Epididymitis is the inflammation of the epididymis, the tubular structure in which sperm mature and which connects the testicle to the vas deferens.
This condition causes severe pain and swelling and is often very uncomfortable for men. In addition, during the time the disease lasts, the man loses sexual potency.
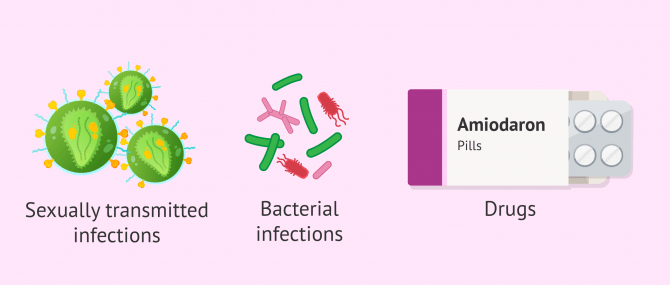
Epididymitis is usually caused by a bacterial infection or by sexually transmitted infections, such as gonorrhea and chlamydia. However, the cause of this pathology can also be viral and fungal, although these are more rare cases.
Provided below is an index with the 9 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 1.1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 5.
- 6.
- 6.1.
- 6.2.
- 6.3.
- 6.4.
- 6.5.
- 6.6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
What are the causes of epididymal inflammation?
The main cause of epididymitis is the spread of microorganisms from tissues near the epididymis, such as the urethra, prostate, and bladder. Depending on the type of triggering agent, a distinction is usually made between bacterial, fungal, viral, and non-bacterial epididymitis.
The following are the most common reasons that can lead to inflammation of the epididymis:
- Sexually Transmitted Infections
- caused by bacteria such as Neisseria gonorrhoea (which causes gonorrhea), and Chlamydia trachomatis (which causes chlamydia). This is the most common cause of epididymitis in sexually active men between the ages of 19 and 35.
- Bacterial infections
- produced by bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and ureoplasma. This case is typical of boys and men over 35.
- Other
- Intake of a drug for abnormal heart rhythms called amiodarone or genitourinary malformations in children under 2 years of age can cause epididymitis. In addition, fungal or viral infections can also cause inflammation of the epididymis.
Risk factors for epididymitis
This pathology is only present in men and, usually, if they are between 19 and 35 years old, it is usually due to sexually transmitted infections. Therefore, some risk factors in this group of patients are as follows:
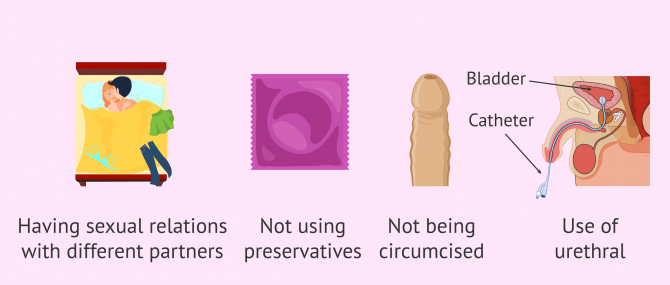
- Having sexual relationships with different partners on a regular basis.
- Having a previous sexually transmitted disease (STD).
- Not using a condom.
When epididymitis is independent of sexual transmission, other factors that increase the risk of this condition are:
- Not being circumcised.
- Recent surgery on the urinary tract.
- Regular use of a urethral catheter.
- Prostate disorders such as prostatic hypertrophy and prostatitis
- Tuberculosis.
For all these reasons, it is best to maintain safe sex and always follow the guidelines established by the specialists.
Symptoms of epididymitis
Epididymitis symptoms usually appear suddenly and can vary from mild to severe depending on the patient's condition. When the inflammation of the epididymis lasts longer than 6 weeks or recurs after a while it is a chronic epididymitis.
The most frequent clinical manifestations of epididymitis are the following, although not all of them need to be present:
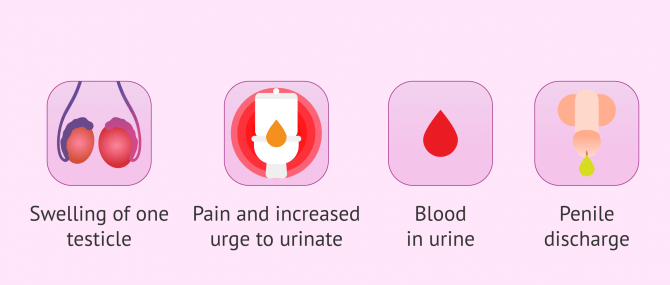
- One-sided pain and swelling of the genital area.
