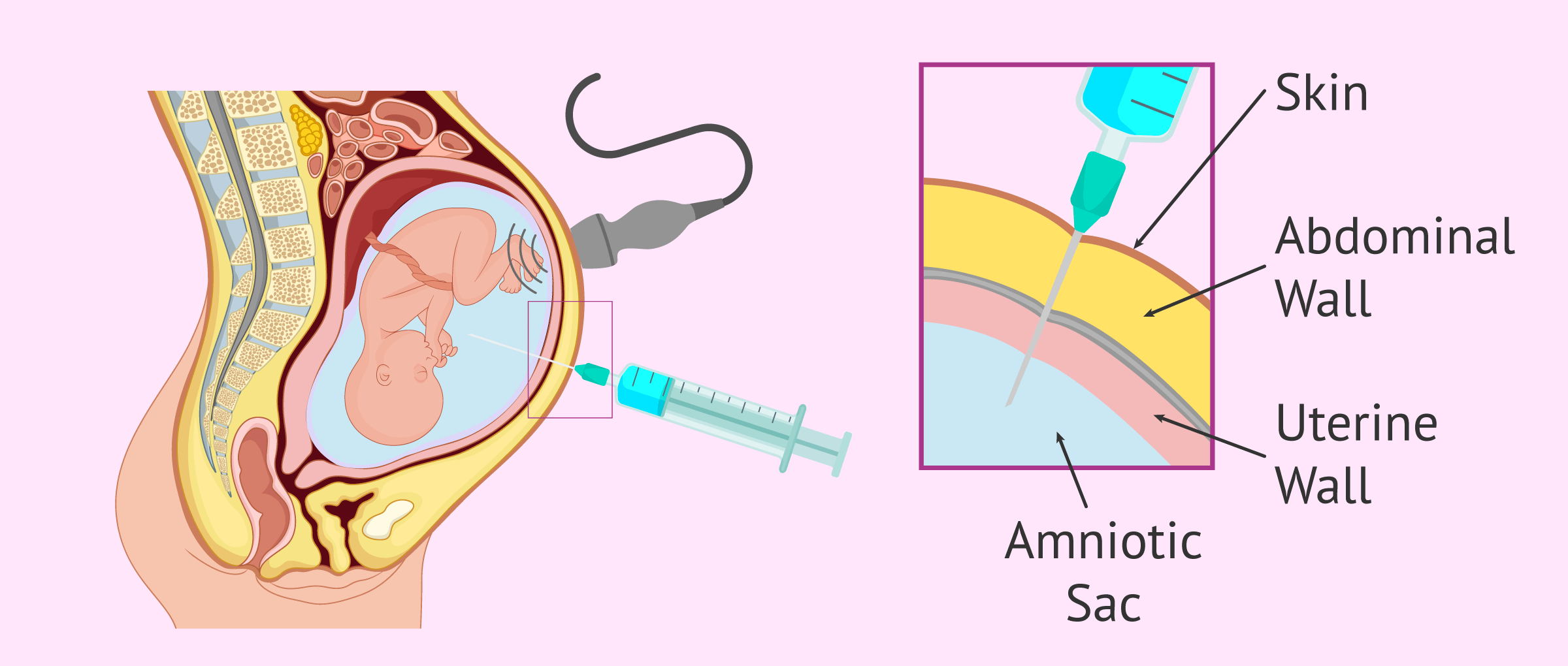
Amniocentesis is a prenatal test in which a sample of the amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus is removed for testing.
Because it is an invasive diagnostic test, amniocentesis has some risks that compromise pregnancy. However, it is very useful when it comes to detecting if the fetus presents any anomaly or malformation.
This amniotic fluid test is generally recommended for all women over the age of 35.
Provided below is an index with the 8 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 1.1.
- 1.2.
- 1.3.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 5.1.
- 5.2.
- 5.3.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
Definition of Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is the study of the fluid inside the amniotic sac to determine if the fetus is developing correctly or, on the contrary, has some disease or alteration.
