Surrogacy or surrogate motherhood, mistakenly defined by many as the rental of wombs or "womb-for-rent" service, is a fertility treatment by which a woman other than the intended mother carries the pregnancy to term and gives birth to the baby.
This method involves great complexity from an ethical and emotional perspective, as it breaks with tradition to provide a new understanding of family formation.
Provided below is an index with the 5 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 4.3.
- 5.
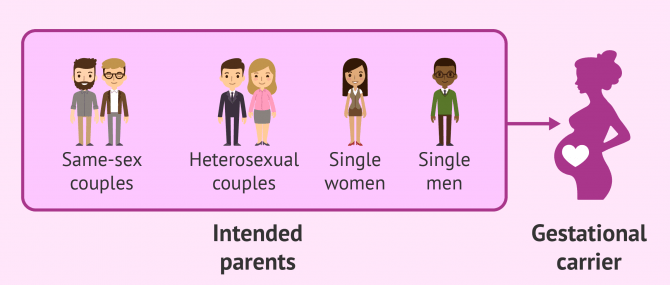
Different types of surrogacy
Surrogacy is a fertility procedure that involves a woman who agrees to carry someone else's baby. This woman is known as surrogate or gestational carrier, while the patients are usually called intended parents.
We can distinguish between two types of surrogacy depending on how the surrogate achieves pregnancy:
- Traditional, partial, genetic, or straight surrogacy: In this case, the surrogate contributes an egg as well, and therefore her genetic load. In this case, surrogacy is done through intrauterine insemination with the intended father's sperm, although IVF using the surrogate's eggs is possible as well.
- Gestational, host, or full surrogacy: The surrogate or gestational carrier does not contribute an egg for the creation of an embryo. In this case, the genetic material of the baby-to-be is that of the intended mother. Using donor eggs is possible as well.
It should be noted that traditional or genetic surrogacy has almost fallen into disuse nowadays, as it would mean the surrogate developing a greater emotional attachment to the unborn baby. Ideally, the intended mother should be the one contributing the egg; failing that, then egg donation could be used as alternative plan B.
The gestational, host, or full surrogacy option is commonly the only type allowed in the vast majority of countries where this fertility treatment is permitted.
On the other hand, surrogacy can be classified into two more types if we take into account the financial compensation surrogates can get in certain countries. Depending on whether she is economically compensated or not, we can distinguish between:
- Commercial surrogacy: Surrogates are paid for carrying the pregnancy, apart from being given a compensation in recognition of the expenses derived from the process.
- Altruistic surrogacy: Surrogates can be financially compensated in recognition of the expenses derived from the pregnancy such as maternity clothes, prenatal visits, special meals required, visits to the hospital, etc.
The total cost of the treatment will depend on the type of surrogacy chosen. For instance, commercial surrogacy, as well as the need for turning to donor eggs and/or sperm, would add to the overall costs of the treatment. In addition, surrogacy fees vary from country to country, depending on each destination's particularities.
Why surrogacy might become necessary?
The group of patients for which surrogacy is often necessary are heterosexual or straight couples which find themselves in one of the following situations:
- Absence of the uterus
- Uterine malformations or alterations
- Diseases and conditions preventing women from becoming pregnant because the baby's and mother's health would be at risk
- Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL)
- Repeated IVF failure (RIF)
Also, single women and lesbian couples suffering from one of the above mentioned issues could become mothers thanks to surrogacy.
Likewise, single men and same-sex male partners often resort to surrogacy to have a baby, as it is the only way for them to have a genetic child using their reproductive cells. In these cases, surrogacy is required just because human males do not have the anatomy needed for natural embryonic and fetal development.
Surrogacy around the world
Surrogacy has always been considered to be a controversial fertility option, which boundaries between what's ethical and what's not are still blurred. The reason behind should be understood in legal terms: surrogacy is not allowed everywhere. That is why many patients have no alternative but to cross borders to have the chance to create a family.
On the other hand, it should be borne in mind that even countries which are in favor of surrogacy, this fertility treatment is surrounded by a number of restrictions and particularities that might make it difficult for foreign citizens to make their dream come true.
Some countries like the United States allow all types of surrogacy, whether it is commercial, altruistic, partial, or full surrogacy. Also, all family types can access this fertility treatment: single men or women, same-sex or straight couples. Other countries such as Canada allow every family type to undergo surrogacy, but just the altruistic option.
In Russia, only heterosexual couples can undergo surrogacy, which means gay couples and single individuals do not have the chance to become parents through this method. Spain, France, and Germany are examples of countries in which this fertility treatment is forbidden or not contemplated in national law.
For example, surrogacy is not allowed in Spain because the Law on the Application of Human Assisted Reproduction Techniques explicitly says the legal mother is the woman who gives birth to the baby. Also, every agreement made for the purpose of waving the entitlement of maternity in favor of another woman is legally void.
FAQs from users
In which cases should you use a surrogate to have a baby?
In general, the two reasons for the use of surrogacy are the absence or abnormality of the uterus or a medical contraindication.
Cases of absent/abnormal uterus:
- MRKH syndrome. Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome is a disorder where the female is born with an underdeveloped or absent uterus and vagina.
