Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is an assisted reproductive technique most commonly used to fertilize eggs in the laboratory during in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment.
Previously, it was usual to fertilize eggs by the conventional method: eggs and sperm were incubated together for a few hours until they united. In contrast, ICSI is increasingly used, without the need for a clear benefit in patients for it.
Despite this, ICSI is sometimes indicated, as it offers better pregnancy rates than conventional IVF. In particular, ICSI is recommended when there are severe infertility problems or problems with sperm motility.
Provided below is an index with the 7 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 1.1.
- 1.2.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 4.3.
- 4.4.
- 4.5.
- 4.6.
- 4.7.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
Male fertility
Poor sperm quality is one of the main reasons for resorting to ICSI during assisted reproduction treatment.
The advantage of ICSI over a malefactor, whether mild, moderate, or severe, is to be able to choose the best sperm to fertilize the egg. In addition, it is not necessary for the sperm to travel through the tubes, since the embryologist himself introduces the best sperm selected into the egg.
Male infertility
The indications for ICSI in male infertility are as follows: oligozoospermia, asthenozoospermia, teratozoospermia, cryptozoospermia, azoospermia and the combination of disorders such as oligoasthenozoospermia, for example.
In milder cases, it will be necessary to evaluate whether to perform conventional IVF or ICSI, but when the sperm factor is severe, the egg can only be fertilized with the microinjection of a spermatozoon into the egg.
It should be noted that in the case of a total absence of sperm (azoospermia), the sperm for ICSI will have to be obtained previously with a testicular biopsy or aspiration of the epididymis. This solution for obtaining spermatozoa will only be possible if the type of azoospermia is obstructive.
When azoospermia is secretory, there will be no sperm formation and, therefore, the only reproductive option for the male will be sperm donation.
Other indications
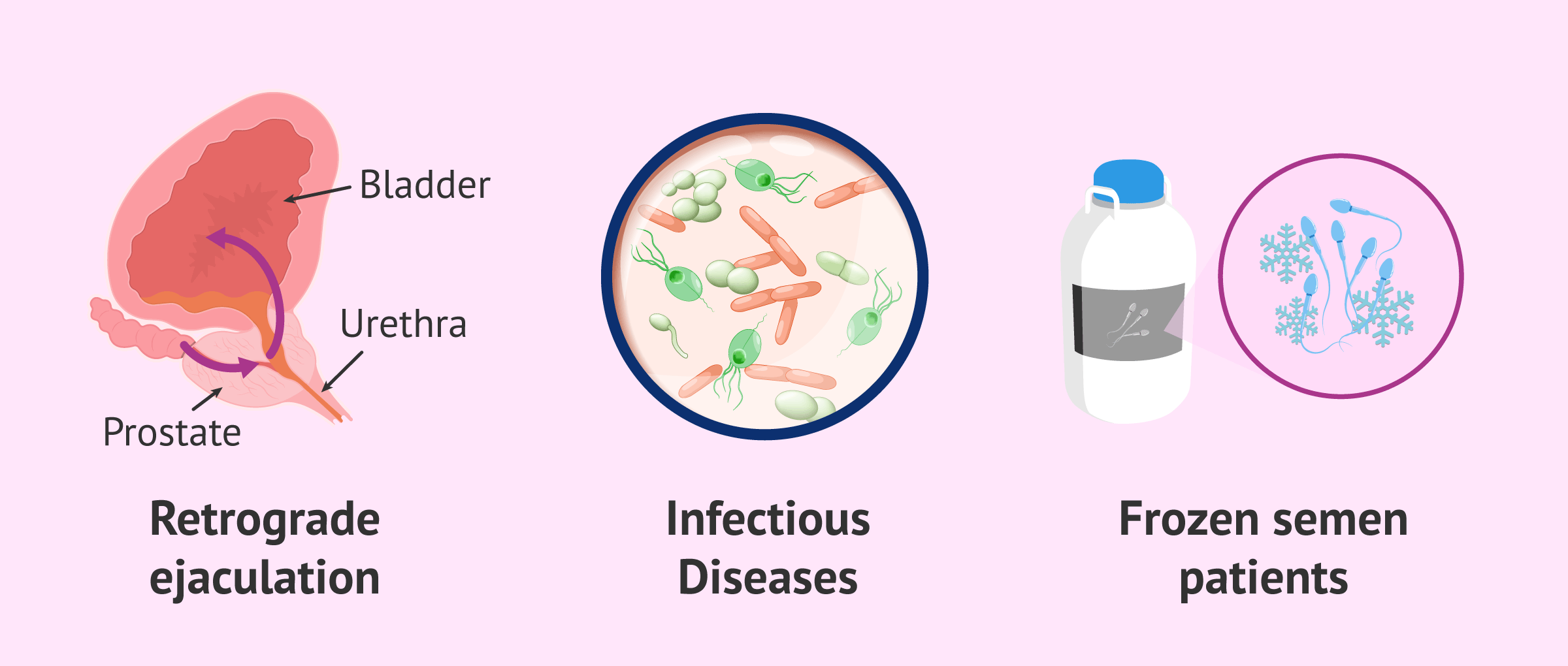
Other male-related indications for ICSI include the following:
- Anejaculation or retrograde ejaculation, in which sperm can be obtained from urine.
