Low ovarian response to stimulation is a problem that occurs in between 9% and 24% of patients undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatments. This percentage increases in women over 38 years old, mainly due to ovarian aging and decreased ovarian reserve.
However, it is important not to confuse the ovaries’ low response to hormonal drugs with a low ovarian reserve, as they are different terms. A woman may have a low number of eggs but still respond well to hormonal stimulation.
In the following video, embryologist Silvia Azaña explains low ovarian response to stimulation in assisted reproduction treatments. However, you can later explore the topic in more detail by reading the article.
Provided below is an index with the 8 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 4.3.
- 4.4.
- 5.
- 5.1.
- 5.2.
- 5.3.
- 5.4.
- 5.5.
- 5.6.
- 5.7.
- 5.8.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
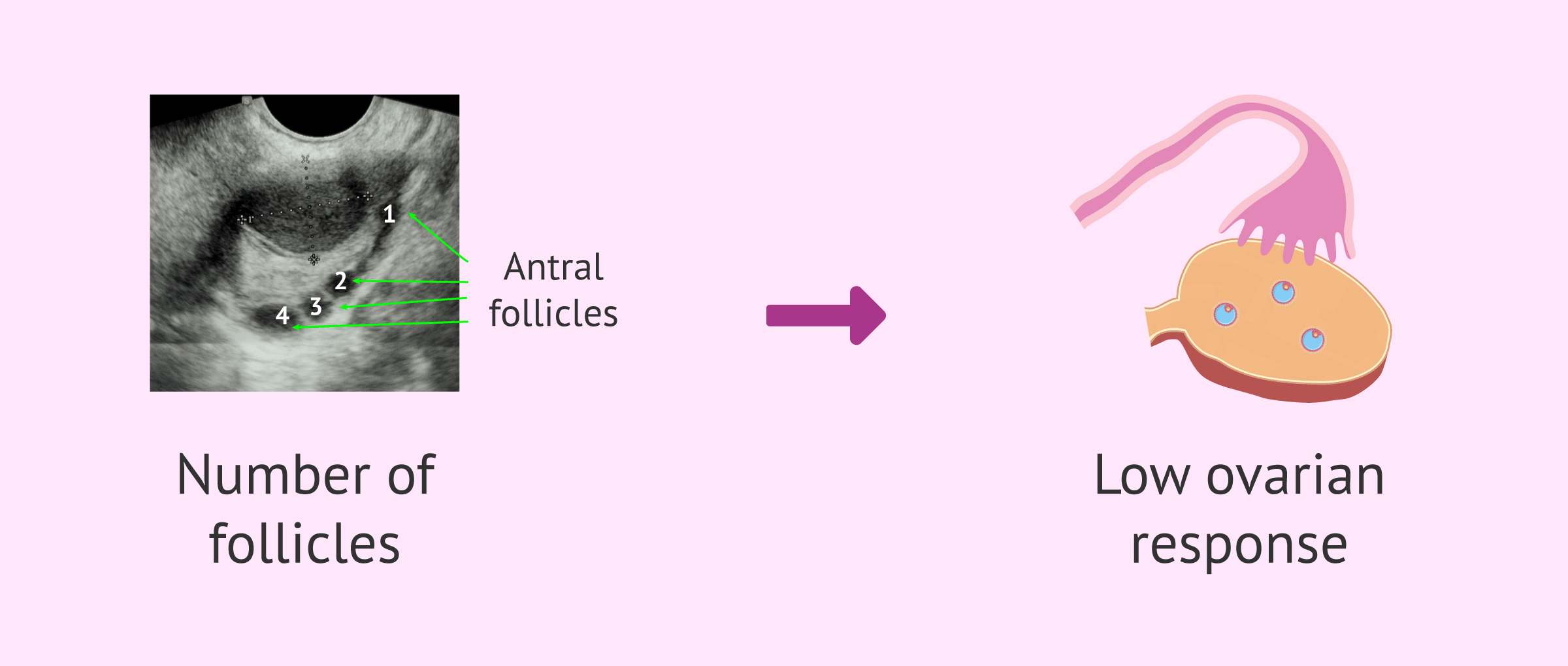
What is low ovarian response?