- A feeling of heaviness and warmth in a testicle.
- Pain or discomfort when urinating, accompanied by frequent urination.
- Blood in the urine and semen.
- Penis discharge.
Sometimes inflammation of the epididymis also leads to inflammation of the testicles, which is called epididymo-orchitis. The pain of the testicles should always be taken into account and you should go to the doctor immediately, especially if you feel a stinging sensation after a blow, no matter if it has been 2 or 3 days.
Diagnosis of an inflamed epididymis
Epididymitis can sometimes be confused with testicular torsion. Therefore, it is of vital importance to establish a proper diagnosis in order to choose the best treatment.
Testicular torsion is a condition in the male characterized by bending of the arteries, veins, nerves and spermatic cord, which causes blockage of seminal fluid circulation. Testicular torsion is an unknown cause and appears suddenly.
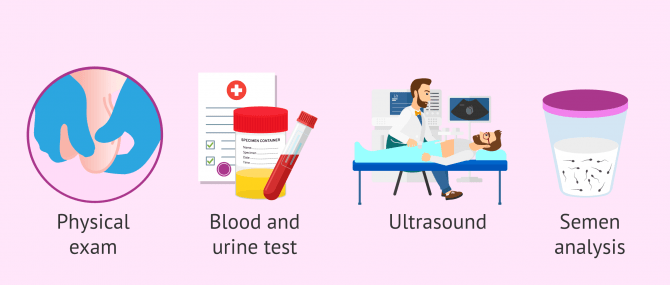
The doctor will perform a physical examination of the penis, prostate, and scrotum. In addition, the specialist will ask the patient about the symptoms and any previous pathology in order to take a medical history.
Subsequently, it will be necessary to request the following medical tests:
- Blood and urine tests
- to assess for bacterial infection.
- Ultrasound
- allows the study of blood flow in the testicles to rule out testicular torsion. This test is essential because testicular torsion needs immediate surgery.
- Semen Analysis
- Performing a seminogram is also an option to study the presence of leukocytes in the semen, which would be indicative of infection.
With the results of all these diagnostic tests, the specialist will be able to determine if epididymitis is present and the cause of the epididymitis.
Is there a treatment for epididymitis?
The treatment of epididymitis depends on the cause of the inflammation. Specifically, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics to stop the bacterial infection. If the inflammation of the epididymis is the result of a sexually transmitted infection, then specific antibiotics will be used, but they will also have to be administered to the sexual partners.
Sometimes it is necessary to administer analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs to calm the swelling and pain.
In case the epididymitis is caused by amiodarone, the treatment will consist of a lower dose or a change of medication directly.
Home remedies for epididymitis
Although antibiotics are most commonly used against epididymitis, there are also home treatments or recommendations to alleviate the discomfort of an inflamed epididymis:
- Bed rest by elevating the scrotum.
- Apply ice to the genital area.
- Visit the doctor after a few days of treatment.
In the absence of treatment, or poorly cured epididymitis, this condition can become chronic. In these situations, the male does not show swelling, but pain in the genital area. If epididymitis becomes complicated, it may lead to infertility. Therefore, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible to treat this infection and avoid future complications.
Epididymitis and fertility
Generally, when a male suffers from an STD, there can be sequelae and the obstruction of the epididymis or testicular infarction can appear. Therefore, sperm vitality would decrease and lead to male fertility problems.
The main reason for this is that when the epididymis is obstructed, the sperm cannot get out and azoospermia occurs, i.e. there are no sperm in the ejaculate.
Natural pregnancy is complicated in this situation and assisted reproduction techniques must be used. If there is azoospermia, a testicular biopsy will be necessary for the recovery of spermatozoa, and then an in vitro fertilization by means of sperm microinjection (IVF-ICSI) will be performed.
Furthermore, inflammation of the epididymis produces a rise in the temperature of the testicular area, which negatively affects sperm production (spermatogenesis). Therefore, in the most serious cases of epididymitis, the solution would be to use donor sperm to achieve a pregnancy.
FAQs from users
Can I work out with epididymitis?
Epididymitis is an inflammation of a part of the testicle called the epididymis, which is located at the back of the testicle. The function of the epididymis is to store and transport sperm. Among the causes of epididymitis, the most common are sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, other urinary tract and prostate infections, or trauma.