- Males with infectious diseases, such as HIV or hepatitis.
- Valuable semen samples: frozen semen in patients undergoing radiotherapy/chemotherapy or men who have had a vasectomy.
If you are interested in reading more about this, you can enter the following post: What causes male infertility?
IVF-ICSI for female infertility
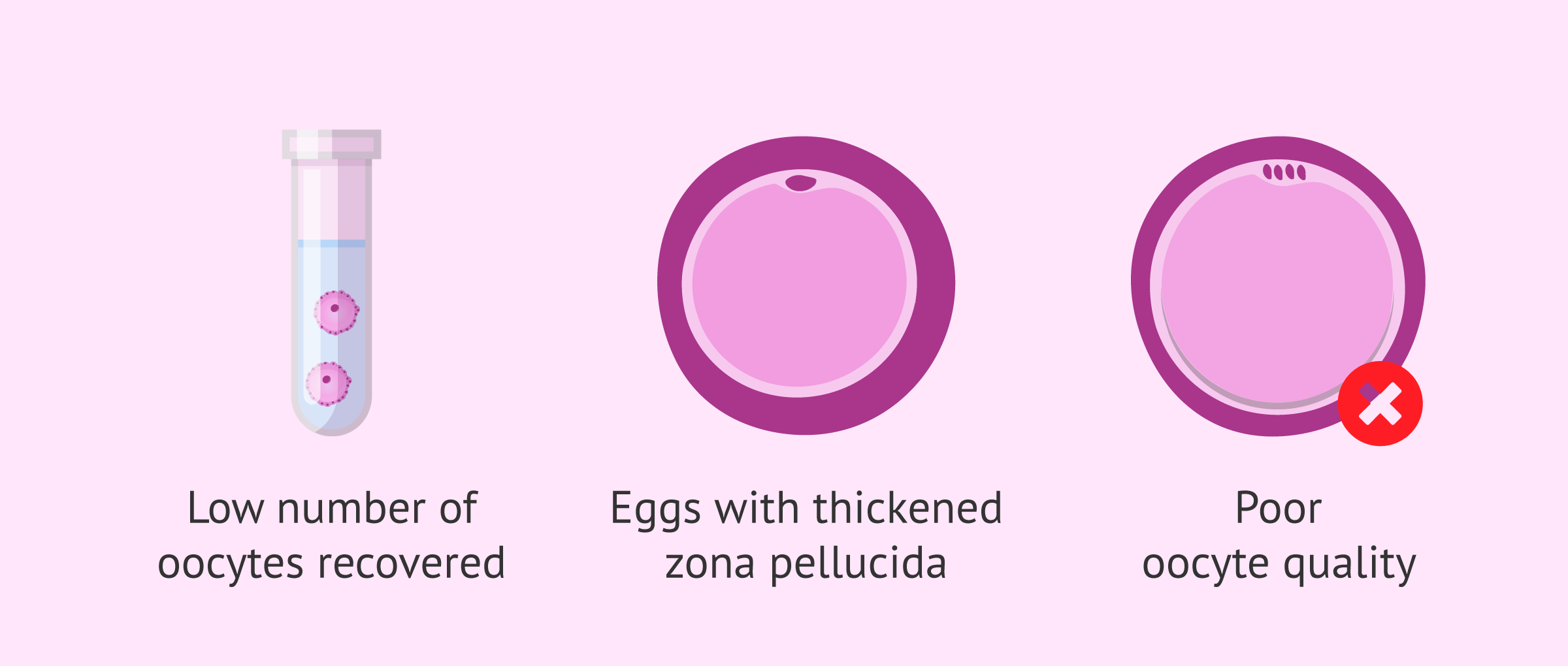
It is more rare to find a specific female indication that requires ICSI. However, we can name the following cases:
- Obtaining a low number of oocytes in follicular puncture.
