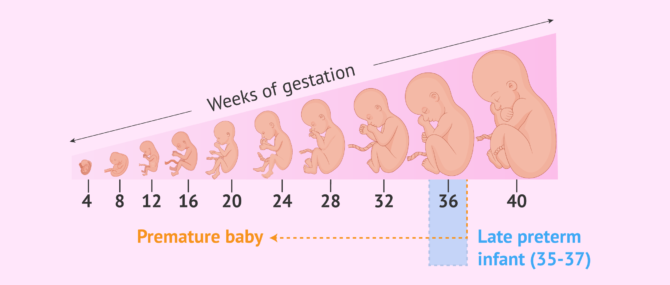
Uneventful pregnancies last 40 weeks since the first day after the last menstruation. Therefore, newborns are classified in different groups according to their week of birth:
- Preterm delivery: to be discussed later on.
- Full term delivery: a birth that takes place between the weeks 37-42.
- Post-term delivery: a birth taking place beyond the 42nd week.
However, when preterm labor occurs, special care of the baby is important. These babies may have immature lungs, which can cause breathing problems. In addition, premature babies have a lower body temperature and a weak cry, among other characteristics.
Provided below is an index with the 8 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 1.1.
- 2.
- 2.1.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 5.1.
- 5.2.
- 5.3.
- 5.4.
- 5.5.
- 5.6.
- 5.7.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
What is a preterm birth?
A premature newborn, also known as preemie baby, is a baby who is born before the 37th week of gestation as a result of a delivery that takes place sooner than expected.
This is the case of 8-12% of pregnancies. Once the main causes of infant mortality are considered, nowadays the chances of survival are higher than ever: a fairly solid 80% of preterm newborns survive.
Those that are born between the 35th-37th week would not arguably be labeled as late prematures. It is unlikely that staying in ICU is necessary. Nonetheless, they must be observed in a way full-term newborns do not need.
What characterizes a premature baby?
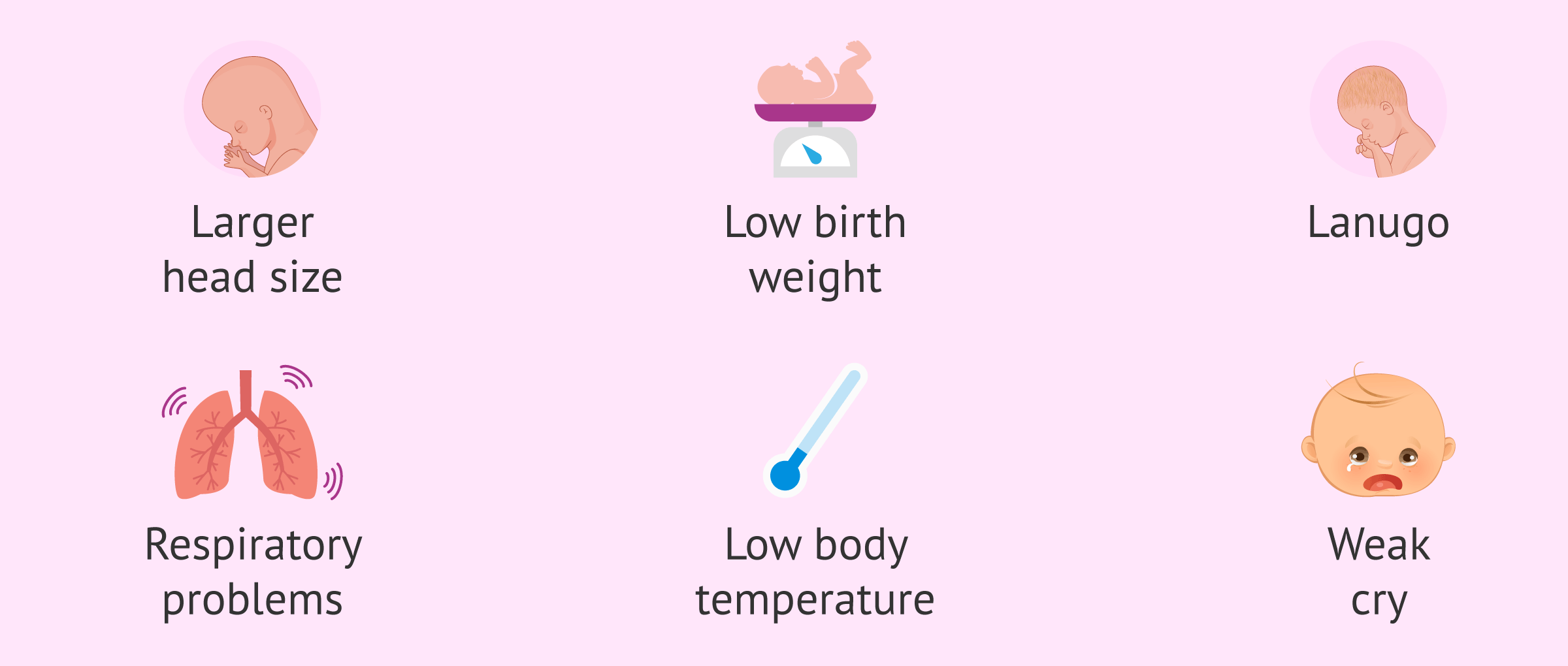
Primarily, a premature infant differs from a full-term infant by the following characteristics:
- Big head, low weight (<2.5 kg) and poor muscle mass.
