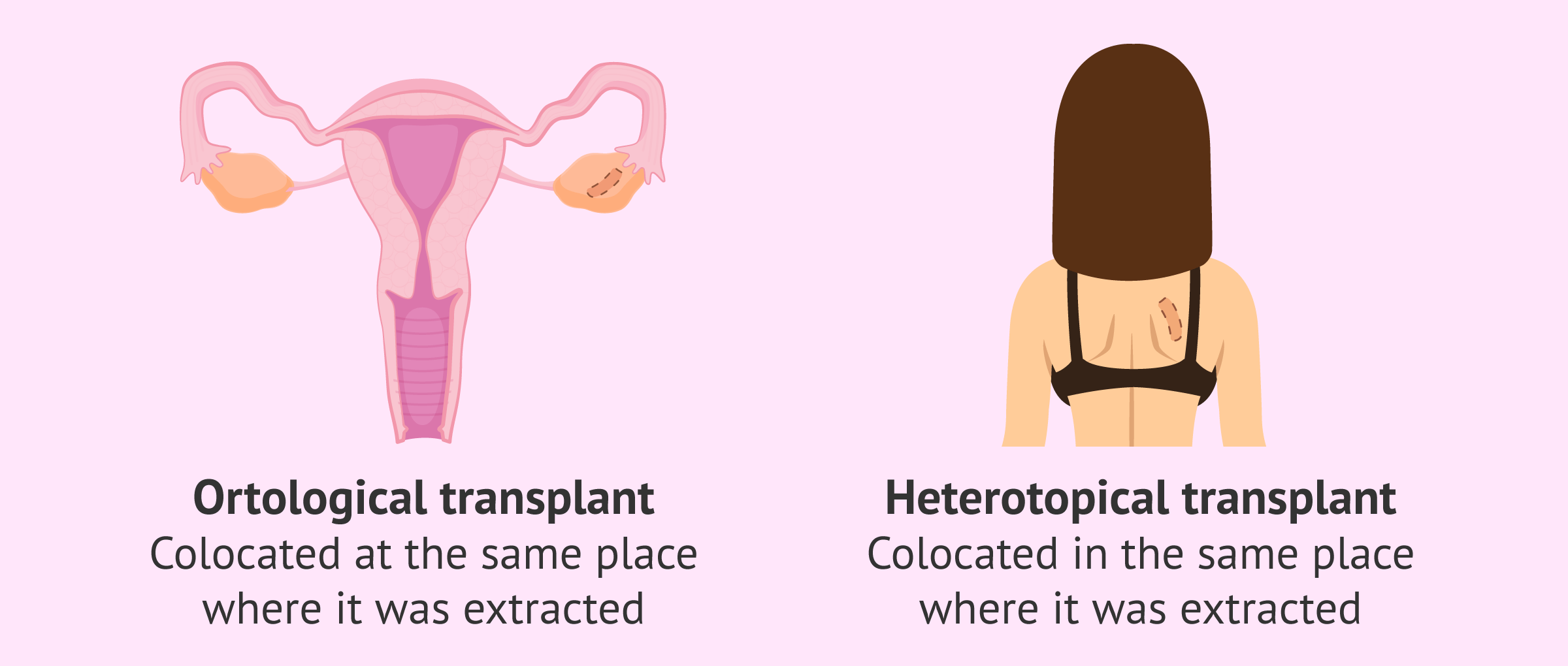
When the patient has overcome her oncological treatment and wishes to regain her fertility, the ovarian tissue is re-injected. Depending on the location of the transplant, it can be classified as follows:
- Orthopic transplant: the tissue of the ovarian cortex is grafted back onto the ovary. If the transplant is successful, the patient's hormonal cycle can be restored and she can ovulate normally. In this way, it is expected that the patient will be able to become pregnant naturally.
- Heterotopic transplant: the transplant is placed in a different area of the body. This can be the forearm or the back. Women who have this type of transplant cannot ovulate on their own. They need a cycle of ovarian stimulation and the extraction of the mature eggs in order to be fertilised in an assisted reproduction laboratory.
Read the full article on: What Is Ovarian Tissue Transplantation? ( 70).
By Blanca Paraíso M.D., Ph.D., M.Sc. (gynecologist), Cristina Mestre Ferrer B.Sc., M.Sc. (embryologist), Juan Antonio García Velasco M.D., Ph.D. (gynecologist), Laura Parra Villar B.Sc., M.Sc. (embryologin), Marita Espejo Catena M.D., M.Sc., Ph.D. (gynecologist) and Romina Packan (invitra staff).
Last Update: 04/15/2020