The physiological changes that a woman undergoes during pregnancy occur in order to progressively adapt her body to pregnancy and to meet all the demands required for the baby's development. Therefore, once the baby is born, the changes gradually reverse in the postpartum period.
These changes during pregnancy may be more or less noticeable to the woman and generate more or less discomfort. In addition, they affect different organs and systems, such as the cardiovascular, digestive, urinary and, of course, the reproductive and breast.
Provided below is an index with the 13 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 10.1.
- 10.2.
- 10.3.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
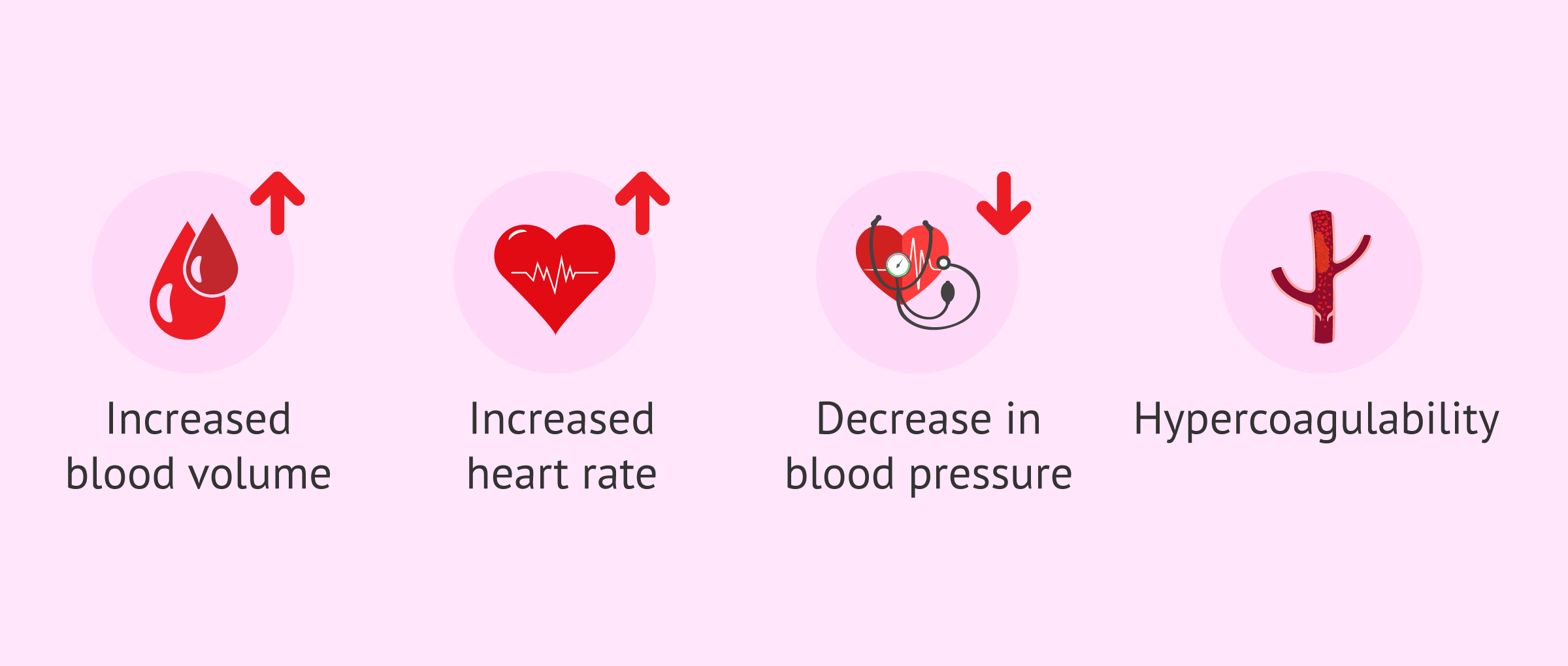
Cardiovascular changes
Among the main physiological changes at the cardiovascular level that women may experience during pregnancy are the following:
- Increase in blood volume, almost 50%, which can lead to a slight physiological anemia (because the blood is more diluted).
- Increase in cardiac output, i.e., the volume of blood pumped by the heart in a given time.
- Increased heart rate, which can reach up to about 90 beats per minute at rest.
