Oocyte quality is one of the key factors when it comes to achieving pregnancy. For the fertilization, implantation, and development of the embryo to take place, it is essential to have eggs of good morphological and genetic quality.
Low oocyte quality is one of the main causes of female infertility and this is directly related to the women’s age.
From the ages of 35 years onwards, the quantity and quality of eggs begin to decrease considerably. However, it must be kept in mind that both concepts are not the same, as having a good number of oocytes does not imply that they will be of good quality.
Provided below is an index with the 8 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 2.1.
- 2.2.
- 2.3.
- 2.4.
- 2.5.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 5.1.
- 5.2.
- 5.3.
- 5.4.
- 5.5.
- 5.6.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
Egg quantity vs. Egg quality
A woman's ovarian reserve, i.e. the number of eggs she will have throughout her reproductive life, is already established from the moment of birth. Girls are born with between 1 and 2 million immature eggs, Approximately. However, by the time they hit puberty, this ovarian reserve has already decreased to 500,000 oocytes.
From this moment on, the woman will release a mature egg in each menstrual cycle, while many others will undergo a process called atresia and will be lost.
All this shows how a woman's ovarian reserve gradually decreases over time until it is completely exhausted when she reaches menopause.
However, not only does the number of eggs decrease with age, so does their quality. As they age, the eggs accumulate mutations in their DNA, which can lead to defective embryos that end up in abortion or the birth of a sick baby.
Just because a 40-year-old woman has a good number of antral follicles seen by ultrasound, that is, her ovarian reserve is good, does not automatically mean that all these eggs will develop normally or will be of good quality.
The age of the woman is essential so that the eggs that mature are of good quality. From the age of about 35, the quality of the eggs will worsen and their numbers decrease.
Oocyte quality analysis
Today, there are several diagnostic tests to evaluate the state of a woman's ovarian reserve, such as an antral follicle count by ultrasound, antimullerian hormone analysis, or determination of blood FSH levels.
However, knowing the quality of the eggs is not so easy. In IVF treatments, there is no proof that the recovered oocytes have chromosomal alterations. The only viable option would be to fertilize them and perform a preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) of the embryos generated.
On the other hand, during IVF treatment it is possible to evaluate the morphology of the eggs under a microscope, although the alterations in their structure in principle have no relation to the genetic alterations.
In the following section we will comment on what a normal oocyte would look like and what oocyte dysmorphisms might be found during its evaluation.
What does a normal egg look like?
An oocyte must have a rounded shape and, in addition, have all of the following structures correctly defined:
- A homogeneous cytoplasm, with no foreign body to attract attention inside
- A single polar body in the perivitelline space, slightly flattened and of homogeneous content
- A perivitelline space that is hardly perceptible, only in the zone where the polar body is
- A uniform Zona Pellucida (ZP) of suitable thickness
