During pregnancy, in order for the fetus to develop properly and give birth to a healthy baby, it is important to provide it with the nutrients necessary for its development and growth.
Therefore, it is essential to control the mother's diet during pregnancy, since it must provide all the nutrients that guarantee her own health, as well as all the nutrients needed by the developing baby. In addition, a good diet can lead to adequate weight gain in pregnancy, so that it is neither excessive nor insufficient.
Thus, eating a healthy, balanced and varied diet, together with keeping active (as long as the specialist has not contraindicated physical activity), will help the woman to have a healthy pregnancy.
Provided below is an index with the 7 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 2.1.
- 2.2.
- 2.3.
- 2.4.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 4.3.
- 4.4.
- 4.5.
- 4.6.
- 4.7.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
Why is it important to eat well?
A pregnant woman's diet should be balanced and varied, including a wide variety of healthy and nutritious foods that meet all the requirements of this special stage. In this way, not only the correct fetal development is favored, but also the good health of the mother during the months of gestation and after childbirth.
However, in addition to the above, eating well during pregnancy will help a woman to have adequate weight gain during this period. If weight gain during pregnancy is excessive with respect to what is recommended by the specialist, it may be associated with gestational diabetes and hypertension. On the other hand, if you do not gain enough kilos during pregnancy, your baby may have a low birth weight.
Finally, pregnancy brings with it a series of changes in a woman's body, such as slower and heavier digestion, and a series of symptoms such as nausea and vomiting or constipation. Eating right can reduce or alleviate these discomforts.
However, it is important to mention that you should eat healthily at any time of your life, not only during pregnancy, although it is true that this period requires paying a little more attention to your diet.
What should pregnant women eat?
During pregnancy it is not necessary to eat for two, but it is necessary to eat a balanced and varied diet that includes all the necessary nutrients for the woman and the baby. In addition, in the case of needing a nutritional supplement, it will be the physician who will indicate and control the dosage, according to the particular situation of the woman.
The following are some general recommendations, but the pregnant woman should always follow the indications given by the specialist.
Vegetables and fruits