- Gradual decrease in blood pressure until the second trimester of gestation. However, this change is reversed during the third quarter.
- Shifting of the heart upward and to the left, due to the enlargement of the uterus.
- Hypercoagulable state, to avoid excessive blood loss in childbirth. However, this situation also increases the risk of blood clots.
In addition, swelling in the legs, feet and ankles is frequent, because venous return is hindered by the enlarged uterus. Vulvar and leg varicose veins may also appear.
Gastrointestinal changes
The hormonal changes typical of pregnancy are also related to one of the most common symptoms of pregnancy: nausea and vomiting. However, at the gastrointestinal level there are also other changes during pregnancy, such as the following:
- Relaxation of the esophagus-stomach junction (lower esophageal sphincter), due to the action of progesterone. As a result, reflux, acidity and heartburn are favored.
- Displacement of the stomach, which changes its position, due to the enlargement of the uterus. This change will also favor reflux and acidity.
- Slower and heavier digestion, due to elevated progesterone levels. Thus, it is possible that the pregnant woman may have gas and suffer from constipation. However, it also contributes that intestinal transit is hindered by the pressure exerted by the uterus. Constipation, together with difficulties in venous return, can also lead to hemorrhoids.
Finally, some pregnant women notice a certain rejection of foods they used to eat, or cravings for a certain food. The cause may be related to hormonal changes and to the sharpening of smell and taste.
If you want more information about digestive discomfort in pregnancy and what you can do to alleviate it, you can read this article: What causes heartburn and other digestive discomfort in pregnancy?
Changes in the endocrine system
During pregnancy there are many changes in the endocrine system. The increase in hCG hormone leads to an increase in estrogen and especially progesterone as it maintains the ovarian corpus luteum. Subsequently, the placenta will acquire an important endocrine function.
On the other hand, the pituitary gland increases in size because the cells that produce prolactin grow in size and number. Thus, prolactin is elevated to prepare the woman for lactation.
In addition, the increase of certain diabetogenic hormones and increased insulin resistance can lead to the onset of gestational diabetes.
Respiratory changes
The respiratory rate increases to cope with the increased oxygen consumption. In addition, the sensation of choking and shortness of breath is also common, especially when exerting oneself.
This is because the pregnant uterus causes the diaphragm to rise and there is less total lung capacity.
