Ectopic or extrauterine pregnancy occurs when the embryo implants outside the uterus and, therefore, the pregnancy cannot develop normally. The most frequent location where the embryo is found in this type of pregnancy is the fallopian tubes, in 95% of the cases.
Once an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed by the physician, there are several treatment options depending on the woman's situation and the status of the extrauterine pregnancy.
Provided below is an index with the 10 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 7.1.
- 7.2.
- 7.3.
- 7.4.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
Is treatment of an ectopic pregnancy necessary?
The uterine cavity is the only place where pregnancy can develop properly. Therefore, an ectopic pregnancy will not be able to go to term and, in fact, may even compromise the woman's health.
As the weeks of gestation pass, the fallopian tube containing the ectopic pregnancy may rupture. If this occurs, the hemorrhage produced could lead to life-threatening hemorrhagic shock.
Thus, it is imperative to make an early diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy and address the situation before it occurs. However, there are several treatment options and deciding on one or the other will depend on:
- Weeks of gestation.
- The symptoms presented by the woman and her gestational desire.
- The concentration of hCG hormone (hormone that determines pregnancy).
- The place where the embryo has implanted.
In any case, the woman should be informed of all the possibilities and the benefits and risks of each of them.
Expectant management
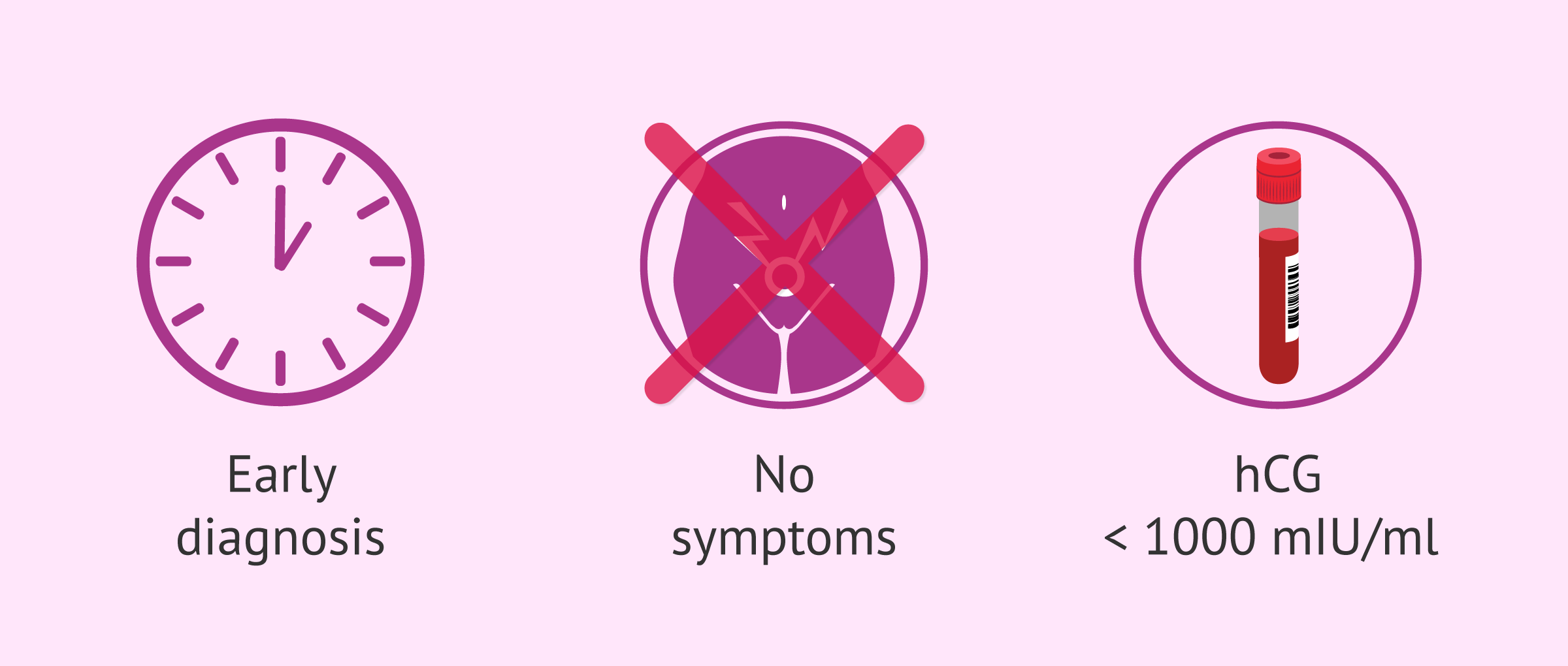
Expectant management of ectopic pregnancy consists of watching for a spontaneous outcome of the pregnancy, without any intervention.
