Implanon is a subdermal implant that is placed in the arm and offers a fairly high contraceptive protection. This hormonal contraceptive contains etonogestrel, as well as barium sulfate and other components.
The contraceptive effect of Implanon lasts for 3 years. In addition, Implanon can be removed at any time, thus restoring the woman's fertility.
Provided below is an index with the 7 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 1.1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
What is implanon?
Implanon NXT is a contraceptive implant whose active ingredient is etonogestrel, a synthetic progestin. The effect of this type of subdermal implant lasts 3 years, that is, it offers contraceptive protection for 3 years from its placement and after this time it must be removed.
This contraceptive implant consists of a plastic rod that is about 4 cm long and about 2 mm thick. In addition, this contraceptive contains barium sulfate, so it would be visible by X-ray. Other components of Implanon are ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer and magnesium stearate.
Mechanism of action of Implanon
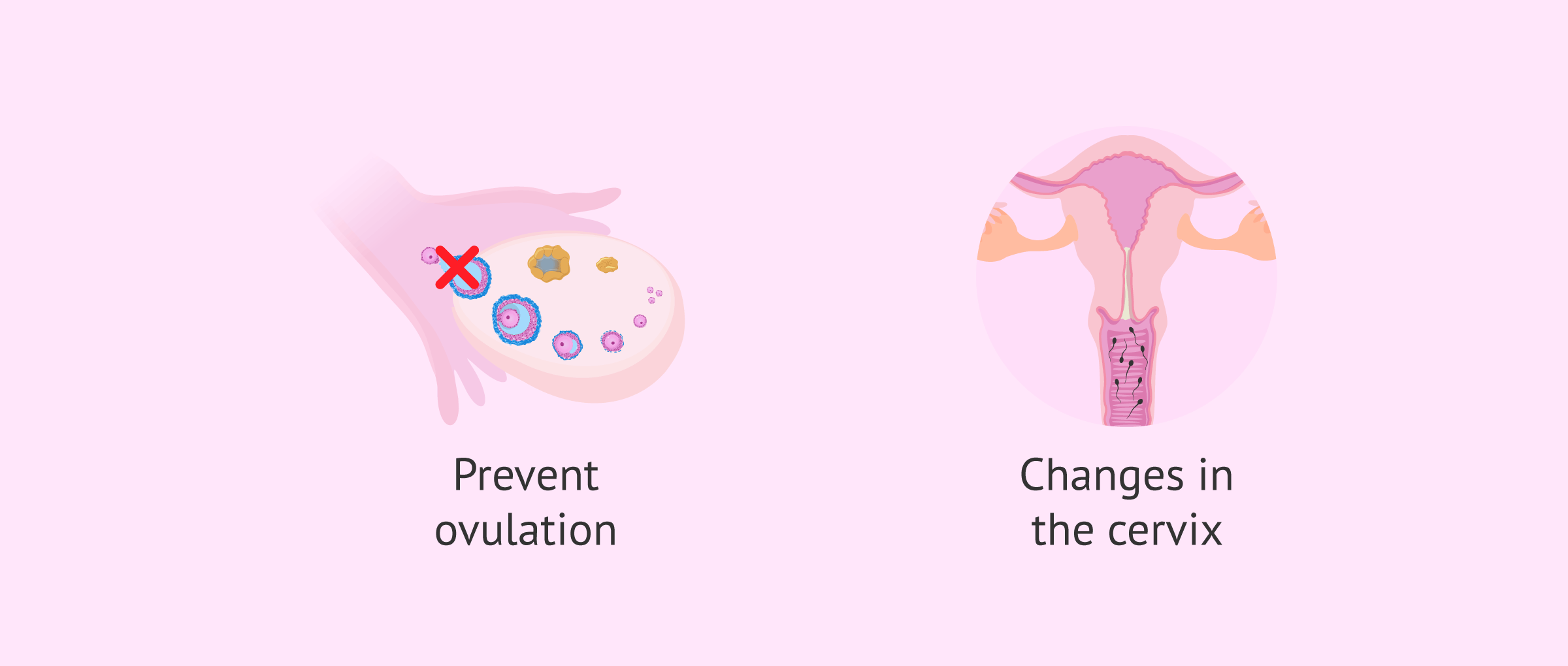
Implanon consists of 68 mg of etonogestrel. This hormonal contraceptive works by releasing a small amount of the active ingredient into the blood continuously. Thus, the purpose of Implanon is:
- Prevent ovulation, i.e., the release of the egg.