The inflammation usually produces significant pain and redness and swelling of the testicle. Recommended measures to improve symptoms include rest, moving the testicle can worsen inflammation and cause pain, so it is not recommended. Bed rest, lying down with the scrotum elevated, applying cold compresses to the inflamed area, using a testicular jockstrap, avoiding efforts such as picking up heavy objects and avoiding sexual relations.

What factors favor epididymitis?
Factors that increase the risk of epididymitis or inflammation of the epididymis are recent male surgeries, structural problems in the urinary tract, frequent use of catheters, sexual intercourse, and prostatic hypertrophy.
It should be noted that epididymitis is usually due to the spread of a bacterial infection.
Read more
Does epididymitis cause erectile dysfunction?
The epididymis is a tubular structure in charge of transporting sperm from the testicle to the seminal vesicle. Acute or chronic inflammation of the testicle is called epididymitis.
The most frequent causes of this condition are infectious, and the symptoms are recognized by testicular pain, increased scrotal size, urethral discharge, and even fever. Erectile dysfunctions in cases of epididymitis are secondary to the above-mentioned symptoms.
Can you have sex during treatment for epididymitis?
Yes, in theory, no problem. However, specialists recommend using a condom to avoid any type of transmission to the partner if the cause of the epididymitis is a bacterial infection.
How long does epididymitis last?
The inflammation of the epididymis may persist for up to approximately 6-8 weeks. However, since this condition is diagnosed and the appropriate treatment is administered, the patient should be noticing improvement in relation to the discomfort, as well as a decrease in the inflammation.
If not, it will be necessary to consult the urologist again to find out what guideline to follow.
Can epididymitis be a complication of vasectomy?
Yes. Once a vasectomy is performed, a man may feel a sense of heaviness or discomfort in the genital area. In addition, he may have some testicular inflammation and pain, which could lead to epididymitis.
In these cases, it is essential to inform the specialist so that he can establish the best treatment for each particular case and some advice on how to alleviate the patient's symptoms.
Suggested for you
Another pathology that can cause seminal infection is inflammation of the prostate. If you want to learn more about it, we recommend you to visit the following article: Prostatitis: Types, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment.
One of the consequences of epididymitis is azoospermia, which makes pregnancy difficult to achieve. If you would like more information about this sperm alteration, you can visit the link: What is azoospermia?- Causes, symptoms, and treatment.
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Brugo-Olmedo S, Chillik C, Kopelman S. Defnición y causas de la infertilidad. Rev Co-lomb Obstet Ginecol 2003; 54: 227-248.2 (View)
Casals RK, Kovell RC, Weiss DA. A Teenager With Recurrent Epididymitis. Urology. 2020 Apr 22. pii: S0090-4295(20)30433-7. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2020.04.051 (View)
Huidobro C. Infertilidad masculina. Rev Med Clin Condes 2010; 21: 368-375 (View)
Palma C, Vinay JI. Infertilidad masculina. Rev Med Clin Condes 2014; 25: 122-128.3 (View)
Ramjit A, Shin C, Hayim M. Complete testicular infarction secondary to epididymoorchitis and pyocele. Radiol Case Rep. 2020 Feb 12;15(4):420-423. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2020.01.001 (View)
FAQs from users: 'Can I work out with epididymitis?', 'What factors favor epididymitis?', 'Does epididymitis cause erectile dysfunction?', 'Can you have sex during treatment for epididymitis?', 'How long does epididymitis last?' and 'Can epididymitis be a complication of vasectomy?'.
Authors and contributors







Hi, I started having pain in my testicle some time ago, I went to my urologist and he said it was epididymitis. He prescribed antibiotics but I’ve been on them for 8 months now and he said it’s chronic epididymitis. In all this time I have tried to get pregnant, but it hurts so much… My wife told me to do a semen analysis and it turns out that I have azoospermia… but I don’t know if it’s important, they didn’t explain anything else. What can we do?
Hi George,
Azoospermia is one of the consequences of chronic epididymitis since the epididymis becomes obstructed and the sperm cannot get out. Therefore, azoospermia is a seminal disorder characterized by the absence of sperm in the ejaculate. For more information, you can read in the following article: What is azoospermia? – Causes, diagnosis, and treatment.
One option to achieve pregnancy would be to perform a testicular biopsy to see if there is a possibility of recovering any sperm directly from the testicle. From this point on, in vitro fertilization with sperm microinjection (IVF-ICSI) would be necessary.
I recommend that you access the Fertility Report, a totally free tool with which you will obtain a personalized document from the clinics in your area of interest that meet our quality criteria and which best adapt to your needs. You will also receive information on prices, services included, some advice, etc.
Hope this helps you,
Best regards