- Smooth, thin, bright skin being almost traslucid, some veins and arteries are easy to distinguish.
- Smooth and flexible ear cartilage.
- Reddened feet and hand palms, poor crease-formation.
- Presence of lanugo hair.
- Low body temperature.
- Breathing problems due to underdeveloped lungs and risk of pulmonary bleeding.
- Weak weeping.
- Newborn's jaundice and risk of hypuglucaemia.
- Weak suction and swallowing.
- Underdeveloped genitalia: enlarged clitoris in girls and small scrotum in boys.
In addition, the joints of premature babies are much looser than those of full-term babies. The movement of premature babies is less and may sometimes be in the form of jerking.
If delivery occurs before 32 weeks gestation, the baby may have transient hypertonia. This is an increase in muscle tone from head to toe.
Problems of a premature baby
A fetus grows the most during the last 8 weeks of gestation. In the first 32 weeks, the baby grows up to a third of the total weight, and during the last 8 weeks, the unborn reaches the 2/3 left. The fetal organs have a similar pattern, being these last 8 weeks essential to achieve a full growth.
Premature newborns can suffer problems in the long term, but it is not possible to make prudent prediction of the clinical evolution of the baby relying only on the gestational age or weight at birth.
Thus, the smaller or underdeveloped the newborn is, the greater the risks are. The respiratory, nervous, digestive, renal, immunologic and visual sistems might be compromised, being the respiratory one of the most affected.
Other complications in the premature infant
Complications in babies born before their due date will depend on the exact time of delivery. The earlier the preterm birth occurs, the worse the fetal consequences will be since the baby will be less mature.
The following are some of the complications that can arise in premature babies:
- Respiratory distress syndrome
- also known as respiratory distress syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by closed alveoli due to the lack of surfactant, that is, the substance that coats the alveoli and whose function is to reduce surface tension so that they do not collapse.
- Apnea
- is shortness of breath for 20 seconds or more. Apnea may also be associated with bradycardia.
- Intraventricular hemorrhage
- usually occurs in infants who do not reach a weight of more than 1.5 kg. The prognosis will depend on the degree of extension of the hemorrhage.
- Arterial hypotension
- es decir, el recién nacido tendrá baja la tensión arterial.
In addition to all these complications, premature babies are more prone to infections. Their defense mechanisms are not fully developed, so there is a higher risk of pneumonia and urinary tract infections.
Premature baby care
To establish a set of measures, the newborn has to be assessed immediately. Usually, this kind of babies need to be tube-fed until breastfeed due to their suction and deglutition problems before 34th week. Also, the newborn may require assistance to overcome any respiratory deficiency, although it depends on the stage of prematurity of the newborn.
Therefore, an early baby cannot be taken care of at home, because the newborn needs specialized caring. He/she will have to stay in an incubator, which plays the role of a transitory uterus. It will keep the baby warm an under specific humidity conditions (30 °C, 80-90%).
The premature baby will be released in the moment assisted respiration and the warmth of the incubator are no longer required, being also necessary to have a proper weight and to suckle well.
Preterm birth prevention
In order for a preterm birth to be prevented, and for the baby to be born in due date, prospective mothers are recommended:
- To be in good health condition prior to getting pregnant.
- To receive prenatal cares as soon as possible, keeping them until the baby is born.
Sometimes, preterm birth can be treated with a drug that blocks uterine contractions. Such drug is the betamethasone, but most of the times these attempts to delay it turn out to be ineffective.
FAQs from users
Is a preterm birth more likely with twins?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a preterm birth occurs when the child is born before the week 37 of pregnancy. Some of the most common causes of preterm birth are:
- Overdistention of the uterus: loss of tone in the uterine musculature that prevents this organ to recover its normal size.
- Infection or uterine inflammation: certain bacteria can damage fetal membranes by causing its rupture and triggering a preterm birth. An infection that affects the uterus directly may lead to preterm birth as well.
- Decidual bleeding: a type of vaginal bleeding that may occur while a woman is pregnant.
There exist many risk factors that can lead to premature birth, including obesity, high blood pressure, etc. A multiple pregnancy is one of these factors.
Is there an increased risk of preterm delivery in IVF?
There are several scientific studies that have shown a slightly increased risk of preterm delivery in children conceived by in vitro fertilization (IVF) compared to children conceived naturally.
It is also known that many of the causes of infertility in women who require IVF are the same causes that have a higher risk of preterm delivery. This is the example of diabetes, thyroid problems, alterations in the coagulation system, immune disorders, adenomyosis, fibroids, advanced age, etc.
What should a premature baby be fed?