This option is possible when the ectopic pregnancy has been diagnosed early and in an asymptomatic woman. In addition, hCG levels should be below 1000 mIU/ml and decrease.
When expectant management is chosen, the woman should undergo several hCG hormone determinations and serial ultrasounds. These tests allow the specialist to monitor how the ectopic pregnancy is progressing.
The hCG hormone should decrease in levels until it becomes undetectable if the ectopic pregnancy is resolving spontaneously.
In the event that the hCG does not drop as expected or if the patient begins to present symptoms or hemoperitoneum (presence of free blood in the peritoneal cavity), expectant management should be abandoned in order to perform some type of medical or surgical intervention.
Medical treatment with methotrexate
Methotrexate is a drug that is administered by intramuscular injection and stops the progression of gestation. This option is widely used for the medical treatment of ectopic pregnancy when the patient has no symptoms or only mild symptoms.
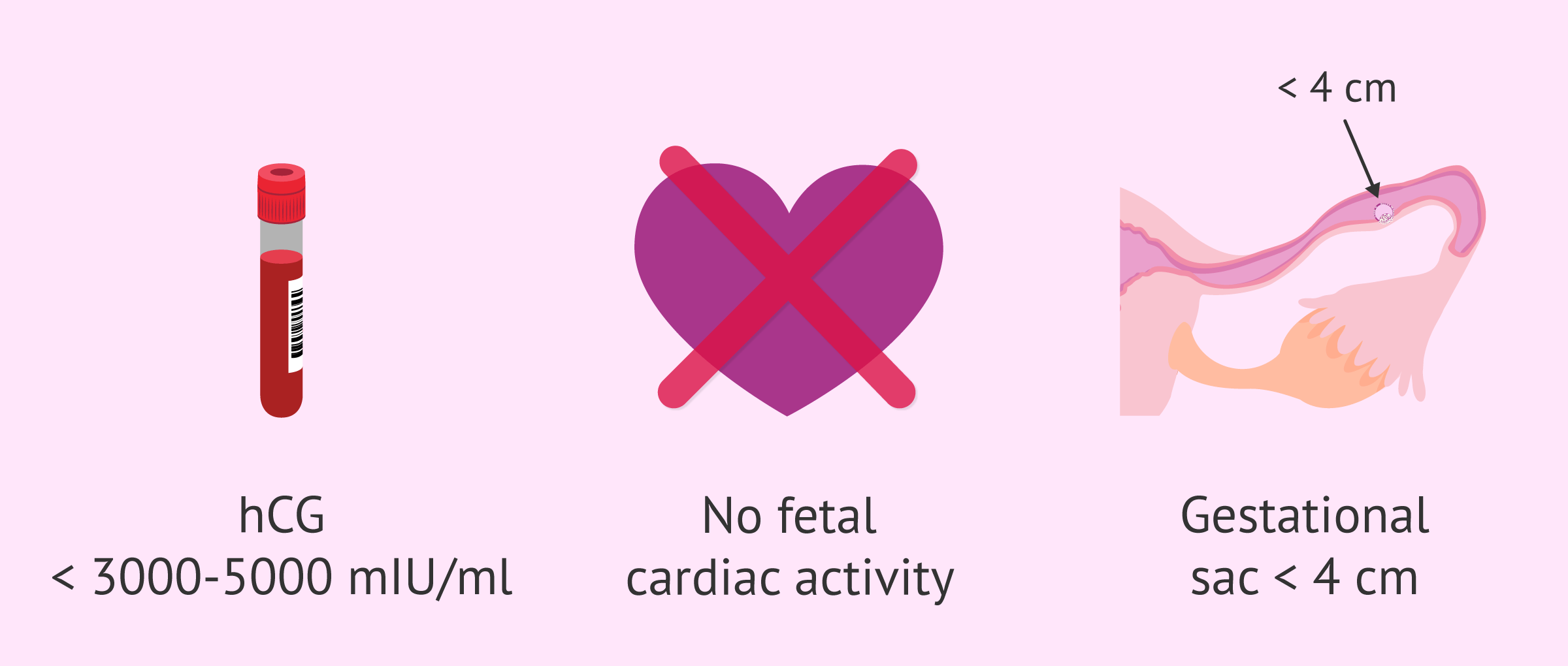
This drug is usually used when hCG values are below 3000-5000 mIU/ml, although it can be used with higher levels. However, this treatment is not usually used if there is cardiac activity in the ectopic pregnancy or if the diameter of the gestational sac is greater than 4 cm.