Pregnant women should consume a wide variety of vegetables. It is advisable to take two portions a day and they should occupy half of the plate (the other half will be for farinaceous and protein foods).
Fruits are also a very good option as a dessert or for a healthy snack, the ideal being 3 servings a day.
This type of food will provide fiber, vitamins and minerals and, therefore, are essential in the diet during pregnancy.
However, during pregnancy, special care must be taken and raw fruits, vegetables and aromatic herbs such as fresh basil must be properly washed and sanitized. Similarly, it is important to ensure that they have been properly sanitized if they are eaten away from home or, for example, if they are bagged salads.
In the case of frozen vegetables or fruits, these should be fully cooked before being consumed by the pregnant woman.
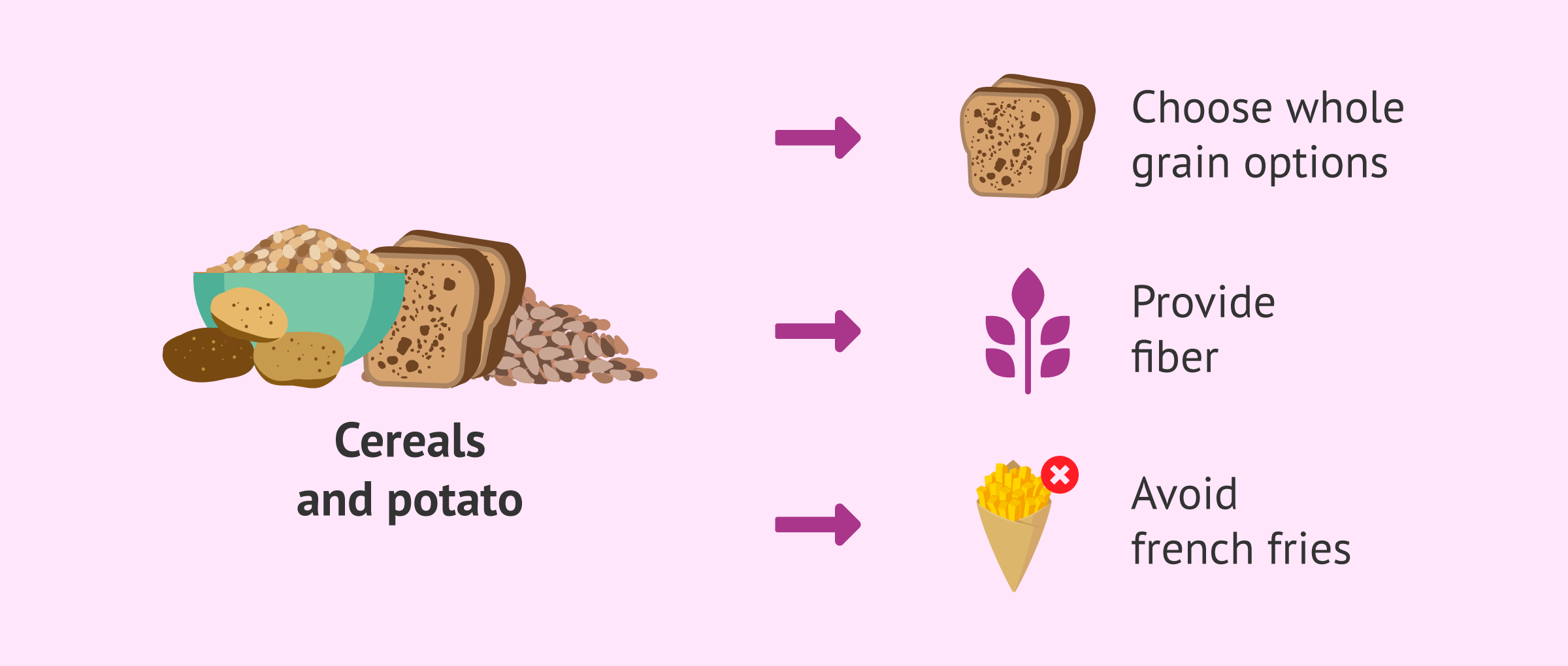
Cereals and potato
These are the farinaceous group, which should constitute a quarter of the pregnant woman's plate.
As for cereals, whole grain options should be chosen (brown rice, whole wheat pasta, whole wheat breads...), thus avoiding refined flours. This will increase fiber intake (in addition to other nutrients) which, with adequate hydration and staying active, will help prevent or alleviate constipation in pregnant women.
Potatoes can also be part of the diet during pregnancy. However, fried foods should be avoided due to their high calorie and salt content.
Foods rich in protein
A quarter of the pregnant woman's plate should be made up of foods rich in protein, which is very important for the baby's growth.
Lean meats or poultry should be chosen. However, care must be taken to ensure that it is fully cooked, with no juices released when cut and no pink color in the center (reaching 71oCeven in the center of the piece).
As for fish, it is recommended that pregnant women include 3 or 4 servings each week, also for its contribution in omega-3 fatty acids. You should always refuse to consume raw, smoked or marinated fish and seafood, i.e., it must be fully cooked. As an additional precaution, bluefin tuna, swordfish or emperor fish, shark and pike should be avoided due to their high mercury content.
Eggs are also a good option, as they have high quality proteins, as well as other nutrients. However, eggs should not be consumed raw or undercooked, or in preparations or desserts that contain raw or undercooked eggs.
Legumes are rich in vegetable proteins and fiber and it is recommended to eat them 2-3 times a week.
Dairy
Dairy products are a great source of calcium, important for bones and teeth and for other systems such as the muscular and nervous systems. Therefore, they should be consumed several times a day (about 2 or 3 times).