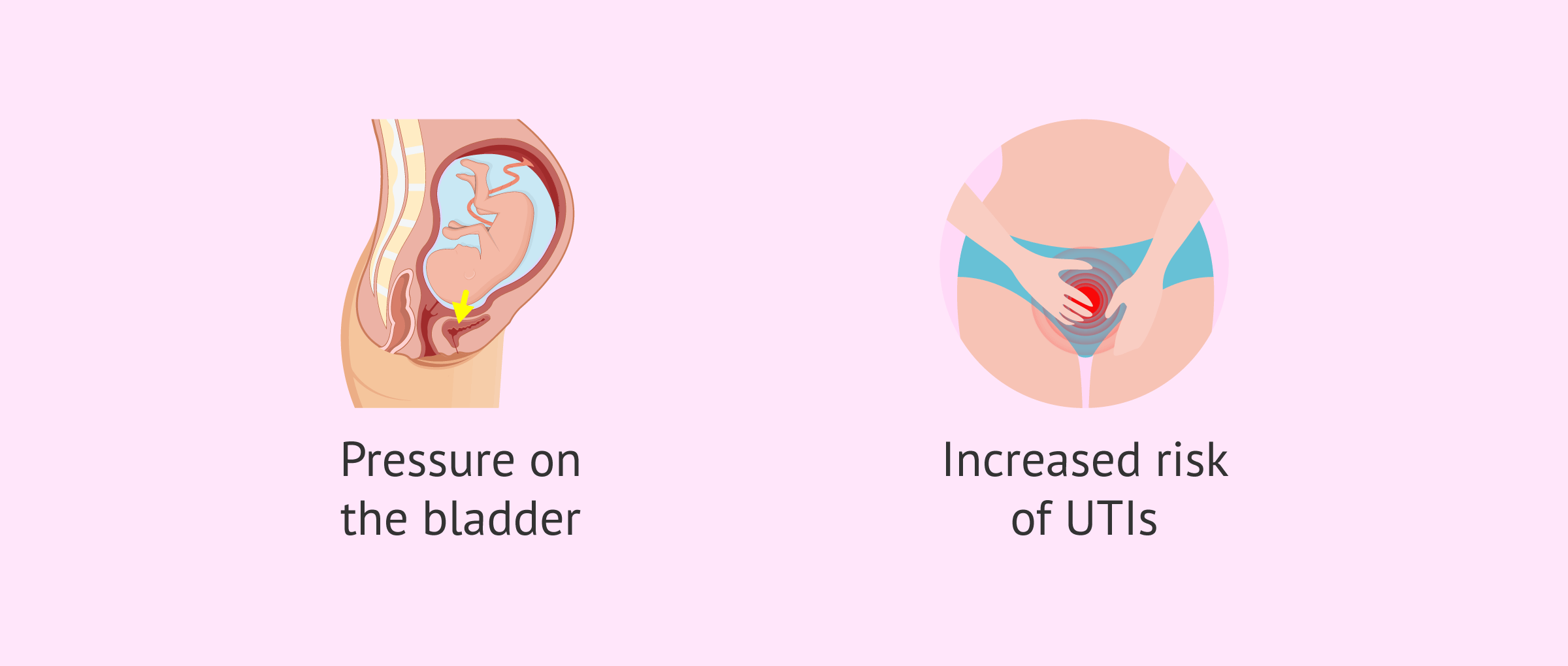
Changes in the urinary system
Due to the increase in blood volume mentioned above, the kidneys must also increase the volume of blood they filter in pregnancy.
On the other hand, the bladder is pressured because the uterus has increased in size. This causes an increase in the frequency with which a woman needs to go to the bathroom during pregnancy.
In addition, there are some changes in the urinary system that may favor the development of urinary tract infections (UTIs) during pregnancy. We tell you about it in the following article: Why are urinary tract infections so frequent in pregnancy?
Musculoskeletal changes
As the volume of the abdomen increases, the woman changes her posture by leaning slightly backwards. This postural change involves a change in the center of gravity that the pregnant woman makes to compensate and maintain balance.
On the other hand, relaxin is a hormone that makes joints and ligaments more relaxed and lax. Its purpose is to prepare the woman's pelvis for the enlargement of the uterus and for childbirth, but it may cause the woman to feel some instability.
Skin changes
The appearance of brownish spots on the skin (especially on the face) during pregnancy is common. This is called melasma, chloasma gravidarumor, more commonly, cloth or mask of pregnancy.
Again related to hormonal changes in pregnancy, melanin production increases. Melanin is the pigment that gives color to the skin and, therefore, this hyperpigmentation causes the skin to darken.
Thus, certain spots may appear on the skin of the pregnant woman's face. However, areolas and nipples, vulva, perineum, armpits, inner thighs and the linea nigra (from the navel to the pubis) also darken.
You can find information on how to avoid facial skin spots during pregnancy in this article: Why do skin spots appear during pregnancy? How to avoid them?
On the other hand, due to the stretching to which the skin is subjected during pregnancy, stretch marks often appear on the abdomen, hips, breasts, thighs...
Changes in the reproductive system
During pregnancy, a woman's reproductive system undergoes major changes. Some of the main changes would be the following:
- Absence of menstrual cycle.
- Increase in size of the uterus. This change can be perceived externally by the bulging of the abdomen, which becomes more evident as the weeks of gestation progress.
- Increased vaginal discharge. This is normal due to hormonal changes and increased blood supply to the vagina.
However, it is important to distinguish when vaginal discharge is normal and when it may indicate a vaginal infection. If there are changes in the color, odor or appearance of the discharge, or if there is itching or burning in the vaginal area, a specialist should be consulted.