The presence of the first polar corpuscle indicates that the egg has reached nuclear maturity and is therefore suitable for fertilization. Mature oocytes are said to be in metaphase II.
Cytoplasm alterations
As we have discussed, the egg must be spherical and its cytoplasm must be completely regular with no visible structure inside.
Some alterations that we can find in the cytoplasm are the following:
- Granular content
- Refractory bodies
- Necrotic bodies with granular content
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (opaque and large) and vacuoles (round and transparent)
- Cluster: granular and dark area in the center of the oocyte
Polar body alterations
A mature ovum has a single polar body, round and elongated, and perfectly delimited. The alterations that may appear in the oocyte referring to polar body are the following:
- Multiple polar bodies, i.e. there is more than one
- Fragmented polar body
- Amorphous or very flat polar body
Periviteline space alterations
The perivitelline space is the space between the zona pellucida (outer layer) and the oocyte itself. A perivitelline space that is hardly perceptible, only in the zone where the polar body is, Therefore, the alterations referring to the perivitelline space are the following:
- Wide perivitelline space or with irregular wide and narrow areas
- Presence of cellular debris in the perivitelline space
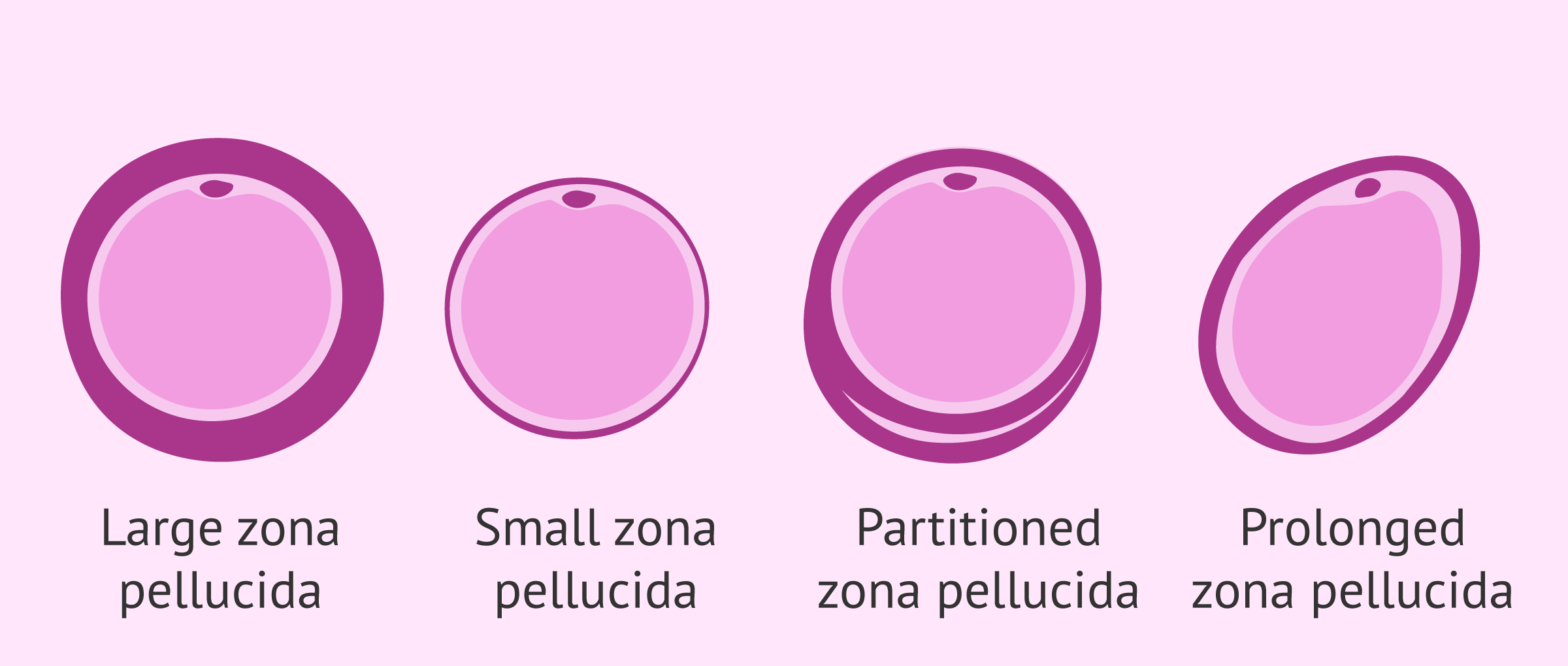
Zona pellucida alterations
The zona pellucida is the outer layer that surrounds the egg. It should have a proportionate amplitude of about 15-20 microns.
The alterations that can be found in the ZP of an oocyte are the following:
- Too thick or too narrow an amplitude
- Loose (light) or too dense (dark)
- Irregular ZP, with areas thinner than others
- Rugged inner zone
- Partitioned ZP forming an independent section
- Elongated ZP
All these dysmorphisms can make it difficult to fertilize the eggs, although by using intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) it is possible to fertilize them.
It is also possible that partitioned, elongated or ZPs that are too thick may cause problems when hatching, i.e. when the blastocyst-state embryo detaches from its zona pellucida to be able to implant into the endometrium.
In this case, the embryologist would consider the option of assisted hatching.
What are the causes for poor egg quality?
We have already commented that the advanced age of women is the main cause of poor oocyte quality, especially from the age of 35.
In addition, other pathologies or unhealthy habits can also have a harmful effect on the eggs. We will discuss them below:
- Endometriosis
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Tobacco and alcohol
- Poor eating habits
- Radio/chemotherapy treatments
Therefore, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing sports, and avoiding the consumption of toxic substances will be the best prevention to not have the oocyte quality affected.
If you need to undergo IVF to become a mother, we recommend that you generate your Fertility Report now. In 3 simple steps, it will show you a list of clinics that fit your preferences and meet our strict quality criteria. Moreover, you will receive a report via email with useful tips to visit a fertility clinic for the first time.
Video on oocyte quality and its evaluation
In the following video, Antonio Forgiarini M.D, gynaecologist at Next Fertility Valencia, talks about egg quality and how it can be assessed:
Well, we can define the quality of the oocytes as the possibility to achieve a good pregnancy and a healthy baby.
FAQs from users
How is the quality of the eggs evaluated?