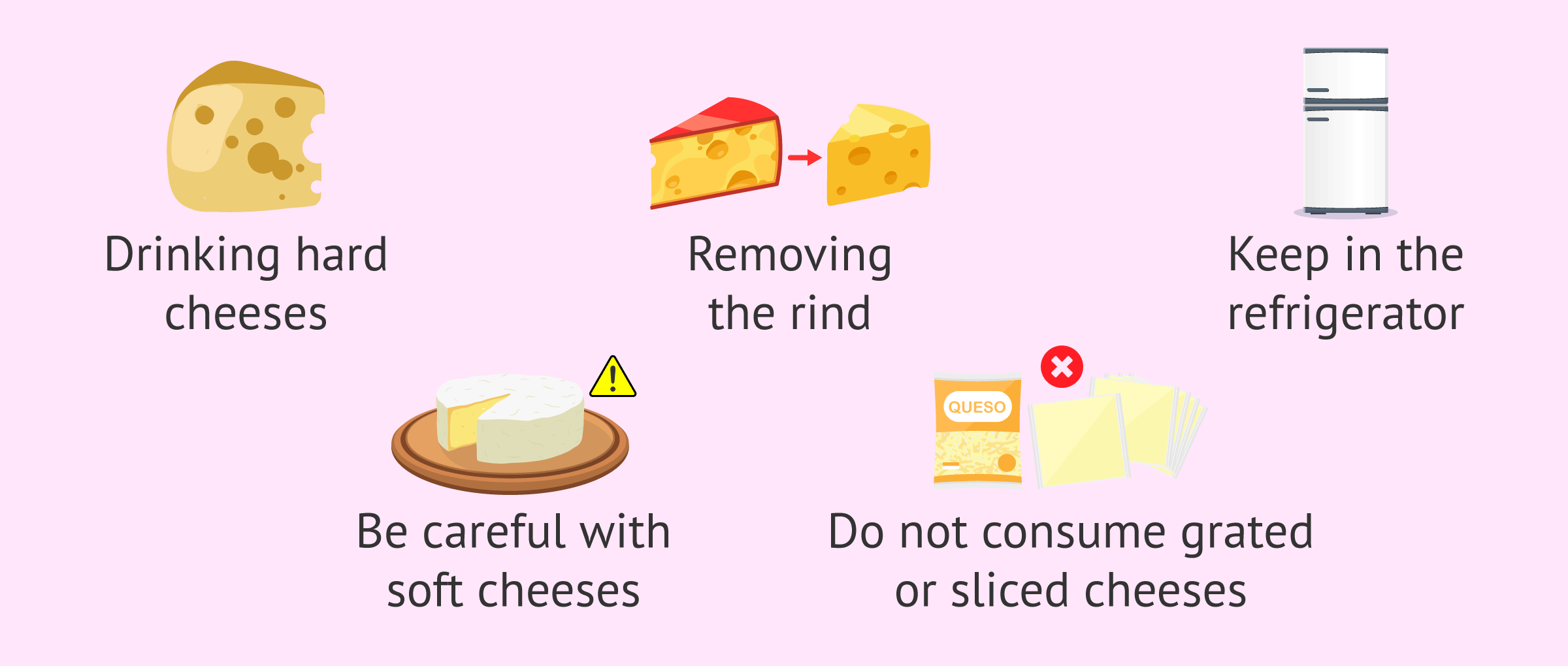
Options include UHT milk, yogurts (without added sugar), cheeses... However, the following considerations should be taken into account with cheeses during pregnancy:
- Must be hard cheeses.
- Always remove the rind.
- The cheese should be kept in the refrigerator.
- In the case of soft cheeses, they can be eaten as long as they have not been made with raw milk, so it will be necessary to look carefully at the labeling and, in addition, consume them soon.
- Cheeses that are already sliced or grated cannot be consumed.
As the most important conclusion about dairy products, it is forbidden to consume raw milk or dairy products made from raw (or unpasteurized) milk during pregnancy due to the risk of listeriosis.
What foods are recommended in pregnancy?
As a guideline, we are going to mention some foods whose consumption is interesting during pregnancy because they are healthy foods that provide nutrients that the pregnant woman and the baby need:
- Green leafy vegetables: such as spinach, rich in folates, fiber, iron, potassium and vitamins C, A and E.