- Oocytes with thickened zona pellucida.
- Poor oocyte quality.
The reason for resorting to ICSI when few or poor-quality eggs are obtained is to ensure that fertilization can take place.
In situations where the zona pellucida of the eggs is thickened, it will be difficult for the sperm to get through on their own in conventional IVF. Therefore, it is necessary to microinject them. Embryos resulting from this fertilization are also likely to require assisted hatching.
Assisted procreation, as any other medical treatment, requires that you rely on the professionalism of the doctors and staff of the clinic you choose. Obviously, each clinic is different. Get now your Fertility Report, which will select several clinics for you out of the pool of clinics that meet our strict quality criteria. Moreover, it will offer you a comparison between the fees and conditions each clinic offers in order for you to make a well informed choice.
In what other situations is IVF-ICSI indicated?
There are other situations in which it is necessary to resort to ICSI, either because of other causes of infertility or because the conditions of the treatment require it. Below, we will discuss some examples:
- Fertilization failures.
- Previous IVF failures.
- Previous failures of artificial insemination (AI).
- Immunological sterility due to antisperm antibodies.
- Rescue microinjection for non-fertilization after conventional IVF.
- In vitro maturation of oocytes.
- When preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is to be performed.
- When donor eggs or sperm are used.
- In the devitrification of eggs.
In the case of PGT (formerly known as PGD), the eggs are always fertilized by ICSI to avoid the permanence of sperm attached to the surface of the egg, which could later cause an error in the genetic diagnosis.
On the other hand, when the eggs come from devitrification, it is also necessary to microinject them by ICSI. Devitrified embryos are decumulated, i.e., without granulosa cells around them. This makes ICSI vitally important in these cases.
Before doing an ICSI or vitrifying eggs, it is necessary to do a decumulation to remove the surrounding cumulus cells.
For all these reasons, the ICSI technique is the one that has made it possible to preserve the fertility of women. If the eggs could not be fertilized by ICSI, they could not be vitrified beforehand either.
FAQs from users
What are the requirements for IVF-ICSI?
Among the necessary requirements to undergo IVF-ICSI treatment are the following:
- Sufficient ovarian reserve.
- Uterus that allows gestation.
- Do not present a history of diseases that contraindicate pregnancy or IVF.
- Analytical and clinical history that prove that the patient is healthy, hemogram and blood coagulation corresponding to less than 6 months.
- Serologies of HBV, HCV, HIV and syphilis of the last three months.
- Cervical cytology.
- Semen with a count greater than 5 million motile spermatozoa per mL of ejaculate.

Karyotyping is not a mandatory test, although infertile couples present a higher percentage of karyotype alterations than spontaneously gestated couples. The increase in these alterations is very low and does not justify performing this test in all couples.
What is the main indication for IVF with ICSI?
There are two types of in vitro fertilization techniques; IVF itself and intracytoplasmic sperm microinjection. The main indication for IVF is a motile sperm count above 3 million. Therefore, any semen sample below this count will be indicative of ICSI (severe male failure).
Other possible indications for ICSI would be a previous IVF fertilization failure, semen samples with teratozoospermia or patients requiring preimplantation genetic diagnosis treatment.
Is ICSI as effective as conventional IVF?
ICSI usually offers a higher pregnancy rate than conventional IVF. However, this depends very much on the cause of infertility and the embryologist's ability to microinject the sperm into the egg. It should be noted that the laboratory staff needs to have a lot of practice and experience to be able to do this technique correctly.
Can a man with teratozoospermia have ICSI?
Yes, in fact, it is one of the male indications, since ICSI allows the selection of the sperm with the best morphology for microinjection. In addition, for cases of severe teratozoospermia, there is an improved ICSI technique called IMSI, which allows the spermatozoa to be observed in more detail for better selection.
Could an immotile sperm fertilize the egg by ICSI?
Yes, ICSI is also used in severe cases of asthenozoospermia. If it is not possible to find any moving sperm, an immobile sperm is microinjected. Fertilization is possible as long as this sperm was alive and with its DNA intact.