When surrounding the fetus throughout gestation, the amniotic fluid contains fetal cells, which are detached from the fetus' skin and intestine, as well as chemicals produced by the fetus that can be tested.
How is it performed?
To obtain the amniotic fluid, a puncture is necessary with a long, thin needle, which is inserted through the abdominal wall and through the uterine wall and amniotic sac.
Between 20 and 25 ml of amniotic fluid is then collected and the needle is carefully removed.
This intervention is controlled by ultrasound to avoid damaging the fetus at any time.
Once the cells contained in the amniotic fluid have been obtained, it is possible to make a karyotype of the baby, i.e. a detailed analysis of all his chromosomes.
When is it done?
Amniocentesis is usually performed in the second trimester of pregnancy, when the woman is between 15 and 20 weeks gestation.
At this point, the risk of miscarriage is lower, since the woman has already passed the first trimester barrier.
Apart from that, before the 15th week of pregnancy, the amount of amniotic fluid is still not enough and, in addition, the amniotic membrane is still too solid to make the puncture.
It is best to do amniocentesis between the 16th and 18th week at the latest, as at this time it is still possible to terminate the pregnancy if it is confirmed that the fetus has some serious pathology.
Indications
The main indication for amniocentesis is maternal age.
This test is recommended with the mother is 35 years old and upwardss, as the risk that the baby presents some genetic anomaly or chromosomal disease begins to be higher. From the age of 40, an amniocentesis is almost obligatory.
It is also very important to consider the mother's medical history. For example, if there is a previous miscarriage or especially if there has been previous pregnancies with chromosomal alterations or fetal malformations.
Finally, if any previous diagnostic test has been performed that has given an abnormal result, an amniocentesis will also be necessary to confirm the result. This would be the case with triple screening done at 10-12 weeks of pregnancy.
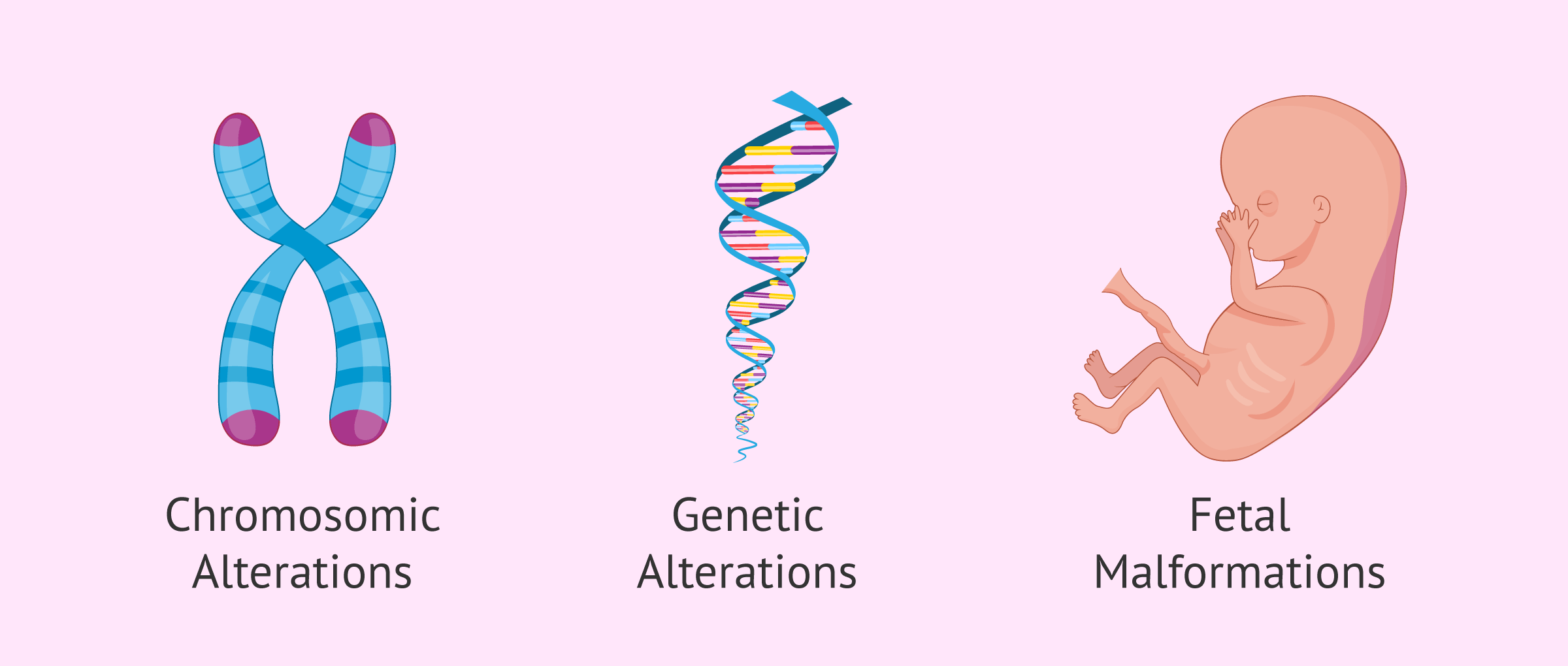
What does amniocentesis detect?
This prenatal diagnostic test has the advantage of being able to detect a multitude of fetal alterations, but the most common results are the following:
- Chromosomal Alterations
- especially those that affect the number of chromosomes, such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome or Turner syndrome.
- Chromosomal Alterations
- if there is a hereditary disease, amniocentesis can detect most of these genetic diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell disease.