- Broccoli: it is a source of folates, vitamin C, proteins and fiber.
- Oranges: rich in vitamin C and folates. Other citrus fruits and fruits rich in vitamin C such as strawberries or kiwi can also be taken.
- Whole-grain bread and cereals: better option than refined varieties, due to their higher fiber content.
- Salmon: this oily fish contains proteins, monounsaturated, unsaturated and omega-3 fatty acids, iodine and vitamins B, D and E.
- Egg: source of protein and monounsaturated fatty acids. It also contains vitamin D, vitamin A, and folates. Do not consume raw or undercooked.
- Lentils: provide vegetable protein, fiber, iron and folate, among other nutrients.
- Almonds and walnuts: rich in healthy fats, proteins, fiber, vitamins and minerals.
- Milk and yogurt: provide protein and calcium. Do not consume raw milk due to risk of listeriosis. Yogurt should be natural and without added sugar.
- Avocado: contains healthy fats and vitamins C, E and B group.
- Olive oil: provides healthy fats and vitamin E. It should be used for cooking as a substitute for animal fats such as butter, as well as to be taken raw in dressings.
- Water: hydration is very important during pregnancy, and consumption should amount to 2.3 liters of water per day (taking into account the water provided by food). Proper hydration can help prevent constipation, skin dryness, etc.
However, this is just a small sample of some healthy foods that women can eat if they wish. However, the pregnant woman should include many more, since the important thing is to have a healthy, varied and balanced diet.
FAQs from users
How does obesity influence the outcomes of fertility treatments?
In the case of obesity, it comes with a series of endocrine and metabolic disorders that cause several gynecological alterations, including, but not limited to, hyperandrogenism (androgen excess), hyperinsulinism, and anovulation. In the case of anovulation, when a woman is undergoing a fertility treatment, it means longer ovarian stimulation protocols, higher doses of gonadotropins, higher drop-out rates due to poor ovarian response, lower implantation and pregnancy rates, and an increased miscarriage rate.
Is it possible to follow a vegetarian or vegan diet during pregnancy?
If the woman is vegetarian or vegan, it is possible to maintain a vegetarian or vegan diet during pregnancy, but it will be very important for the woman to check with her specialist or with the help of a nutritionist that she is consuming enough protein, calcium and vitamin B12.
What should I eat during pregnancy?
In general, your body needs extra nutrients, minerals, and vitamins when you are pregnant. As a matter of fact, you may need to add 350-500 extra calories each day, especially during the second and third trimester of pregnancy.
Keep in mind that key nutrients are essential for the baby's development, and poor eating habits may increase the risk of gestational diabetes and birth complications.
How to alleviate digestive discomfort in pregnancy with food?
One of the most widespread recommendations to avoid digestive discomfort during pregnancy is to eat small meals, but several times a day.
It can also be a good idea to relieve nausea by opting for soft, bland foods that are easy to digest. Similarly, cold foods and drinks may be better tolerated.
As for constipation, proper hydration and eating foods rich in fiber should help, as well as staying active.
For heartburn, it is best not to overfill the stomach with large meals, which will promote reflux. In addition, you should eat slowly and chew well. On the other hand, you should avoid fried foods, spicy foods, coffee, tea, soft drinks... and it will be better to wait a certain time before bending over, exercising or lying down after eating.
What diet to follow in summer if you are pregnant?
Nutrition is always a very important aspect to take care of, especially during pregnancy.
In summer, increased sweating can lead to dehydration. Therefore, in addition to staying hydrated by drinking water (avoiding sugary drinks), pregnant women can also eat certain foods that contribute to a healthy supply of water to their bodies. Among these foods are fruits and vegetables, which are also a source of vitamins and minerals and are very refreshing. Remember to wash fruits and vegetables well before eating them.
You can also follow other tips such as not eating very large meals so as not to feel too heavy (better to eat small meals and frequently) and control salt intake.