After the administration of methotrexate, the woman may experience certain adverse effects such as abdominal pain, gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, vomiting, etc. and it is essential to monitor all these symptoms and to check that the hCG hormone levels decrease until they become negative.
Once methotrexate treatment has been tried, there are occasions when it may be necessary to resort to surgery to treat the ectopic pregnancy. This occurs if, during follow-up, the woman's hCG levels do not decrease at the expected rate or increase.
In addition, the patient should go immediately to the emergency department if she presents with abdominal pain or if she feels dizzy after methotrexate administration. The reason is that these symptoms could be produced because the treatment has not worked and the tube has ruptured.
Surgical treatment
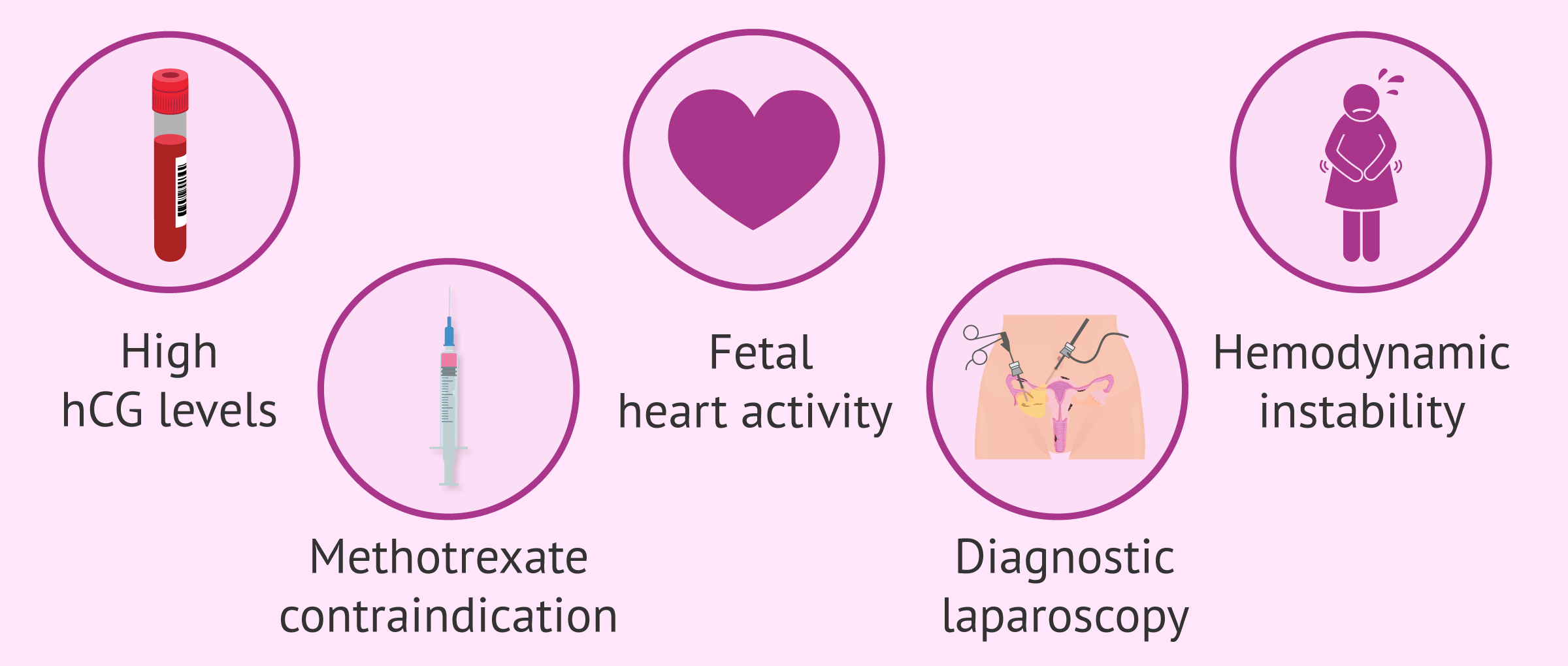
The third option to resolve ectopic pregnancy is surgery. This route is used when there is:
- High hCG levels.
- Fetal cardiac activity.
- Hemodynamic instability.
- Contraindication to medical treatment with methotrexate.
- Need for diagnostic laparoscopy.
The most common surgical approach to ectopic pregnancy is performed laparoscopically, since this type of intervention involves less discomfort and less hospitalization time for the woman than laparotomy.
However, especially when the woman is hemodynamically unstable and it is urgent to stop the bleeding, laparotomy can also be used for the treatment of ectopic pregnancy.
The main difference between the two techniques is that laparoscopy is performed through small holes in the abdomen through which a small camera and surgical instruments are introduced, while laparotomy is an open abdominal surgery.