Low ovarian response refers to the poor retrieval of mature eggs after ovarian stimulation in an IVF treatment. However, there is no general agreement among specialists on how to define low ovarian response to stimulation.
According to the Bologna Criteria, a low response is considered to exist when at least two of the following criteria are met:
- Age over 40 years or another risk factor for low response.
- Previous cycle with low response. A cycle is considered to have had a low response if 3 or fewer oocytes are retrieved after following a standard ovarian stimulation protocol.
- Ovarian reserve test with reduced results: antral follicle count (AFC) below 5-7 or anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) lower than 0.5-1.1 ng/ml.
In addition, a woman is also considered a poor responder when, after undergoing two cycles of ovarian stimulation with maximum doses, two poor responses are obtained.
However, the later POSEIDON Classification achieved better patient stratification, based on age (younger or older than 35 years) and ovarian reserve (AFC higher or lower than 5 and AMH higher or lower than 1.2 ng/ml).
The prevalence of low ovarian response to stimulation in fertility treatments is variable, but it is estimated to occur in 9–24% of women. Therefore, it is essential that fertility treatment, as well as ovarian stimulation, be personalized from the start.
How to predict a low response?
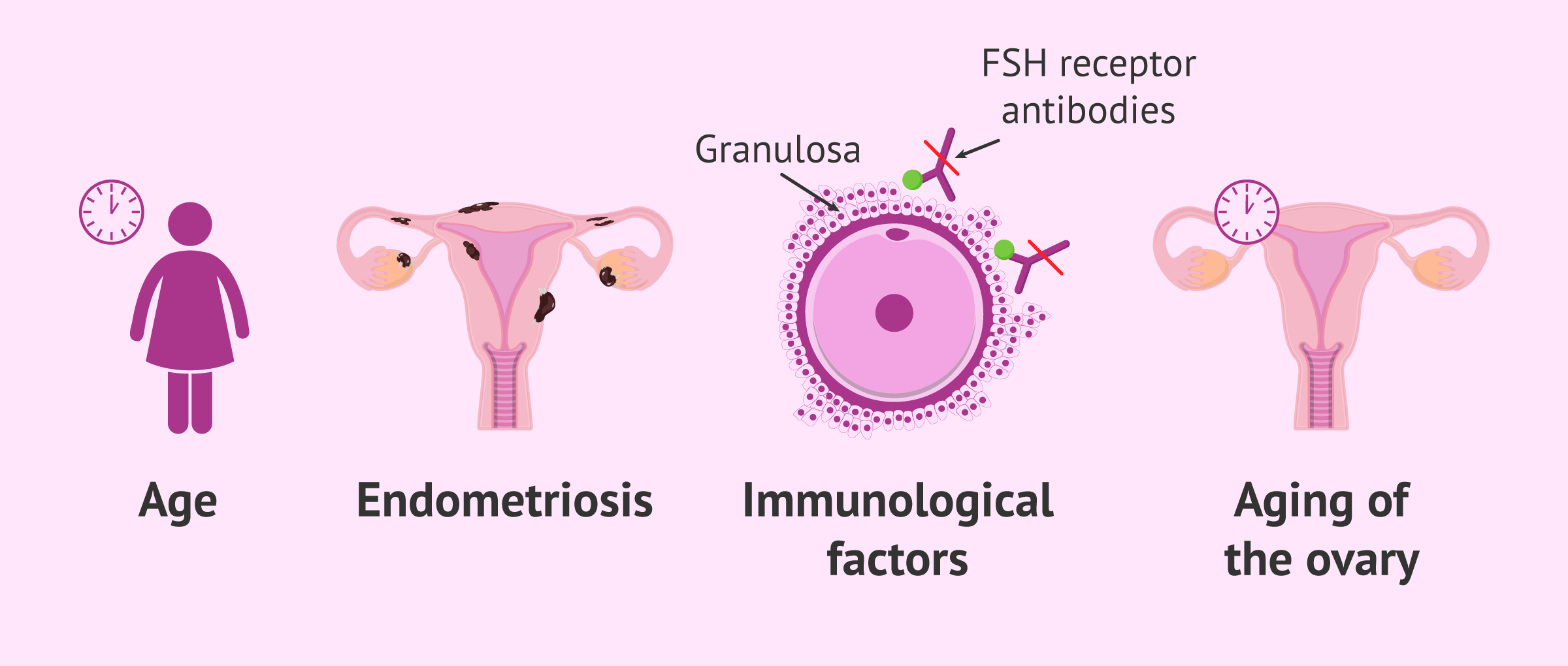
Cases of low response are confirmed after ovarian stimulation. Although the causes of low response are not fully understood, some related factors have been described that could help predict the ovaries’ response to the medications used for stimulation:
- Age: inversely related to ovarian reserve. The older the woman, the fewer eggs available, and the poorer the response to ovarian stimulation.
