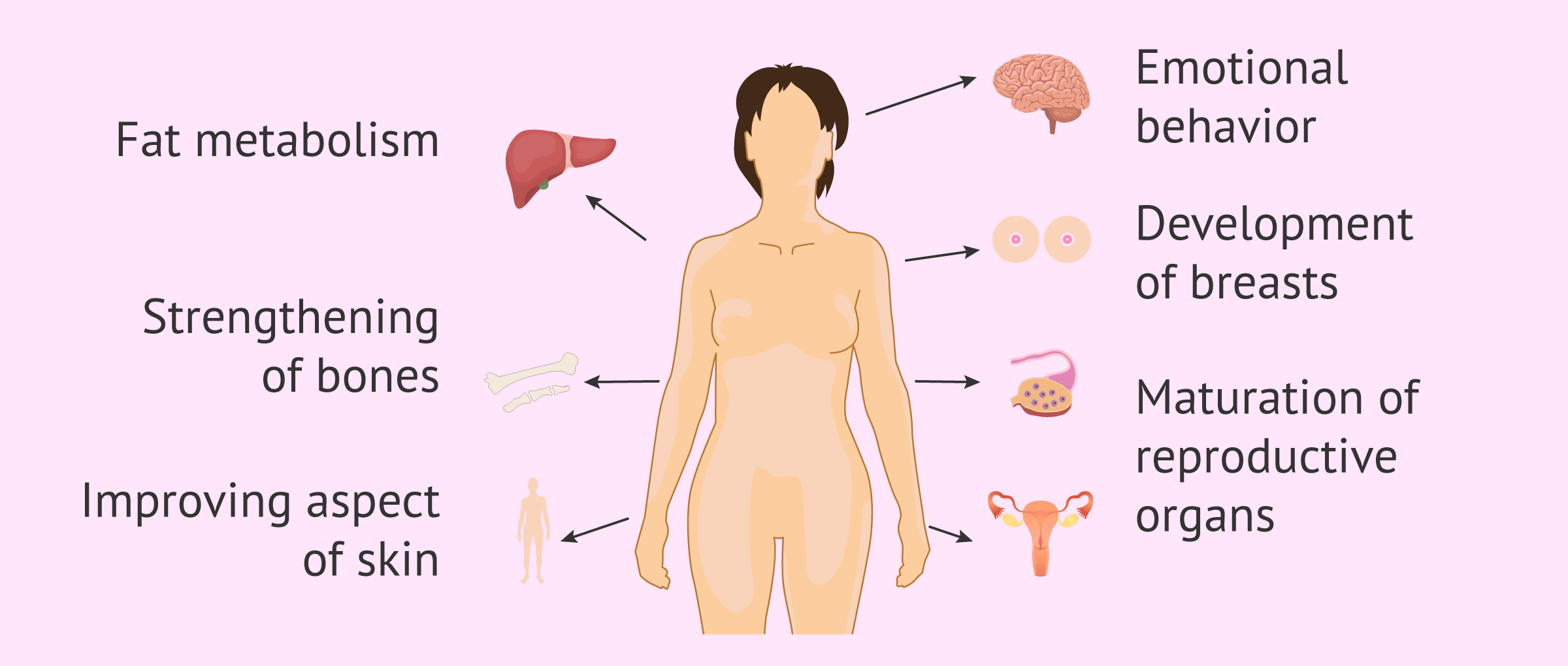
Functions
Estrogens are responsible for sexual development during a woman's puberty. Once the ovaries begin to function and secrete estrogens, female sexual characteristics appear:
- Ripening of the reproductive organs: vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes
- Breast development
- Appearance of hair, especially in the pubic area
- Changes in the woman's tone of voice
- Appearance of the menstrual cycle, i.e. menstruation
You can get more information about this in the following article: Female Fertility: Parts of the Female Reproductive System
Another function of estrogens is to regulate the synthesis of proteins in cells, so these hormones have a fundamental role in many processes of the body, some of which we discuss below:
- Bone strengthening
- oestrogens prevent the loss of calcium, thus contributing to maintaining the consistency of the skeleton and avoiding osteoporosis.