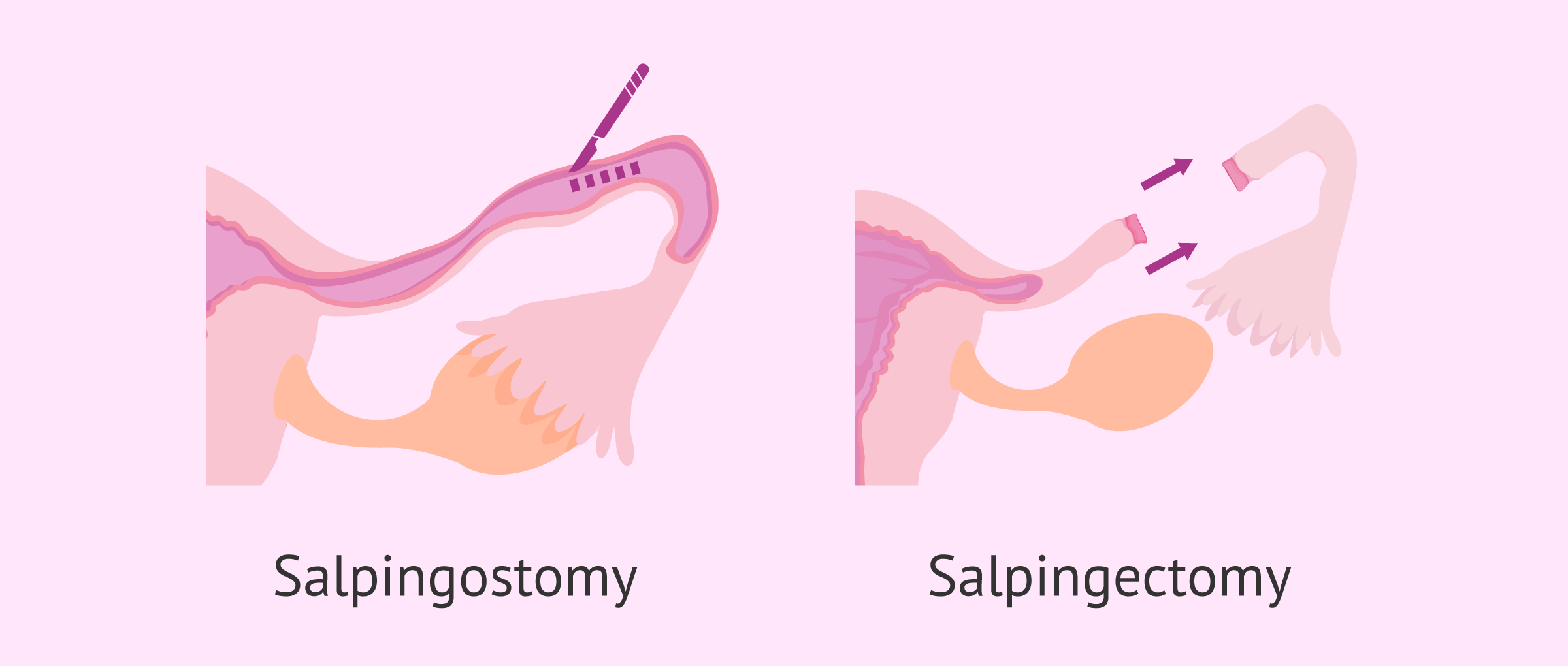
On the other hand, there are two possible alternatives when it comes to performing surgery to treat ectopic pregnancy:
- Salpingostomy
- only the embryonic tissue is removed, which allows the tube to be preserved. This approach requires follow-up to assess the decrease in hCG levels. Occasionally, after a salpingostomy, subsequent treatment (with methotrexate or surgery) may be necessary because embryonic remnants have remained.
- Salpingectomy
- the tube affected by the ectopic pregnancy is removed, making it a more radical approach.
Thus, the gynecologist should discuss with the woman the possibility of performing one or the other procedure, taking into account her wishes for motherhood in the future. However, there are occasions in which the specialist will have to make a decision once the surgery has begun, after seeing the state of the tube.
Non-tubal ectopic pregnancy
Although the most frequent location of an ectopic pregnancy is the fallopian tube, there are other possible sites. In these cases, the treatment of ectopic pregnancy will be similar:
- Ovarian
- when possible, laparoscopic surgery will be performed, trying to preserve the ovary.
- Abdominal.
- treatment is usually by laparotomy. In addition, this type of ectopic pregnancy may require the administration of methotrexate after the operation.
- Cervical, cornual or interstitial
- ideally, methotrexate treatment should be attempted prior to surgical treatment, as this may ultimately require hysterectomy, i.e. resection of the uterus.
However, as in tubal ectopic pregnancy, the specialist must assess with the patient the advantages and disadvantages of each possible intervention.
Pregnancy after ectopic pregnancy