- Ovarian aging.
- Reduction of ovarian tissue due to surgery, chemotherapy, or endometriosis.
- Autoimmune process.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Exposure to toxins.
- Smoking or alcoholism.
- Increased Body Mass Index (BMI).
- Genetic causes.
For more information on how to measure ovarian reserve, you can continue reading the following article: Ovarian reserve tests: What they are and how to interpret them.
Consequences of low response in an IVF cycle
The purpose of controlled ovarian stimulation in an IVF treatment is to retrieve a sufficient number of eggs and achieve the transfer of at least one embryo. Therefore, the goal is for several ovarian follicles to develop, unlike in a natural cycle where only one egg is released.
For this reason, low ovarian response has undesirable consequences, as only a small number of eggs are retrieved for fertilization. This reduces the chances of pregnancy since the risk of having to cancel embryo transfer increases.
Thus, poor responders may need continuous emotional support, as cycles are more likely to be canceled, requiring repeated stimulation treatments.
In addition, egg quality may deteriorate (especially when age is the cause), compromising the retrieval of viable blastocysts for transfer, which worsens the situation for these women.
In the following article, you can read more about this topic: How many eggs do you need to obtain to perform IVF?
Solutions for poor responders
Currently, more experimental techniques are being used for low ovarian response, such as ovarian rejuvenation. However, in addition to these experimental options, there are several alternatives for women with low ovarian response in fertility treatments. Each of them is discussed below.
Conversion of an IVF cycle into an IUI cycle
If only 1 or 2 follicles are observed by ultrasound, it may be possible to convert the IVF cycle into an intrauterine insemination (IUI) cycle. This is only possible after evaluating other factors and provided there is no severe male factor.
Androgen pretreatment
After a poor response in a previous stimulation cycle, an androgen pretreatment may be attempted to obtain a greater number of follicles during stimulation.
These treatments may include transdermal testosterone or DHEA, although their effectiveness in these cases has not been proven.