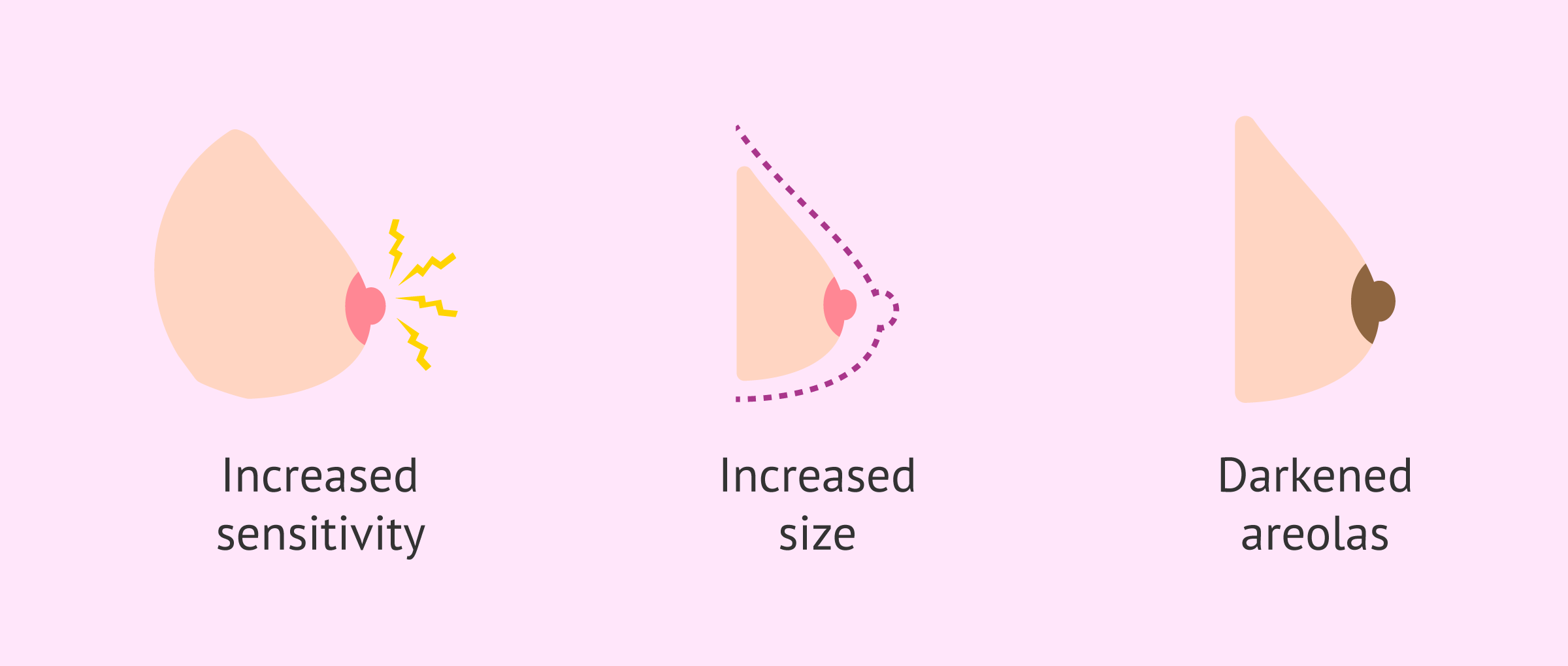
Breast changes
The breasts also undergo evident changes during pregnancy, due to the action of hormones, as they prepare for the baby's lactation. Some of the changes are:
- Increased sensitivity, sensation of tension and swelling. The woman may notice this change from the first weeks of pregnancy.
- Increase in size, due to the stimulation of the development of the glands that produce milk.
- Enlargement of mammary areolas and nipples, which also darken.
- Appearance of Montgomery's tubercles (lumpy, whitish spots on the areola) whose secretion helps protect and lubricate the nipple.
- Increased visibility of superficial veins.
In addition, in the final stretch of pregnancy, it is also possible that the woman may notice colostrum secretion. Colostrum is the food that the baby will drink in its first days of life, until milk production begins. It is a more yellowish secretion than milk, but not all women start producing it before delivery.
FAQs from users
Are there psychological changes in pregnancy?
Yes, pregnancy is a time of great changes for women, also on an emotional and psychological level.
The hormonal changes typical of pregnancy, together with the worries and responsibilities related to this new stage, can cause frequent mood swings, increased irritability, some anxiety... In addition, the woman's self-esteem may also decrease due to the bodily changes that pregnancy entails.
Towards the end of pregnancy, it is common for certain fears about the moment of delivery to arise, mixed with the illusion and excitement of soon having the baby in her arms.