On the other hand, summer is a favorable season for eating more meals away from home and, being pregnant, you should be especially careful with the way you have prepared these foods and, of course, avoid foods that are not recommended in pregnancy.
What should you eat during the two week wait?
Broadly speaking, following a balanced diet which includes fruits, vegetables, meat, fish, etc. is the most advisable. Some specialists recommend including dried fruits and nuts, as well as gelatin, which is a protein-rich food. On the other hand, eating ham is unadvisable, as it increases the risk of having toxoplasmosis in case you're pregnant.
As for what to drink, alcohol and fizzy drinks should be avoided at all costs. Staying hydrated is a must, so pay attention to drinking plenty of water. Include orange juice and isotonic drinks as well, given their high content in mineral salts.
What should I eat during the ninth month of pregnancy?
Keeping in mind that your baby is almost complete, at this stage he or she will be accumulating baby fat. For this reason, you should eat foods that are high in fiber, calcium, iron, vitamin C and A, and folic acid. Since your baby needs to add on weight during these days, it is recommended that you make your meals a little bigger in quantity.
Suggested for you
If you want to know more about the recommended weight to gain during pregnancy, you can visit the following link: How many kilos should you gain during pregnancy? Recommendations
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Amati F, Hassounah S, Swaka A. The Impact of Mediterranean Dietary Patterns During Pregnancy on Maternal and Offspring Health. Nutrients. 2019 May 17;11(5):1098. doi: 10.3390/nu11051098. PMID: 31108910; PMCID: PMC6566342. (View)
Avnon T, Paz Dubinsky E, Lavie I, Ben-Mayor Bashi T, Anbar R, Yogev Y. The impact of a vegan diet on pregnancy outcomes. J Perinatol. 2021 May;41(5):1129-1133. doi: 10.1038/s41372-020-00804-x. Epub 2020 Sep 1. PMID: 32873905. (View)
Chen X, Zhao D, Mao X, Xia Y, Baker PN, Zhang H. Maternal Dietary Patterns and Pregnancy Outcome. Nutrients. 2016 Jun 7;8(6):351. doi: 10.3390/nu8060351. PMID: 27338455; PMCID: PMC4924192. (View)
Kind KL, Moore VM, Davies MJ. Diet around conception and during pregnancy--effects on fetal and neonatal outcomes. Reprod Biomed Online. 2006 May;12(5):532-41. doi: 10.1016/s1472-6483(10)61178-9. PMID: 16790095. (View)
Monthé-Drèze C, Rifas-Shiman SL, Aris IM, Shivappa N, Hebert JR, Sen S, Oken E. Maternal diet in pregnancy is associated with differences in child body mass index trajectories from birth to adolescence. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021 Apr 6;113(4):895-904. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa398. PMID: 33721014; PMCID: PMC8023853. (View)
Nansel TR, Cummings JR, Burger K, Siega-Riz AM, Lipsky LM. Greater Ultra-Processed Food Intake during Pregnancy and Postpartum Is Associated with Multiple Aspects of Lower Diet Quality. Nutrients. 2022 Sep 22;14(19):3933. doi: 10.3390/nu14193933. PMID: 36235585; PMCID: PMC9572643. (View)
Shin D, Bianchi L, Chung H, Weatherspoon L, Song WO. Is gestational weight gain associated with diet quality during pregnancy? Matern Child Health J. 2014 Aug;18(6):1433-43. doi: 10.1007/s10995-013-1383-x. PMID: 24162550. (View)
Wang X. Healthy diet during pregnancy-navigating the double-edged sword. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021 Aug 2;114(2):414-415. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqab168. PMID: 34038942; PMCID: PMC8326046. (View)
FAQs from users: 'How does obesity influence the outcomes of fertility treatments?', 'Is it possible to follow a vegetarian or vegan diet during pregnancy?', 'What should I eat during pregnancy?', 'How to alleviate digestive discomfort in pregnancy with food?', 'What diet to follow in summer if you are pregnant?', 'What should you eat during the two week wait?' and 'What should I eat during the ninth month of pregnancy?'.
Authors and contributors