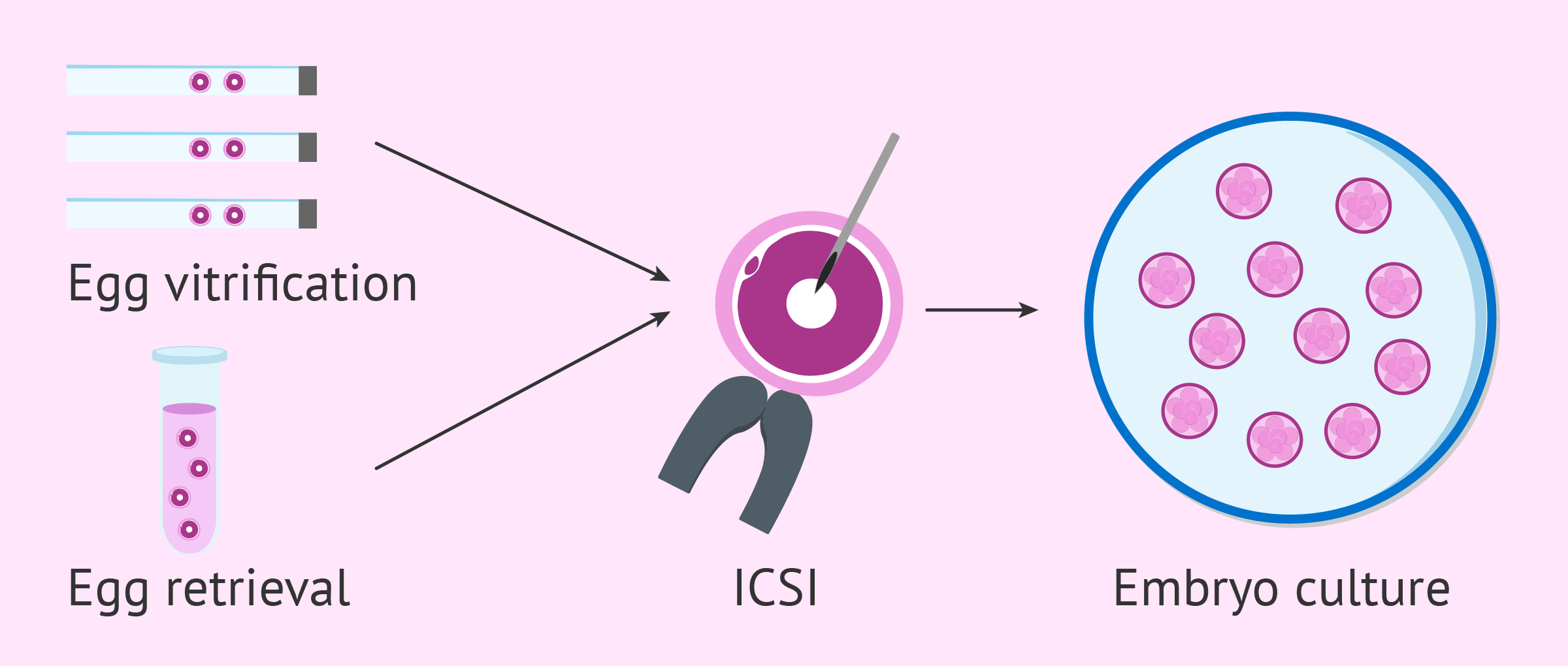
Egg accumulation with vitrification cycles
To obtain a higher number of eggs in the lab and increase the chances of producing quality embryos for transfer, several egg accumulation cycles can be performed.
This involves vitrifying all the eggs retrieved in each cycle until reaching an optimal number. At that point, they are thawed, combined with those obtained in the last retrieval, and fertilized through ICSI.
Alternatively, the same “egg accumulation” strategy can be applied by performing two stimulations in a single cycle, known as double stimulation.
Egg donation
When several IVF cycles have already been canceled due to low ovarian response, the most successful alternative is egg donation.
In IVF with egg donation, eggs donated by an egg donor are fertilized with the sperm of the recipient woman’s partner.
This reproductive option has high success rates, but it also comes with the drawback of giving up the woman’s genetic contribution and its high cost.
Due to delayed motherhood in today’s society, egg donation is widely used in fertility clinics, as egg quality declines with age. For this reason, if a woman has not previously preserved her eggs, egg donation may be necessary to achieve pregnancy.
You can find more information about egg donation at the following link: What is IVF with egg donation and how much does treatment cost?
FAQs from users
Is the natural cycle a good option for poor responders?
In women who are poor responders, there is medical evidence for similar live birth rates using high dose ovarian stimulation vs. Natural cycle, particularly in younger women. This is presumably because poor responders do not produce many eggs and high does’ stimulation may be detrimental to egg quality. Younger reproductive aged women have the advantage of better egg quality. In older reproductive age women who are poor responders, the option of egg donation is usually much more successful in achieving a live birth. However, the optimal approach to the poor responder is far from certain.
Can a low antimüllerian be indicative of a low response?
Antimüllerian hormone (AMH) in women informs us of the number of ovarian follicles available, independent of the menstrual cycle and the age of the patient, although it is usually related to her reproductive age.