- Improve the appearance of the skin
- estrogens are involved in the formation of collagen and the regeneration of the dermis, thus helping to have a healthier appearance of the skin. Estrogens also strengthen nails and hair, preventing them from falling out.
- Fat metabolism
- oestrogens activate the production of HDL, the so-called good cholesterol, thus helping to strengthen the functioning of the cardiovascular system and reduce the risk of heart attacks.
- Emotional Behavior
- oestrogens favour blood flow and the arrival of glucose to the brain, which stimulates neuronal development and the synthesis of neurotransmitters. For this reason, low estrogen levels can lead to mood swings, insomnia, and irritability.
On top of that, estrogens control the menstrual cycle and ovulation during a woman's reproductive life, thanks to their regulatory action on the pituitary gland in the brain.
If you are interested in obtaining detailed information on this subject, we recommend you to access the following post:
Estrogen level
As indicated above, estrogen synthesis begins with puberty in girls, when the ovaries begin to function.
From this point on, the estrogen level will remain more or less stable for the next 25 years, i.e. at the fertile stage of the woman.
Once menopause has arrived, the level of estrogen suffers a drastic drop, so that the woman's body will suffer various changes, such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness.
The normal values of estradiol in a fertile woman are between 27 and 161 pg/ml approximately. For men, the normal estrogen value is between 10 and 37 pg/ml.
Some fertility disorders, such as menstrual cycle irregularities or difficulty getting pregnant, are related to hormonal changes. For this reason, the blood test for the determination of estrogens is a common test in the study of female fertility and also male.
In the case of women, the blood test should be done at the beginning of the menstrual cycle, 3 to 5 days after the arrival of the period. In the following section we are going to interpret what the results mean.
Low estrogen
The reasons a person may have a low estrogen level are as follows:
- Early menopause
- Premature ovarian failure
- Turner syndrome
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Eating disorders, such as anorexia nervosa
As for the level of estriol during pregnancy, a low value may indicate that something is wrong or that the fetus has a birth defect, so more medical tests will be needed.
High estrogens
On the other hand, a too higher estrogen level may indicate one of these disorders:
- Tumor in the ovaries, adrenal glands, or testicles
- Cirrhosis
- Precocious puberty in girls
- Delayed puberty in children
Higher estriol levels during pregnancy are a sign that labor will soon begin.
Estrogen drugs
Estrogen therapy has several indications, from hormonal contraception to menopause treatment.
Estrogen medications are usually taken as pills or transdermal patches, although it is also possible to find estrogen in cream or gel form.
Here are some of the indications for estrogen treatment:
- Early ovarian failure
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Alterations in menstruation
- Delayed puberty
- Acne Treatment
- Decreased symptoms of breast or prostate cancer
- Prevention of osteoporosis
Besides, estrogen drugs are also used in other processes such as the following:
Assisted Reproduction
One of the functions of oestrogens during the first half of the menstrual cycle is to promote the growth of the endometrium so that presents adequate thickness thus allowing embryo implantation.
For this reason, women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment will also need oestrogen drugs to achieve optimal endometrial thickness and become pregnant.
In particular, estradiol patches are used during endometrial preparation treatments to transfer frozen embryos or in the course of an ovodonation.
If you are interested in more information about this topic, click here:
In menopause
During the treatment of menopausal symptoms, combined estrogen/progestin drugs, or conjugated estrogens, are often used. It's what's known as hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
The main benefits of this therapy in menopausal women are the following:
- Relief from hot flushes and hot flashes
- Improved vaginal dryness, resulting in reduced pain during sexual intercourse and urinary tract infections
- Increases good cholesterol (HDL) and reduces bad cholesterol (LDL)
- Improves sleep quality
If you think you are entering the pre-menopausal stage and are looking for information, you can continue reading here: How do I know if I enter Menopause?
FAQs from users
What are the consequences of taking two estradiol tablets by mistake?
The administration of two tablets together by mistake does not affect the course of an assisted reproduction cycle, since the intake of estradiol can be divided into two or three doses.