After an ectopic pregnancy, it is possible for a woman to have a normal pregnancy in the future. However, the chances of ectopic pregnancy are increased if the woman has already had a previous ectopic pregnancy.
For this reason, as soon as a woman becomes aware of a new pregnancy, she should inform her gynecologist. Thus, the specialist will be able to evaluate the location of the new pregnancy at an early stage.
At this point, it is important to clarify that a pregnancy following the ectopic pregnancy is possible, even if a salpingectomy has been performed, since the other fallopian tube would be intact after the intervention. In addition, in case the patient has a tube that has remained damaged (or absent), pregnancy would still be possible thanks to in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Assisted procreation, as any other medical treatment, requires that you rely on the professionalism of the doctors and staff of the clinic you choose. Obviously, each clinic is different. Get now your Fertility Report, which will select several clinics for you out of the pool of clinics that meet our strict quality criteria. Moreover, it will offer you a comparison between the fees and conditions each clinic offers in order for you to make a well informed choice.
You can find more information about this treatment in the following article: In vitro fertilization (IVF) - What is it and how much does it cost?
FAQs from users
Are there other medications for ectopic pregnancy besides methotrexate?
An ectopic pregnancy is the implantation of the fertilized egg outside the uterine cavity. Other medical treatment options such as Prostaglandins, Actinomycin D, Potassium Chloride, Hyperosmolar Glucose, Monoclonal Antibodies or simple aspiration have been used, but none of these have shown more efficacy than the use of Methotrexate.
