Vitamin A, also known as Retinol or Antixerophthalmiccontributes to the maintenance and development of tissues. In addition, this vitamin plays essential roles in vision, reproduction, embryonic development, bone growth, and in the immune and nervous systems.
Therefore, adequate vitamin A intake is essential throughout gestation. However, being a fat-soluble vitamin, it is stored in the body and vitamin A supplementation may not be necessary.
It should be noted that misuse or abuse of certain nutrients negatively affects the baby's development. For this reason, before taking any vitamin during pregnancy, it is advisable to consult your doctor.
Provided below is an index with the 6 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 2.1.
- 3.
- 3.1.
- 3.2.
- 3.3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
What are the functions of vitamin A?
Retinol is a fat-soluble vitamin that dissolves in fats, but is not released in the urine. This vitamin has two forms of presentation.
- Provitamin A, the most frequent being beta-carotene in plant foods.
- Vitamin A found in foods of animal origin.
Vitamin A deficiency is related to blindness, as it is involved in cell differentiation and maintenance of ocular integrity. However, this is not the only function attributed to vitamin A. Other functions of this vitamin are the following:
- Development and keritination of epithelial tissue.
- Intervention in the reproduction process.
- Participation in the immunity process.
- Protection against oncological processes.
In addition to these functions, vitamin A is also recommended during pregnancy and lactation.
Vitamin A during pregnancy
A pregnant woman needs a daily intake of approximately 800 micrograms of vitamin A, which is equivalent to eating a medium carrot.
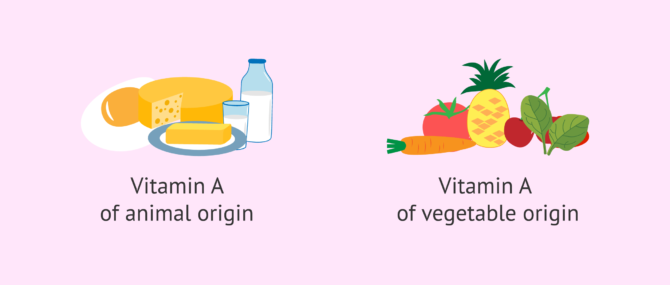
In this sense, it is possible to opt for foods of animal or vegetable origin:
- Vitamin A of animal origin
- is found in foods such as milk, cream, butter, egg yolk, liver and pate, among others.
- Vitamin A of vegetable origin
- for example, is the case of carrots, pumpkin, tomatoes, red peppers, tangerines or apricots.
Therefore, to cover the requirements of the pregnant woman and the future baby, it is sufficient to eat foods rich in Vitamin A, without the need for extra intake of this vitamin.
Altered vitamin A levels
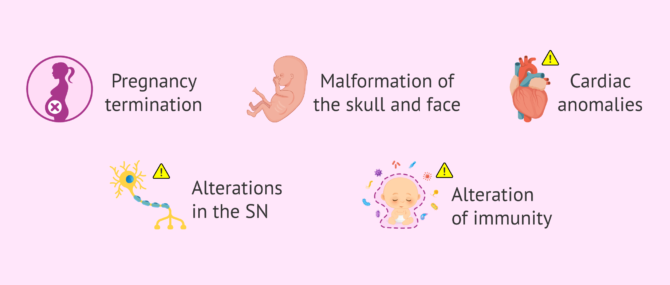
The amount of vitamin A a pregnant woman has should be controlled since excessive levels of this vitamin can cause the interruption of pregnancy. In addition, high amounts of vitamin A in pregnant women can also cause congenital anomalies in the fetus such as:
- Skin darkening
- Facial and skull malformations.
- Cardiac abnormalities.
- Alterations in the nervous system (NS).
- Alteration of immunity.
Normally, excess vitamin A is due more to the abuse or misuse of vitamin supplements than to the consumption of foods rich in this vitamin.
It should be noted that a lack of this vitamin is also bad for pregnancy. Pregnant women who suffer from vitamin A deficiency during the first trimester of pregnancy are at increased risk of developing infections that affect the fetus.
Vitamin A is teratogenic both when it is in large or small amounts, as it can cause fetal malformations and even death of the fetus.
For all these reasons, it is advisable to follow all medical indications at all times, to lead a healthy lifestyle and a balanced diet throughout gestation.
FAQs from users
Is it necessary to take vitamins before pregnancy if I am seeking pregnancy through assisted reproduction?
Vitamin D supplementation before pregnancy is not a routine practice in the field of assisted reproduction. However, such supplementation would be indicated in those women who are seeking pregnancy and who are known to be vitamin D deficient, since vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy has been associated with an increased risk of miscarriage and complications during pregnancy.
Women at higher risk of vitamin D deficiency are those with dark skin, vegan diet, little exposure to sunlight, or a history of a baby with rickets or a body mass index (BMI) > 30.
Read more
Is vitamin A beneficial for fertility?
Vitamin A, like other vitamins, has benefits for male and female fertility. One of the effects is that vitamin A helps in the formation of steroids. This is an organic compound that forms the basis of sex hormones.
In the case of the male, vitamin A also helps to prevent oxidative stress of the sperm. This vitamin has an antioxidant effect, thus protecting the sperm and improving semen quality.
What is the recommended daily dose of vitamin A?
The recommended amount of vitamin A per day depends on age and whether the person is a woman or a man.
For example, adolescent boys should consume about 900 micrograms of vitamin A per day; while for girls it should be 700 micrograms.
Similarly, the recommended amount of vitamin A in adult men is 900 micrograms and in adult women 700 micrograms, although if they are pregnant, they should take about 770-800 micrograms of this vitamin.
Suggested for you
In addition to vitamin A, there are other vitamins that provide benefits both for a woman's fertility and pregnancy. If you want to know more about this topic, we recommend you to visit the following article: What vitamins should be taken during pregnancy?
Apart from vitamins, it is also important to control the diet. Therefore, we invite you to read the following article if you are looking for a pregnancy: What are the types of foods that promote female fertility?
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Christine L Parr, Maria C Magnus, Øystein Karlstad, Kristin Holvik, Nicolai A Lund-Blix, Margareta Haugen 6, Christian M Page, Per Nafstad, Per M Ueland, Stephanie J London, Siri E Håberg, Wenche Nystad. Vitamin A and D intake in pregnancy, infant supplementation, and asthma development: the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. 2018 May 1;107(5):789-798. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy016 (View)
Han Chen, Nianfeng Qian, Liyu Yan, Hongqing Jiang. Role of serum vitamin A and E in pregnancy. Exp Ther Med. 2018 Dec;16(6):5185-5189. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6830. Epub 2018 Oct 5 (View)
K W Kizer, A M Fan, J Bankowska, R J Jackson, D O Lyman. Vitamin A--a pregnancy hazard alert. West J Med. 1990 Jan;152(1):78-81 (View)
Sabina Bastos Maia, Alex Sandro Rolland Souza, Maria de Fátima Costa Caminha, Suzana Lins da Silva, Rachel de Sá Barreto Luna Callou Cruz, Camila Carvalho Dos Santos, Malaquias Batista Filho. Vitamin A and Pregnancy: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2019 Mar 22;11(3):681. doi: 10.3390/nu11030681 (View)
FAQs from users: 'Is it necessary to take vitamins before pregnancy if I am seeking pregnancy through assisted reproduction?', 'Is vitamin A beneficial for fertility?' and 'What is the recommended daily dose of vitamin A?'.