- Fetal malformations
- such as spina bifida, anancephaly or other neural tube disorders. This is done by measuring the level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), a substance produced by the liver of the fetus and found in the amniotic fluid.
- Lung condition
- in a late amniocentesis, around 32 and 36 weeks, it is possible to determine whether the lungs are mature enough for the fetus to be born safely, in case of risk of premature birth.
- Rh Factor
- It’s purpose is to assess the severity of fetal anaemia in the event of Rh incompatibility with the mother. In this case, the bilirubin content in the amniotic fluid will indicate whether the baby requires an intrauterine transfusion.
- Infections in the uterus
- caused by microorganisms that could affect the fetus.
- Polyhydramnios
- if there is excess amniotic fluid, amniocentesis may be used as a treatment to decrease the amount of fluid.
- Sex of the baby
- although it is not the purpose of the test, analysis of sex chromosomes will give information about the sex of the fetus.
Associated risks
As we have already mentioned, amniocentesis is an invasive test and therefore involves some risks when performing the puncture.
Despite this, the risk of miscarriage is less than 1% and is considered a safe test in most cases.
The most important thing is that the procedure is performed by a medical expert, who knows how to see by ultrasound the exact place where to do the puncture without damaging the fetus.
Rarely, in around 1% of the cases, it is not possible to perform the operation correctly on the first attempt and the amniotic puncture must be repeated.
Unfortunately, amniocentesis may hurt when the needle is inserted, and it is also possible to feel discomfort in the abdominal area during the extraction of amniotic fluid.
Other possible risks or side effects of amniocentesis include the following:
- Amniotic fluid loss or bleeding
- Puncture of the fetus or umbilical cord during testing
- Transmission of infections from mother to fetus, such as HIV, hepatitis C, or toxoplasmosis
- Irritation around the puncture site
- Infections in the uterus after testing
Something very important when deciding whether or not to do an amniocentesis is to have a clear idea of what to expect when the results are received. If it is finally revealed that the baby has an abnormality, the woman or couple will have to make the decision to abort or continue the pregnancy despite the findings.
In some cases, the parents are not willing to terminate the pregnancy voluntarily under any circumstances and, therefore, it would not make sense to run the risks of amniocentesis.