Knowing the quality of the eggs before undergoing fertility treatment is very complicated and there are no tests for this. What we can do is approximate the number of eggs we can expect. There are several tests, although the main ones are the measurement of the antimullerian hormone or the antral follicle count in an ultrasound scan. With these two tests, a gynecologist can give you an idea of your ovarian reserve.
The best way to check the quality of the eggs is through an in vitro fertilization cycle. This cycle allows direct observation of the response of the ovaries to hormonal stimulation. After the ovarian stimulation, the gynecologist will count the follicles that have a good size and are developed. After the extraction, the biologist observes the oocytes under the microscope and will analyze the quality according to their shape and the characteristics of their cytoplasm.
Several studies have shown that morphological alterations in the oocytes are associated with a worse pregnancy rate.
Read more
Does evening primrose oil promote oocyte quality?
El aceite de onagra es el extracto concentrado obtenido de las plantas: Oenothera biennis y Oenothera lamarkiana. Este aceite es utilizado desde hace años en múltiples procesos patológicos en la mujer, de hecho, se le conoce coloquialmente como la planta de la mujer.
El aceite de onagra favorece el desarrollo folicular y, por tanto, la calidad de los óvulos, además, mejora los trastornos premenstruales, regula el colesterol, la diabetes etc.
What are the indicators of good egg quality?
Egg quality is one of the most important and probably least known aspects of assisted reproduction. Finding a morphologically normal egg does not guarantee the subsequent achievement of pregnancy, but it does allow the prediction of a high percentage of the embryonic evolution, always taking into account other aspects such as age or ovarian reserve. Thus, we can distinguish three types of indicators, gynecological, morphological, and embryonic.
Read more
How can I improve my egg quality?
First of all, it is important to make it clear that no miracle drug will improve the quality of the eggs. However, healthy lifestyles and a healthy, balanced diet can indeed help boost female fertility.
Foods rich in vitamins, antioxidants, and essential nutrients are those that cannot be missing from the diet. For example green leafy vegetables such as spinach, nuts such as walnuts, legumes such as lentils, fish such as salmon and light tuna, fruits and vegetables such as blueberries, avocado, pomegranate, pineapple, carrots, and so on.
Related post: What should I eat to get pregnant?
Does the Anti-Müllerian hormone measure egg quality?
No. The antimüllerian hormone (AMH) indicates the number of antral and preantral follicles in the ovaries. It is, therefore, an indirect measurement of the ovarian reserve.
AMH levels between 0.7 and 3.5 ng/ml are considered normal, while levels below 0.7 ng/ml are associated with a decreased ovarian reserve.
Does vitamine E boost egg quality?
Yes, specifically what vitamin E does is protect the eggs from suffering alterations. Vitamin E also prevents changes in a woman's menstrual cycle.
Foods rich in vitamin E that contribute to oocyte quality are avocado, almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts, olive oil and sunflower oil, spinach, etc.
Recommended reading
We talked about the ovarian reserve and its close relationship with the quality of the eggs. If you want to continue reading about this subject, do not hesitate to access the following article: What is a woman's ovarian reserve & how does it affect fertility?
To evaluate the morphological quality of the eggs, an IVF-ICSI treatment is necessary. You can find all the information about this technique and how it is done step by step in the following article: https://www.invitra.com/en/intracytoplasmic-sperm-injection-icsi/
If you want to delay motherhood, but don't want your ovarian reserve and egg quality to be compromised by the passing of the years, the best thing to do it to preserve your fertility by vitrifying your oocytes. If you want to learn more about this then we recommend reading the following post: Fertility preservation in young women. Recommendations and ideas.
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Remohí, Bellver, Ferrando, Requena, Pellicer. Manual práctico de Esterilidad y Reproducción Humana. Aspectos clínicos. 5ª edición. Editorial Médica Panamericana.
Romero JL, Gámiz P, Florensa M, Zulategui JF, Remohí J, de los Santos MJ. La morfología ovocitaria y su distribución en pacientes sometidas a hiperestimulación ovárica controlada. In Remohí J, Cobo A, Romero JL, de los SantosMJ, Pellicer A (eds) Manual Práctico de Esterilidad y Reproducción Humana. Laboratorio de reproducción asistida. 2008. Editorial McGraw-Hill / Interamericana de España, S.A.U. 3ª edición, pp.139 - 149.