According to experts, breast milk is the best food for newborns, especially premature infants. However, in the case of premature babies, since they cannot suckle properly, it is necessary to introduce food through nasogastric or stomach tubes. Sometimes, due to the sequelae of prematurity at birth, it is necessary to supplement their diet with iron.
What are the best stimulation exercises for premature babies?
First of all, it is important to know the baby's corrected age, i.e. the number of months he/she would have been if he/she had been born on the due date and not before. In this way, it is possible to know the moment of development in which the baby is in order to start with the early stimulation.
Before carrying out the exercises discussed in this article, it is necessary to practice the following activities with premature babies:
- Infant massage: this consists of holding each of the parts of the baby's body with your hands without moving them, just so that the baby feels the contact and trying to transmit relaxation and tranquility.
- Therapeutic touch: this involves massaging and caressing the baby but without touching him, keeping a distance of about 5-10 cm.
- Place the baby naked on the mother's or father's chest, between the clothes and the bare skin, maintaining the maternal-filial bond. This promotes the production of breast milk and helps regulate the baby's temperature and heart and respiratory rate.
Can a premature baby be delivered naturally?
Yes, it is possible for an early delivery to occur through the vaginal canal. That is, it is not always necessary to have a cesarean section in the case of preterm labor.
What is corrected age in premature infants?
The corrected age is the time the baby would have had if delivery had occurred at 40 weeks gestation. This age is recommended when you want to evaluate the physical and psychomotor development of the baby.
It is calculated by subtracting the weeks of prematurity from the baby's weeks since birth. For example, if the birth occurs in the 32nd week of pregnancy, the baby would be 8 weeks, that is, 2 months premature. If the baby is now 4 months old (16 weeks), the corrected age would be 4 minus 2 months.
Can a 23-week premature baby survive?
It is possible. However, the earlier in the pregnancy the baby is born, the more immature it will be. Therefore, the more premature the baby is, the less likely it is to survive.
The percentage of babies who have been able to survive despite being born at 22-23 weeks of gestation is quite low, but not zero.
Suggested readings
If you would like to learn more about the possible signs of preterm labor, you can visit this article: What Is Preterm Birth? - Signs, Causes & Treatment.
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Alexander Humberg, Ingmar Fortmann, Bastian Siller, Matthias Volkmar Kopp, Egbert Herting, Wolfgang Göpel, Christoph Härtel; German Neonatal Network, German Center for Lung Research and Priming Immunity at the beginning of life (PRIMAL) Consortium. Preterm birth and sustained inflammation: consequences for the neonate. Semin Immunopathol. 2020 Aug;42(4):451-468. doi: 10.1007/s00281-020-00803-2 (View)
Heather A Frey, Mark A Klebanoff. The epidemiology, etiology, and costs of preterm birth. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016 Apr;21(2):68-73. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2015.12.011 (View)
Joshua P Vogel, Saifon Chawanpaiboon, Ann-Beth Moller, Kanokwaroon Watananirun, Mercedes Bonet, Pisake Lumbiganon. The global epidemiology of preterm birth. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2018 Oct;52:3-12 (View)
Kelsie Moroney. Family reflections: premature baby. Pediatr Res. 2021 Feb;89(3):705-706. doi: 10.1038/s41390-020-01296-3. Epub 2020 Dec 8 (View)
FAQs from users: 'Is a preterm birth more likely with twins?', 'Is there an increased risk of preterm delivery in IVF?', 'What should a premature baby be fed?', 'What are the best stimulation exercises for premature babies?', 'Can a premature baby be delivered naturally?', 'What is corrected age in premature infants?' and 'Can a 23-week premature baby survive?'.
Authors and contributors









Hello, I’ve a history of preterm births and I’m 20 weeks pregnant now, worried that it happens to me too, although my pregnancy is going well!! My question is out of curiosity what is the survival rate of preterm babies at different pregnancy weeks? Guessing the earlier, the less chances.
Hello virginia,
Babies born earlier than 28 weeks have the most complications, mainly because most of them are born at extremely low birth weight, which requires treatment with oxygen, mechanical assistance to help them breather…
Around 25% of these very preemie babies develop some serious lasting disabilities (e.g. behavioral problems, learning difficulties, etc.).
I hope this helps,
All the best
My baby delivered at 35 weeks by C-section. Her birth weight was 2 kg 240 gms. She was put on with antibiotics due to high total count. And also in photo therapy due to high total bilirubin. Now her weight is 2kg 100 gms. What should we do for our baby to gain weight? Please give me suggestions.
Dear Vinilashree,
As a premature baby gets stronger, they can start getting milk or formula, and the amount should be increased very slowly. This reduces the risk of an intestinal infection known as NEC (necrotizing enterocolitis).
Also, premature babies find it harder to maintain the proper water balance in their bodies, and therefore become dehydrated or over-hydrated. In this sense, human milk from the baby’s mother is the best for babies born early or with very low birth weight.
Supplements such as human milk fortifier are ideal for premature babies as they may need extra nutrients. This supplement gives them calories, iron, calcium, protein, vitamins, etc.
I hope this helps,
Best wishes