Alternatives
In recent years, new methods of early detection of fetal alterations have been developed in order to reduce the number of amniocentesis performed.
Below, we will discuss some of these alternative tests:
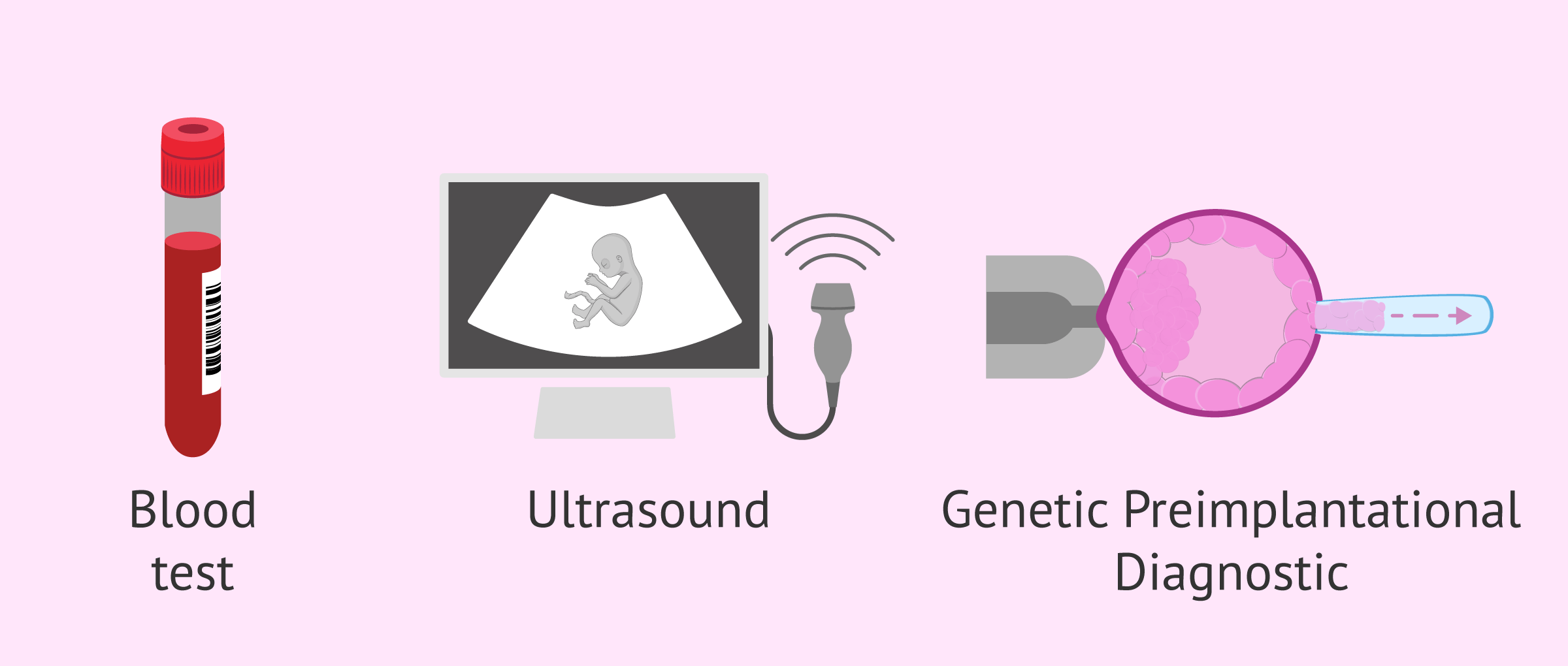
- Non-invasive prenatal test
- consists of a simple extraction of blood from the mother's arm. It has been proven that there is fetal DNA in maternal blood samples from the 9th week of pregnancy, where up to 80% of the chromosomal anomalies that would be diagnosed with amniocentesis can be detected.