- Produce changes in the cervix, making it more difficult for sperm to enter the uterus.
In order for the Implanon to perform its function, it must be incorporated subcutaneously in the arm. This is done between the first and fifth day of menstruation. Otherwise, it is essential to use another method of contraception for 7 days after implant insertion to avoid a possible pregnancy.
Benefits and drawbacks of Implanon
The Implanon contraceptive implant, unlike birth control pills, can be inserted in women with medical contraindications for estrogens. In addition, this hormonal contraceptive is 99% effective, so the possibility of pregnancy using Implanon is practically nil.
Another advantage of using Implanon is that it reduces menstrual cramps and can be stopped at any time the woman wishes. In this case, it is best to inform the physician of the decision.
Despite these benefits of Implanon, there are also some risks in the use of Implanon. It is possible for the implant to move out of place for different reasons such as the practice of contact sports or a bad placement from the beginning. In addition, the contraceptive implant can bend or break.
Side effects of Implanon
Implanon, like other drugs, can cause adverse reactions after placement in the arm. However, this does not mean that all women using this contraceptive implant will show side effects.
Among the most frequent adverse effects are the following:
- Acne
- Headache.
- Weight gain.
- Breast Pain
- Vaginal bleeding.
- Hair loss.
- Dizziness.
- Nervousness.
- Decreased libido.
Other possible adverse effects of Implanon, although less common, are itching, rash, migraines, drowsiness, constipation, back pain, fever, fluid retention, increased blood pressure, seborrhea, etc.
The information published in this article has been extracted from the CIMA (Centro de Información online de Medicamentos Autorizados) Prospectus: information for the user.
FAQs from users
When is the use of Implanon contraindicated?
Like any other hormonal contraceptive, the Implanon implant is not always indicated. Some situations in which the use of this contraceptive implant is not recommended are the following:
- Hypersensitivity to the active ingredient.
- Thrombosis.
- Sex hormone-sensitive neoplasms.
- Hepatic alterations and/or tumors, as well as jaundice.
- Vaginal bleeding without apparent cause.

To what extent do the different types of subdermal contraceptive implants distinguish?
Birth control implants differ in the type of progestin, i.e., synthetic or released progestogen. Thus, it is possible to differentiate between Norplant or Jadelle that release the levonorgestrel progestin or Implanon that releases etonorgestrel.
Suggested for you
In addition to Implanon, there are other contraceptive implants. Therefore, if you are interested in more generic information, we recommend reading this article: The subdermal contraceptive implant: advantages and disadvantages.
If, on the other hand, you would like to change your contraceptive method because you suffer from various adverse effects, then you can continue reading here: Contraceptive methods: types, effectiveness, risks and prices.
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Ken Menon. Implanon® removal technique. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2012 Oct;38(4):271-2.
Kim C Dobromilsky, Penny L Allen, Stephen H Raymond, Bhavna Maindiratta. A prospective cohort study of early postpartum etonogestrel implant (Implanon®) use and its effect on duration of lochia. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2016 Jul;42(3):187-93. doi: 10.1136/jfprhc-2014-101081 (View)
Krishni Thurairajah. Implanon insertion. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2006 Oct;32(4):268 (Ver)
Meike Flore, Xiaoshuang Lilly Chen, Andrew Bonney, Judy Mullan, Bridget Dijkmans-Hadley, Adam Hodgkins, Gina Evans, Haley Frew, Gail Lloyd. Patients' perspectives about why they have their contraceptive Implanon NXT device removed early. Aust Fam Physician. 2016 Oct;45(10):740-744 (View)
Merki-Feld GS, Imthurn B, Rosselli M, Spanaus K. Implanon use lowers plasma concentrations of high-molecular-weight adiponectin. Fertil Steril. 2011;95(1):23-7.
Pushpa Bhatia, Sangita Nangia, Shivani Aggarwal, Chitra Tewari. Implanon: subdermal single rod contraceptive implant. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2011 Aug;61(4):422-5. doi: 10.1007/s13224-011-0066-z. Epub 2011 Sep 28 (View)
Suzanne Pearson, Mary Stewart, Deborah Bateson. Implanon NXT: Expert tips for best-practice insertion and removal. Aust Fam Physician. 2017 Mar;46(3):104-108 (View)
FAQs from users: 'When is the use of Implanon contraindicated?' and 'To what extent do the different types of subdermal contraceptive implants distinguish?'.