It is known that women are born with a finite follicular endowment that is depleted as they get older, therefore, a low antimüllerian is indicative that the number of total follicles available in the ovary is decreased. Fewer follicles available means less response. But this is not entirely true, since we have to take into account another important factor which is the AFR (Antral Follicle Count).
Each menstrual cycle the ovaries make a number of follicles available for development each cycle. This number of available follicles usually decreases with age but does not necessarily depend on the remaining count in the ovary. Let's say that they are complementary because what really defines the low response is the number of follicles available in each cycle (RFA) which is usually lower the AMH. They are usually related, but what really defines the low response is not AMH but the AFR.
What if the number of eggs I produce is insufficient for IVF?
In order to be able to fertilize more than one egg cell in the same IVF cycle, women's ovaries are stimulated using fertility drugs. The number of eggs required depend on the technique used. For IVF, it is enough with 1 or 2; whilst for IVF/ICSI, we should have around 10 eggs ideally. Oftentimes, due to a varied set of causes, the ovarian response of some patients is inadequate and the number of eggs collected is too low (below 5). In such cases, we can turn to the following strategies:
- To cancel the cycle before egg retrieval and start a new stimulation cycle with a different stimulation protocol.
- To freeze using egg vitrification technique the eggs to collect a higher number of eggs in subsequent cycles.
- To freeze using embryo vitrification technique the resulting embryos in order to transfer 2 in the subsequent cycle.
In short, it depends on the history of each couple.
What are the chances of natural pregnancy with a low ovarian response?
The chances of natural pregnancy in women with low ovarian reserve are minimal, although not nonexistent. However, the majority of women diagnosed with low ovarian reserve achieve pregnancy through assisted reproductive techniques.
Would PGD be a possible solution for low ovarian response?
No, preimplantation genetic testing (PGT), formerly known as PGD, does not offer any advantage for women with low ovarian reserve. This complementary technique allows for the genetic analysis of embryos, but it neither improves nor increases the quantity of eggs available in the woman.
Is Omifin recommended for low responders?
Yes. The active ingredient in Omifin is clomiphene citrate, which can be used as an adjuvant treatment. The advantages of using Omifin are as follows:
- It allows for moderate follicular growth.
- There is no blockage of endogenous FSH and LH.
- It allows for a stable and progressive increase in estradiol levels.
- The number of injections for the patient is lower.
In addition, the cost of Omifin is more economical for poor responders.
Can I get pregnant with low ovarian response?
It may be more or less complicated, but it is possible to achieve pregnancy with low ovarian response.
When a low response to hormonal medication is observed during the course of a fertility treatment, there is a possible solution, such as changing from an IVF cycle to an artificial insemination. Another alternative would be to modify the ovarian stimulation protocol or accumulate oocytes during several cycles.
As a final recourse, pregnancy could be achieved in women with low response through in vitro fertilization using eggs from a donor.
Read more
Are low reserve and low ovarian response the same thing?
No. Ovarian reserve refers to the total number of eggs available within a woman's ovaries at any given point in her life. For example, if the woman starts with a maximum of 6 follicles and 4 mature eggs are obtained from the puncture, it would be a normal ovarian response.
In contrast, low ovarian response occurs when the ovaries do not respond as expected to the specific hormonal medication administered during the ovarian stimulation process.
Read more
Recommended readings
Ovarian stimulation is a key step in every IVF cycle. Want to learn more about the process? Read: Ovarian Stimulation Protocols for IVF - Process & Medications Used.
A common doubt between IVF patient is related to the number of eggs that should ideally be retrieved for IVF. If this is your case, you may enjoy some further information reading this: What Is a Good Number of Eggs Retrieved for IVF?
The opposite to low ovarian response is having a high response, a side effect of IVF known as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome or OHSS. Check out this for information: What Is the Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)?