Is ectopic pregnancy treatable?
Yes, there are several treatment options for ectopic pregnancy, which consist of maintaining a watchful waiting attitude to ensure that the pregnancy resolves spontaneously, medical treatment with methotrexate or surgical treatment.
The choice of one option or the other will depend on several factors such as the symptoms presented by the patient or her hCG blood levels, but in any case the ideal is to make an early diagnosis of the ectopic pregnancy, to avoid possible complications.
What does medical treatment of ectopic pregnancy refer to?
Medical treatment for ectopic pregnancy generally refers to the use of methotrexate to stop the progression of the ectopic pregnancy.
This drug is administered by intramuscular injection, in one or several doses, and has the advantage that, whenever it can be used, it can prevent the woman from having to go to the operating room for surgical treatment of the ectopic pregnancy.
What is the best treatment for ectopic pregnancy?
The best treatment for ectopic pregnancy will be the one that best suits the patient's condition and the stage of extrauterine gestation, also taking into account the woman's future gestational desire.
Thus, the patient should be informed of her different options, as well as the advantages and the risks and disadvantages of each of them.
Recommended readings
This article is focused on the treatment of ectopic pregnancy, but if you want to learn more about this type of pregnancy, we recommend you to visit this link: What is ectopic pregnancy - Types, symptoms and diagnosis.
On the other hand, we have also mentioned the importance of monitoring hCG hormone levels. If you want to know more about the values of the "pregnancy hormone", you can visit the following article: What are the normal values of beta-hCG hormone?
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Alalade AO, Smith FJE, Kendall CE, Odejinmi F. Evidence-based management of non-tubal ectopic pregnancies. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2017 Nov;37(8):982-991. (see)
Brady PC. New Evidence to Guide Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosis and Management. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2017 Oct;72(10):618-625. (see)
Hendriks E, Rosenberg R, Prine L. Ectopic Pregnancy: Diagnosis and Management. Am Fam Physician. 2020 May 15;101(10):599-606. (see)
Parker VL, Srinivas M. Non-tubal ectopic pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2016 Jul;294(1):19-27. (see)
Rana P, Kazmi I, Singh R, Afzal M, Al-Abbasi FA, Aseeri A, Singh R, Khan R, Anwar F. Ectopic pregnancy: a review. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2013 Oct;288(4):747-57. (see)
Taran FA, Kagan KO, Hübner M, Hoopmann M, Wallwiener D, Brucker S. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2015 Oct 9;112(41):693-703; quiz 704-5. (see)
Xiao C, Shi Q, Cheng Q, Xu J. Non-surgical management of tubal ectopic pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Dec 17;100(50):e27851. (see)
FAQs from users: 'Are there other medications for ectopic pregnancy besides methotrexate?', 'Is ectopic pregnancy treatable?', 'What does medical treatment of ectopic pregnancy refer to?' and 'What is the best treatment for ectopic pregnancy?'.
Authors and contributors
More information about Cristina Algarra Goosman





Hi, I have been told that they do not see any baby in utero and that I possibly have an ectopic pregnancy. Is there any way to save the pregnancy?
Hi Ashlee98,
An ectopic pregnancy is not viable, the uterus is the designated organ to carry the pregnancy if the embryo implants in any other organ this will be unviable as the development of the pregnancy will be detrimental to the mother’s health and therefore the pregnancy will have to be dissolved.
I recommend that you talk to your doctor so that you can try again in the safest way possible.
I hope all goes well
Hello, is there any way to avoid an ectopic pregnancy? I have had two and I can’t go through another one
Hi Catelynn,
There is no specific cause for ectopic pregnancy but it is true that there are risk factors such as pelvic inflammatory disease, history of abdominal surgery, IUD use, smoking, or a previous ectopic pregnancy.
If these risk factors are controlled as well as a more exhaustive control, the probabilities of an ectopic pregnancy can be lowered.
I hope I have solved your doubt