What is the success of ICSI with PGD?
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis often affects embryo development, resulting in lower success rates. In this case, the probability of delivery per cycle with PGD is 14%.
Why is ICSI indicated after testicular biopsy?
One of the main reasons is that, after a testicular biopsy, the number of sperm may not be too high to perform another type of reproductive technique. With ICSI, only one sperm would be necessary for each egg to be fertilized.
Recommended readings
ICSI is one step in the long process of in vitro fertilization. If you want to know in detail how the whole treatment is, we recommend you to read the following post: How is the ICSI process step by step?
Sometimes it is difficult to determine whether it is better to perform conventional IVF or ICSI. In the next article, we talk about: IVF or ICSI?
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Cutting E, Horta F, Dang V, van Rumste MM, Mol BWJ. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection versus conventional in vitro fertilisation in couples with males presenting with normal total sperm count and motility. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Aug 15;8(8):CD001301. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001301.pub2. PMID: 37581383; PMCID: PMC10426261. (View)
Esteves SC. Who cares about oligozoospermia when we have ICSI. Reprod Biomed Online. 2022 May;44(5):769-775. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2021.11.026. Epub 2021 Dec 11. PMID: 35153142. (View)
Esteves SC, Roque M, Bedoschi G, Haahr T, Humaidan P. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection for male infertility and consequences for offspring. Nat Rev Urol. 2018 Sep;15(9):535-562. doi: 10.1038/s41585-018-0051-8. PMID: 29967387. (View)
Huang JX, Gao YQ, Chen XT, Han YQ, Song JY, Sun ZG. Impact of intracytoplasmic sperm injection in women with non-male factor infertility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Reprod Health. 2022 Oct 28;4:1029381. doi: 10.3389/frph.2022.1029381. PMID: 36388149; PMCID: PMC9650435. (View)
Quaas AM. ICSI for non-male factor: do we practice what we preach? J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021 Jan;38(1):125-127. doi: 10.1007/s10815-020-02016-w. Epub 2020 Nov 20. PMID: 33215354; PMCID: PMC7822992. (View)
Rubino P, Viganò P, Luddi A, Piomboni P. The ICSI procedure from past to future: a systematic review of the more controversial aspects. Hum Reprod Update. 2016 Mar-Apr;22(2):194-227. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmv050. Epub 2015 Nov 18. PMID: 26586241. (View)
Yang L, Liang F, Zhu R, Wang Q, Yao L, Zhang X. Efficacy of intracytoplasmic sperm injection in women with non-male factor infertility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2024 Jan;103(1):30-41. doi: 10.1111/aogs.14698. Epub 2023 Nov 6. PMID: 37930100; PMCID: PMC10755139. (View)
FAQs from users: 'What are the requirements for IVF-ICSI?', 'What is the main indication for IVF with ICSI?', 'Is ICSI as effective as conventional IVF?', 'Can a man with teratozoospermia have ICSI?', 'Could an immotile sperm fertilize the egg by ICSI?', 'What is the success of ICSI with PGD?' and 'Why is ICSI indicated after testicular biopsy?'.
Authors and contributors
More information about Cristina Algarra Goosman








Hello, a few months ago I was told that I had blocked tubes and that it was not possible to continue with the AI treatment we had planned to do. I have read that this technique is indicated, is it so?
Hello Maya,
Indeed, an AI needs to have permeable and functional fallopian tubes, so if they are blocked, pregnancy could not occur.
IVF-ICSI is the best alternative if there are no other pathologies. In this procedure, the oocytes will be obtained and extracted for fertilization in the laboratory. Once the embryo is in the blastocyst stage (5 days) it will be transferred to the uterus where it will be awaiting implantation, not needing in the process the functionality of the fallopian tubes.
I hope I have helped you.
Best regards.
If I do not have any problem but my husband has a problem with sperm motility, would it be necessary to perform this technique?
Hi Cece,
The IVF-ICSI technique is recommended in several situations with either female pathologies, male pathologies, or both.
In the case of a diagnosis of asthenozoospermia (low sperm motility), the ICSI technique would allow choosing the sperm with the correct morphology to be introduced directly into the egg. This would increase the chances of achieving pregnancy compared to the natural conception or another simpler technique.
I hope I have helped you.
Best regards.