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Badawy A, Wageah A, El Gharib M, Osman EE. Prediction and diagnosis of poor ovarian response: the dilemma. J Reprod Infertil. 2011 Oct;12(4):241-8. PMID: 23926510; PMCID: PMC3719310. (View)
Cakiroglu Y, Yuceturk A, Karaosmanoglu O, Kopuk SY, Korun ZEU, Herlihy N, Scott RT, Tiras B, Seli E. Ovarian reserve parameters and IVF outcomes in 510 women with poor ovarian response (POR) treated with intraovarian injection of autologous platelet rich plasma (PRP). Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Mar 22;14(6):2513-2523. doi: 10.18632/aging.203972. Epub 2022 Mar 22. PMID: 35320118; PMCID: PMC9004561. (View)
Cedars MI. Managing poor ovarian response in the patient with diminished ovarian reserve. Fertil Steril. 2022 Apr;117(4):655-656. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2022.02.026. PMID: 35367010. (View)
Conforti A, Esteves SC, Cimadomo D, Vaiarelli A, Di Rella F, Ubaldi FM, Zullo F, De Placido G, Alviggi C. Management of Women With an Unexpected Low Ovarian Response to Gonadotropin. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Jun 27;10:387. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00387. PMID: 31316461; PMCID: PMC6610322. (View)
Di Guardo F, Blockeel C, De Vos M, Palumbo M, Christoforidis N, Tournaye H, Drakopoulos P. Poor ovarian response and the possible role of natural and modified natural cycles. Ther Adv Reprod Health. 2022 Jan 14;16:26334941211062026. doi: 10.1177/26334941211062026. PMID: 35072076; PMCID: PMC8771731. (View)
Drakopoulos P, Bardhi E, Boudry L, Vaiarelli A, Makrigiannakis A, Esteves SC, Tournaye H, Blockeel C. Update on the management of poor ovarian response in IVF: the shift from Bologna criteria to the Poseidon concept. Ther Adv Reprod Health. 2020 Jul 31;14:2633494120941480. doi: 10.1177/2633494120941480. PMID: 32844159; PMCID: PMC7416136. (View)
Ferraretti AP, La Marca A, Fauser BC, Tarlatzis B, Nargund G, Gianaroli L; ESHRE working group on Poor Ovarian Response Definition. ESHRE consensus on the definition of 'poor response' to ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization: the Bologna criteria. Hum Reprod. 2011 Jul;26(7):1616-24. doi: 10.1093/humrep/der092. Epub 2011 Apr 19. PMID: 21505041. (View)
Herlihy NS, Seli E. The use of intraovarian injection of autologous platelet rich plasma (PRP) in patients with poor ovarian response and premature ovarian insufficiency. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Jun 1;34(3):133-137. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0000000000000784. PMID: 35645011. (View)
Roque M, Haahr T, Esteves SC, Humaidan P. The POSEIDON stratification - moving from poor ovarian response to low prognosis. JBRA Assist Reprod. 2021 Apr 27;25(2):282-292. doi: 10.5935/1518-0557.20200100. PMID: 33565297; PMCID: PMC8083858. (View)
FAQs from users: 'Can I have sex as a low responder in ovulation induction?', 'Is the natural cycle a good option for poor responders?', 'Can a low antimüllerian be indicative of a low response?', 'What if the number of eggs I produce is insufficient for IVF?', 'What are the chances of natural pregnancy with a low ovarian response?', 'What does it mean to have a low ovarian response?', 'Can poor responders use supplements to improve IVF outcomes?', 'Would PGD be a possible solution for low ovarian response?', 'Can low ovarian response be predicted?', 'Growth hormone for IVF poor responders, yay or nay?', 'Is Omifin recommended for low responders?', 'What are the consequences of a low response in an IVF cycle?', 'What's the best IVF protocol for poor responders?', 'Are there any possible solutions for low responders?', 'Can I get pregnant with low ovarian response?' and 'Are low reserve and low ovarian response the same thing?'.
Authors and contributors

More information about Cristina Algarra Goosman







Hello dr, this is my 1st ivf cycle and after 7 days on gonal 900 and menopur i have three mature eggs in each ovary… is it normal or i’m a poor responder? i’m 34…
Dear Karli,
If you have 3 eggs in each ovary, that means that you have a total of 6 mature eggs to fertilize. Poor ovarian response is diagnosed when there are less than 6 follicles, so you are within the normal threshold yet.
Wishing you the best of luck!