Sociedad Española de Fertilidad (SEF). Clasificación y cultivo de los ovocitos (ver)
FAQs from users: 'How is the quality of the eggs evaluated?', 'Does evening primrose oil promote oocyte quality?', 'What are the indicators of good egg quality?', 'How can I improve my egg quality?', 'Is oocyte quality the same as oocyte quantity?', 'What is oocyte quality?', 'Does the Anti-Müllerian hormone measure egg quality?', 'Does vitamine E boost egg quality?', 'How is egg quality assessed?', 'What are the causes of poor oocyte quality?' and 'How can egg quality be improved?'.
Authors and contributors


More information about Michelle Lorraine Embleton
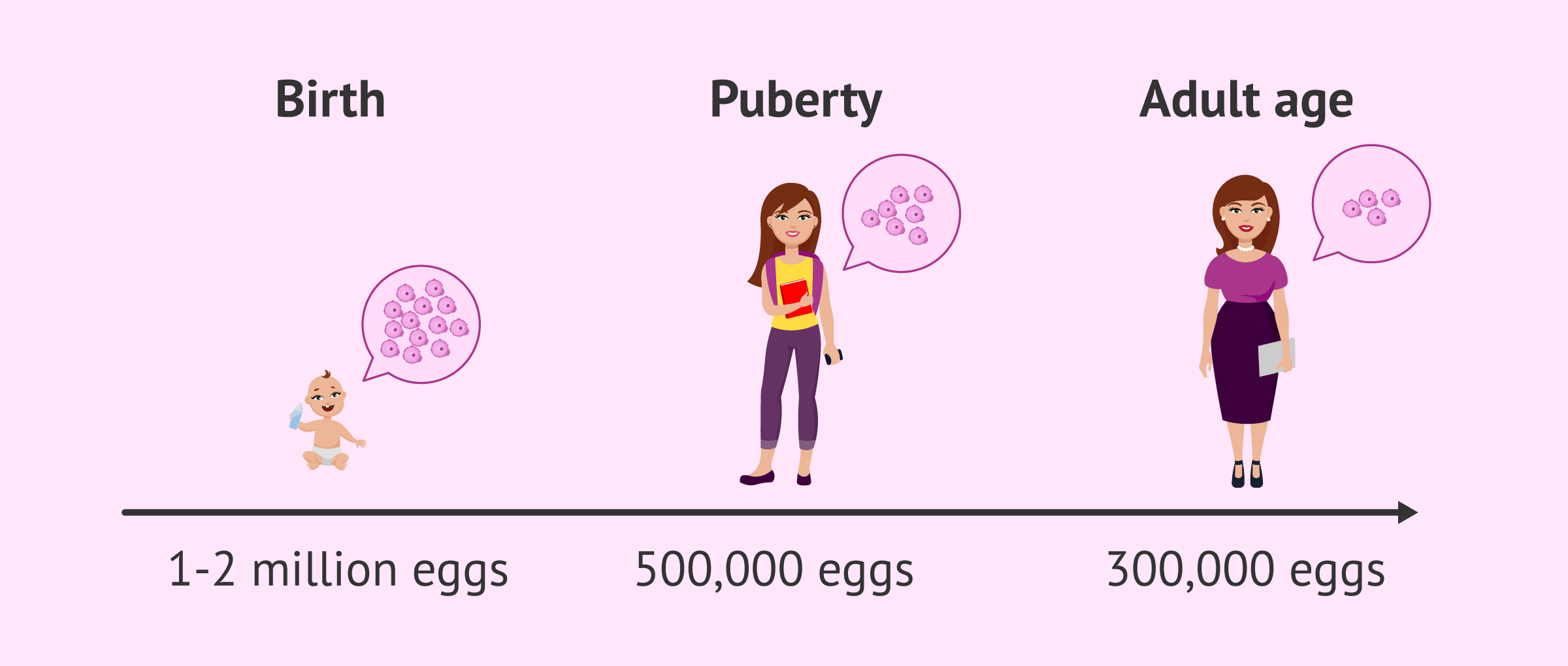






Hi
I am 28 now and I keep seeing adverts to become an egg donor. How do I know if my egg quality is good enough to become a donor?
Hi OliviaV_23
Becoming an egg donor is a very rewarding thing to do, as you will be helping couples who cannot concieve with their own eggs (or couples without oocytes) fulfil their dreams of becoming parents.
Is isn’t possible for you to know the quality of your ooctyes until they have been used for IVF purposes. However, to insure that donated eggs are likely to be of the highest quality, egg donors have to pass stringent criteria including age, phsyical and mental health, have normal ovulatory function, not suffer any genetic, infectious or hereditary diseases, not be adopted and not have more than 6 biological children.
Here are links to two articles which you may find useful:
Egg donation: requirements, procedure and compensation
What are the requirements for egg donation?
I hope this answers your question!
All the best