Finally, it is very important to see a specialist as soon as possible if it is thought that the woman may be suffering from postpartum depression.
What changes favor urinary tract infections in pregnancy?
During pregnancy, many changes occur in a woman's body. Among them, those that occur normally in the urinary system of the pregnant woman favor the development of urinary tract infections or UTIs. Therefore, there is an increased risk of contracting this type of infection in pregnancy.
Among these changes are:
- Dilatation of the ureters, which are the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder.
- Pressure on the ureters and bladder due to the increasing size of the uterus.
- Decreased muscle tone in the ureters.
- Increased reflux from bladder to ureters.
- Increased bladder volume.
- Higher urine pH (urine becomes less acidic) and higher sugar content.
Urinary tract infections or UTIs involve a urine culture with bacteriuria greater than 100,000 colony forming units per milliliter.
What are the physiological changes in the third trimester of pregnancy?
The physiological changes that usually occur in the third trimester of gestation are closely related to the increase in the size of the uterus.
Among the main ones, we can mention:
- Slowing of intestinal transit due to the pressure exerted by the uterus on the intestine.
- Choking sensation and shortness of breath, because the increase in the size of the uterus causes the diaphragm to rise and there is less lung capacity.
- Change in the woman's center of gravity, to compensate for the increased size of the belly and to maintain balance.
- Increased frequency of urination, due to the pressure of the uterus on the bladder.
- Swelling of the feet, ankles and legs, due to difficulties in venous return.
In addition, it is possible to observe that the breasts have begun to secrete colostrum.
Suggested for you
If you want to read more about the most common pregnancy symptoms, you can access this link: What are the pregnancy symptoms throughout the 9 months?
On the other hand, if you want to know which are the most common complications in pregnancy, we recommend you to visit the following article: What are the most common pregnancy complications?
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Anzelc MJ, Bechtel MA. Considerations for cutaneous physiologic changes of pregnancy that fail to resolve postpartum. Int J Dermatol. 2023 Feb;62(2):190-196. doi: 10.1111/ijd.16105. Epub 2022 Feb 7. PMID: 35132624. (View)
Chandra M, Paray AA. Natural Physiological Changes During Pregnancy. Yale J Biol Med. 2024 Mar 29;97(1):85-92. doi: 10.59249/JTIV4138. PMID: 38559455; PMCID: PMC10964813. (View)
Choo E, Dando R. The Impact of Pregnancy on Taste Function. Chem Senses. 2017 May 1;42(4):279-286. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjx005. PMID: 28334158. (View)
Hill CC, Pickinpaugh J. Physiologic changes in pregnancy. Surg Clin North Am. 2008 Apr;88(2):391-401, vii. doi: 10.1016/j.suc.2007.12.005. PMID: 18381119. (View)
Morton A. Physiological Changes and Cardiovascular Investigations in Pregnancy. Heart Lung Circ. 2021 Jan;30(1):e6-e15. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Nov 4. PMID: 33158736. (View)
Patxot M, Stojanov M, Ojavee SE, Gobert RP, Kutalik Z, Gavillet M, Baud D, Robinson MR. Haematological changes from conception to childbirth: An indicator of major pregnancy complications. Eur J Haematol. 2022 Nov;109(5):566-575. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13844. Epub 2022 Sep 4. PMID: 36059200; PMCID: PMC9825915. (View)
Tan EK, Tan EL. Alterations in physiology and anatomy during pregnancy. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2013 Dec;27(6):791-802. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Sep 4. PMID: 24012425. (View)
van Donge T, Evers K, Koch G, van den Anker J, Pfister M. Clinical Pharmacology and Pharmacometrics to Better Understand Physiological Changes During Pregnancy and Neonatal Life. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2020;261:325-337. doi: 10.1007/164_2019_210. PMID: 30968215. (View)
Viggiano M, Vassallo C, Massolo AC, Vicario R, Romiti A, Caforio L, Bagolan P. Physiological changes in cardiac dimensions and function in low-risk pregnancies. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022 Jun;35(12):2407-2410. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2020.1786057. Epub 2020 Jul 1. PMID: 32611213. (View)
FAQs from users: 'Are there psychological changes in pregnancy?', 'What changes favor urinary tract infections in pregnancy?' and 'What are the physiological changes in the third trimester of pregnancy?'.