Read more
What happens if I am pregnant after IVF, but my oestrogen level is too low?
Estrogens in the body have many functions and, focusing on pregnancy, they improve blood circulation in the uterine vessels. In addition, these hormones are involved in endometrial preparation and prevent miscarriages.
If there is an oestrogen deficiency, the specialist may decide to supplement with the appropriate medication for the individual woman and the type of treatment she has undergone.
Read more
What does a low estrogen level mean?
Estrogens are the hormones produced by ovaries. A very low level of estrogen is usually found in a case of non-functioning ovaries (in cases of ovarian failure, menopause, etc.). The consequences of having a very low level of estrogen are the same as during menopause (vaginal dryness, decreased libido, etc.).
In a woman's normal menstrual cycle, for two or three days there is a low level of oestrogen (the first few days of menstruation) but the oestrogens quickly start to rise, until they reach a maximum, when ovulation occurs.
What is the drug Progynova used for?
Progynova is a drug whose active ingredient is estradiol valerate. This hormone is involved in the majority of female sexual characteristics and is ultimately responsible for the changes that women experience during the menstrual cycle, especially in the first phase of the cycle.
In medicine it is possible to use drugs such as Progynova on different occasions. For example, to eliminate the symptoms of menopause, to control the woman's cycle in a transfer of frozen embryos or in egg donation, and so on.
Read more
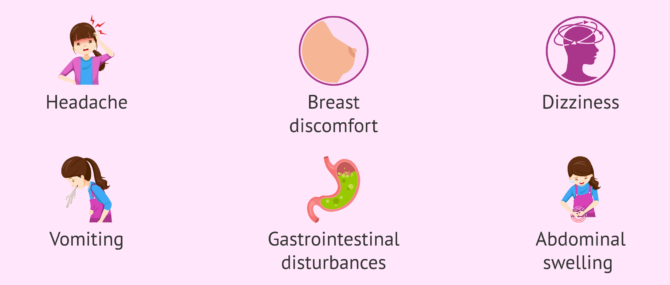
What are the side effects of taking estrogens?
Prolonged use of estrogens may cause some adverse effects on the person such as headache, breast discomfort, dizziness and vomiting, gastrointestinal disturbances, gas, hair growth, changes in sexual desire, etc..
In the most serious cases, estrogen drugs can cause loss of appetite, weakness, hives, abdominal swelling, joint pain, etc.
For this reason, an estrogen treatment should always be applied under a doctor's prescription.
Suggested for you
For more information on the sex hormones that act in the bodies of men and women, please read on in the following article: Male & Female Sex Hormones - Definition & Functions.
On the other hand, if you are looking for information about hormonal contraceptives and their effectiveness, you can access the following post: Which Contraceptives Really Work? - Types of Birth Control Methods.
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Cody JD, Jacobs ML, Richardson K, Moehrer B, Hextall A. Oestrogen therapy for urinary incontinence in post-menopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;10:CD001405 (View)
Gambacciani M, Levancini M. Hormone replacement therapy: who should be treated? Minerva Ginecol. 2015 Jun;67(3):249-55.
Lethaby A, Ayeleke RO, Roberts H. Local oestrogen for vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 31;(8):CD001500 (View)
Lobo RA. Hormone-replacement therapy: current thinking. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017 Apr;13(4):220-231 (View)
Rossetti MF, Cambiasso MJ, Holschbach MA, Cabrera R. Oestrogens and Progestagens: Synthesis and Action in the Brain. J Neuroendocrinol. 2016 Jul;28(7) (View)
Smy L, Straseski JA. Measuring estrogens in women, men, and children: Recent advances 2012-2017. Clin Biochem. 2018 Dec;62:11-23 (View)
FAQs from users: 'What are the consequences of taking two estradiol tablets by mistake?', 'What happens if I am pregnant after IVF, but my oestrogen level is too low?', 'What does a low estrogen level mean?', 'What is the drug Progynova used for?' and 'What are the side effects of taking estrogens?'.