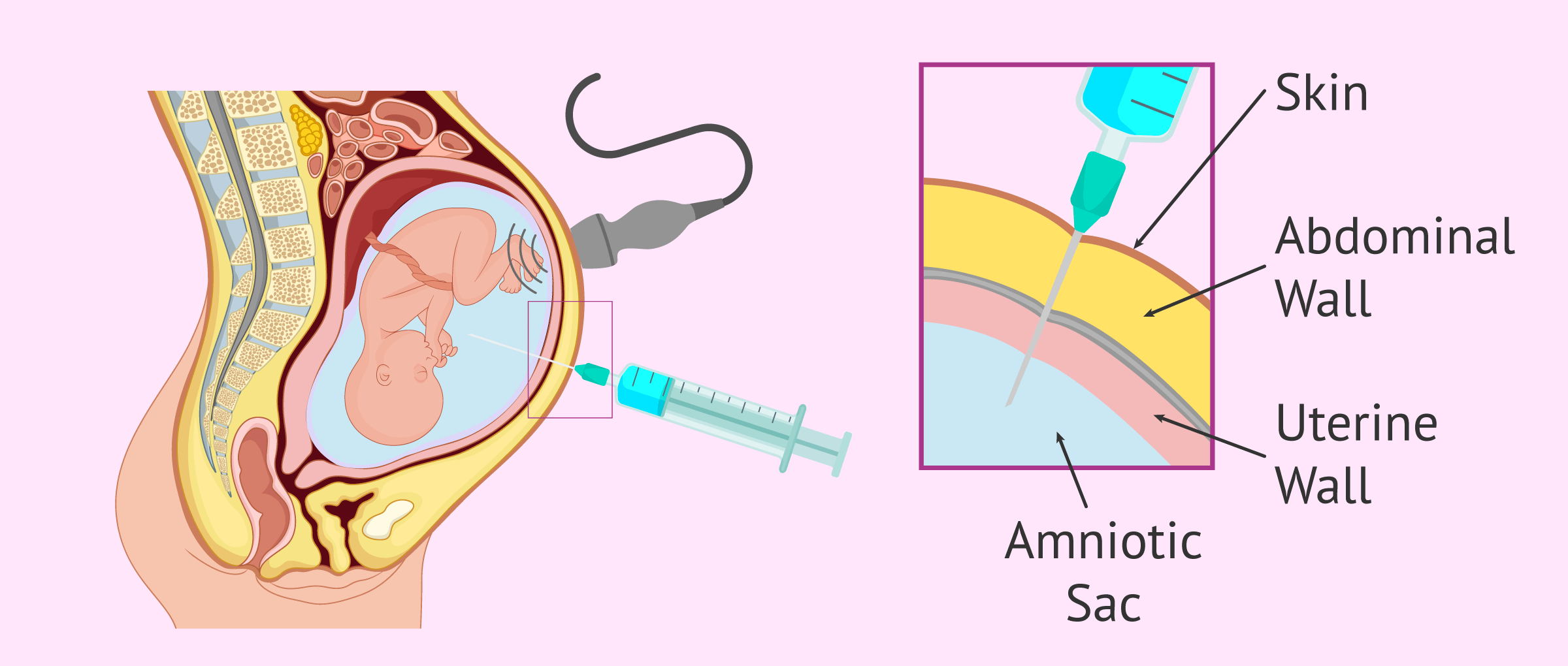
Amniocentesis is an invasive prenatal test that detects fetal abnormalities by collecting cells from the amniotic fluid.
For this purpose, a long, thin needle is used to pass through the abdominal wall, uterine wall and amniotic membrane, and between 20 and 25 ml of amniotic fluid can be aspirated. This whole process is guided through an abdominal ultrasound, in order to prevent damage to the fetus.
Read the full article on: Amniocentesis: Why it is done and what are the possible risks? ( 101).
By Sergio Rogel Cayetano M.D. (gynecologist), Zaira Salvador B.Sc., M.Sc. (embryologist), Michelle Lorraine Embleton B.Sc. Ph.D. (biochemist) and Romina Packan (invitra staff).
Last Update: 09/23/2019