- History of hysterectomy – a surgery to remove the uterus
- Multiple fibroid tumors of the uterus that cannot resolved by a surgery
- Severe intrauterine scarring (Asherman’s syndrome) irreparable
- A single male or gay male couple
- Unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss or unsuccessful embryo implantations
- Inability to develop the uterine lining (endometrium)
Cases of medical contraindications (relative and absolute):
- A serious medical condition that worsens with pregnancy posing risk to mother and fetus
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Turner’s syndrome
- Uterine cancer
What are the different types of surrogacy?
There are two types of surrogacy:
- Traditional surrogacy involves the woman who will carry the pregnancy also to be the source of the egg. She usually will ovulate naturally and undergo intrauterine insemination (IUI). Countries vary in their laws overseeing this arrangement so it is imperative that you consult, in advance of your treatment cycle, with an attorney who is well versed in this area.
- IVF surrogacy is the process of using an egg donor and a separate gestational carrier. Following hormonal stimulation of the egg donor and egg retrieval, the eggs are fertilized with the sperm of one or both partners in a reproductive laboratory through IVF. The embryo is then transferred into the gestational carrier’s uterus, previously prepared hormonally to synchronize optimal receptivity. The resulting baby is genetically unrelated to the carrier.
Can two males have a biological child with the DNA of both in a single pregnancy?
Currently, fertilization of an egg only occurs by one sperm cell that is produced from one man.
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!

After doing some research..What you can expect during pregnancy monitorying: Monthly ultrasound checks from the 12th week of pregnancy. Reports along with video and/or pictures will be send the same or the next day. For trisomy screenings, results will be send within 5 working days.Trisomy 13, 18, 21 – on the 12th week of pregnancy. Trisomy 18, 21 – on the 16th week of pregnancy.
If you will be present during the delivery (only available in the VIP Surrogacy package) you need to come prior to delivery to undergo the medical tests. You will be informed about right time to come by your program coordinator. When your surrogate mother is going for planned hospitalisation your program coordinator will let you know. This may give you the idea of what is the best time to come.
As a rule if the delivery is in a natural way the baby will be discharged in 3-4 days from the maternity house. In case of twins or c-section it might take up to 7 days for the babies to stay in the maternity house. In case of premature birth or any complications, the baby(s) obviously stay in the hospital for a longer period. If your contract is Standard – you will be visiting the baby during the daytime. If your contract is VIP Surrogacy – you will be staying in the hospital with a baby in a separate room.
Hope this helps.
Everyone knows that surrogacy is costly depending on a country/clinic you’re with. Choosing a country for fertility treatment you might consider the following: Does the country legally allow the treatment you require? Do you fall within the legal age limit? Does the country have laws regarding who they can treat? Are there easy and cheap transport links to that country? Are you happy with the laws on anonymity for donors (if needed)? Is the potential cost of treatment within your budget?
Ukraine seems to be one of the fewest places where the laws favor the intended parents rather than a surrogate. Under Ukrainian law, the baby is yours from the moment of conception. Once the baby is born, the birth certificate is issued with your names.A surrogate can’t claim any rights. Lastly, the procedure in Ukraine is time-wise. Pregnancies usually start right after embryos are create because many women participate in surrogacy there.
Once the woman is referred to as surrogate and the other time as gestational carrier. Are those just synonyms or is there a difference?
Hello Pointy Chip,
there is indeed a difference between the two terms. In traditional surrogacy the pregnant woman is called “surrogate”, wheareas in gestational carrier the pregnant woman is referred to as “gestational carrier”.
Hope this helps,
Best,
Romina
If the surrogate receives money for the surrogacy the arrangement is considered commercial surrogacy, if she receives no compensation beyond reimbursement of medical and other reasonable expenses it is referred to as altruistic.
There are plenty of reasons why surrogacy has nothing to do with exploitation of women. First, when one talks about “exploitation”, we assume the woman is being forced to do something against her will. I don’t think gestational carriers are forced to carry a baby, but do it because they’ve a strong desire to help others. Second, a pregnancy is a 9 month period in which the surrogate, unfortunately, feels the same pains and discomforts every woman who gets pregnant naturally feels, so she deserved being compensated in some way. Our capitalist world has decided that this compensation is in the form of money… I’m not going to share my opinion, but if that’s how it should be, or the only way a woman who’s been a surrogate can feel rewarded, then I agree in all terms.
So… you say “plenty of” and then just mention 2? hahaha there’s no way surrogacy can be that perfect, it contravenes many social aspects we humans have been building for a long time… And suddenly we aim to break tradition? it’s not that easy bae
Though thoughts about surrogacy may be very contradicting, I personally have nothing against this option. Moreover for thousands it became the only way possible to get kids into their families.
Seeking support from medical professionals is the only way to get the cause nailed and find a possible solution to you getting your baby. Many IP may be skeptical of using surrogacy. They may fear that the woman carrying their child may change her mind and decide she no longer wants to give the baby up. And that she’ll leave and raise the child as her own. Fortunately under Ukrainian law it’s impossible. The surrogate automatically gives up all the rights and obligations to the baby. IP are considered to be the only legal parents of the baby. This is very important to know law protects the IP.