- Triple screening
- is the estimation of the risk that the fetus has chromosomal abnormalities. It is calculated from the results of a maternal blood test and measurement of the nuchal translucency of the fetus.
- Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD)
- is the earliest diagnostic test available, since it is made from a cell extracted from the embryo itself before being transferred to the mother's uterus. For this, the woman will need to be undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment.
FAQs from users
If I don´t want to have an amniocentesis, what is the best alternative?
Amniocentesis is an invasive technique that can lead to rupture of the amniotic sac or miscarriage in a small percentage of cases. In order to avoid this risk, various options have been developed to try to avoid this test and its sister technique, chorionic villus sampling:
- Ultrasound techniques
- : The measurement of certain fetal parameters (NCD, nuchal fold, nuchal translucency, femur length) or the identification of certain characteristics (presence of nasal bone, absence of malformations) are useful in the identification of possible babies with aneuploidies.
- Analytical techniques
- : Certain substances present in maternal blood during pregnancy can be altered if the pregnancy is aneuploid (PAPPA, B-HCG, Estradiol...).
- Statistical techniques
- The occurrence of familial cases of aneuploidy, or maternal age are statistically associated with the presence of aneuploidy in pregnancy.
- Mixed techniques
- >The combination of all the above techniques can increase the detection of aneuploid fetuses. Nowadays, together with specialized ultrasound, it is the most widely used technique in obstetrics, and in general it is offered to all pregnant women in Spain. The usual protocol is to perform a blood test around the 10-12th week in order to obtain the analytical parameters and a small survey and ultrasound around the 12-14th week in which the statistical and ultrasound parameters are obtained. These parameters are then integrated on the basis of a computerized algorithm, which quantifies the risk of the pregnant woman and compares it with what is desirable and with the group of women of her age.
- Genetic techniques
- The evolution of non-invasive techniques has generated some very interesting genetic-based tests, which are much more reliable than the previous ones (although amniocentesis is still better). These techniques are based on fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood.
Is it necessary to rest after amniocentesis?
Yes, it is convenient to have absolute rest the same day after the amniotic puncture and not to make great efforts during the following 2 or 3 days. It is also not recommended to have sexual relations during the following week.
In case of significant cramps, loss of amniotic fluid or bleeding, it is advisable to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Is amniocentesis necessary in a pregnancy through egg donation?
Well, not in principle. The donated eggs come from young, healthy donors, mostly under 30 years of age. The likelihood of these eggs accumulating genetic mutations is low and therefore amniocentesis is not necessary even if the recipient mother is of advanced maternal age. Combined first-trimester screening is usually done because it does not present any complications or risks.
In spite of everything, it is always advisable to follow the instructions of the doctor responsible for the control of the pregnancy.
Recommended reading
If you want to know about all the tests that are usually done throughout the 40 weeks of gestation, you can read more in the following article: Medical control During Pregnancy
Another test that offers similar results to amniocentesis and can be done before week 15 of pregnancy is chorionic villus sampling. You can learn more about this by reading this article: What is chorionic villus sampling? - Indications and risks.
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Authors and contributors

More information about Michelle Lorraine Embleton



Hi
I don´t understand why I haven´t been offered an amnio when my best friend (the same age as me) has to go for one in 2 weeks. She is 14 weeks pregnant and I am 13 weeks pregnant. I´m 34 and live in Hull if that helps.
Thanks in advance for any replies.
Hi Bailey
How lovely that you and your best friend can share in such a special journey together!
I can understand your confusion, but according to information provided by the NHS, amniocentesis is not offered to all pregnant women. Due to the risks involved it is offered when there is an increased probability of the baby having a genetic condition. This increased probabilty may be due to the results of another antenatal screening test (for example that performed at your 12 week scan or from the triple test results). It could also be because your friend has a family history of a genetic disease.
If you have not been recommended to have one then it is probably because your doctors have not deemed it necessary – which is good news!
I hope this helps and enjoy your pregnancies!