Ovarian tissue transplantation is a promising technique that is still in the experimental phase. To date, at least 60 pregnancies have been achieved using this technique. However, it should be noted that it presents a series of risks and limitations that we will discuss below:
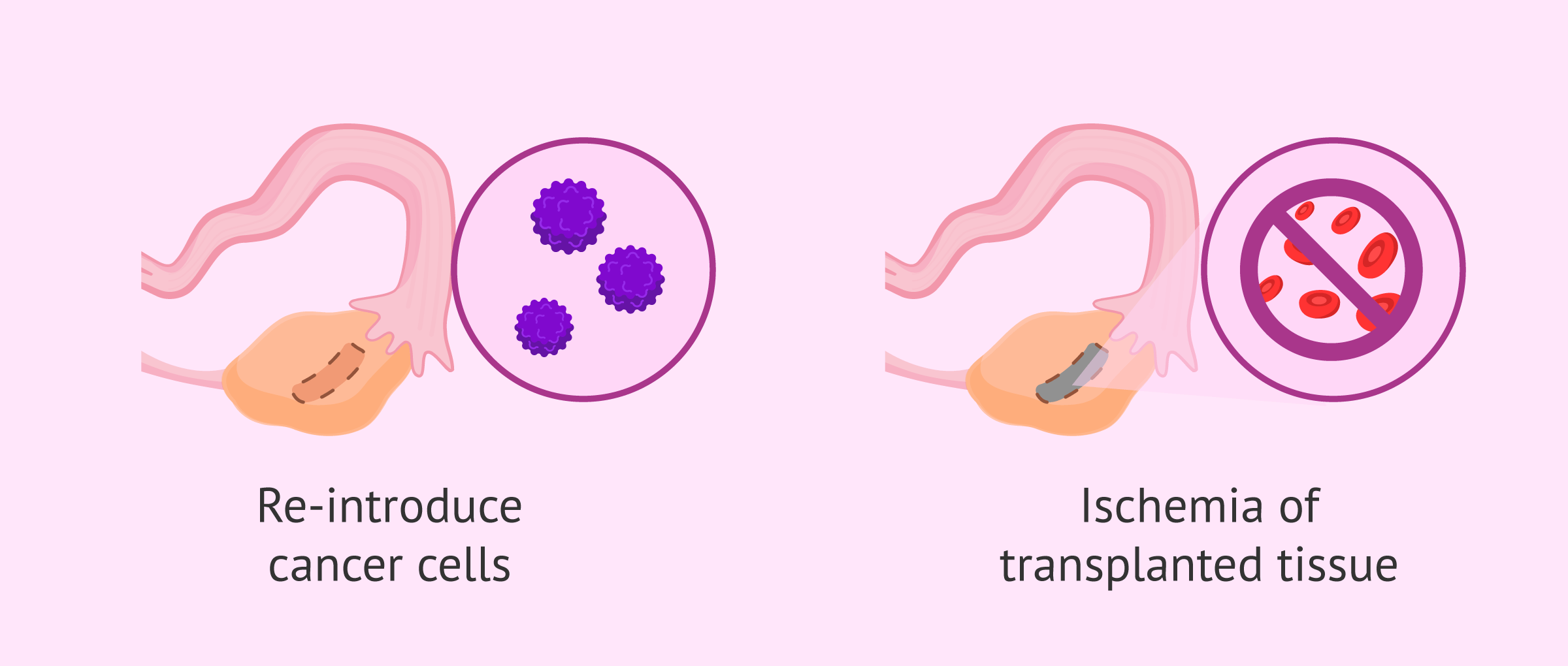
- Reintroduction of cancer cells: not all types of cancer allow this technique to be performed. Cases have been detected of patients with leukaemias of certain characteristics who have developed the cancer again after implantation of the ovarian tissue. The researchers fear that this technique is not the right one in many cases, since there is a danger of reintroducing cancer cells that were extracted with the ovarian graft. Despite the existence of a number of ways to clean the graft of possible malignant cells, they are still not sufficiently purified.
- Production of ischemia of the transplanted tissue: once the ovarian tissue has been transplanted, it is essential that the blood vessels regenerate and can provide the necessary nutrients that come through the bloodstream. If this did not happen, ischemia would occur, the tissue would not integrate with the rest of the ovary and the blood would not reach it. Due to this problem that can occur after ovarian tissue transplant operations, the possibility of cryopreserving the patient's entire ovary is being studied, as the danger of ischemia would be reduced in this case.
Read the full article on: What Is Ovarian Tissue Transplantation? ( 70).
By Blanca Paraíso M.D., Ph.D., M.Sc. (gynecologist), Cristina Mestre Ferrer B.Sc., M.Sc. (embryologist), Juan Antonio García Velasco M.D., Ph.D. (gynecologist), Laura Parra Villar B.Sc., M.Sc. (embryologin), Marita Espejo Catena M.D., M.Sc., Ph.D. (gynecologist) and Romina Packan (invitra staff).
Last Update: 04/15/2020