Unhealthy lifestyles and habits have a big influence on the fertility of both men and women.
Among these factors, poor nutrition, obesity, and other eating disorders contribute to the fact that more and more couples are forced to resort to assisted reproduction in order to have children.
Provided below is an index with the 8 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 2.
- 2.1.
- 2.2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 5.1.
- 5.2.
- 5.3.
- 5.4.
- 5.5.
- 5.6.
- 5.7.
- 5.8.
- 5.9.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
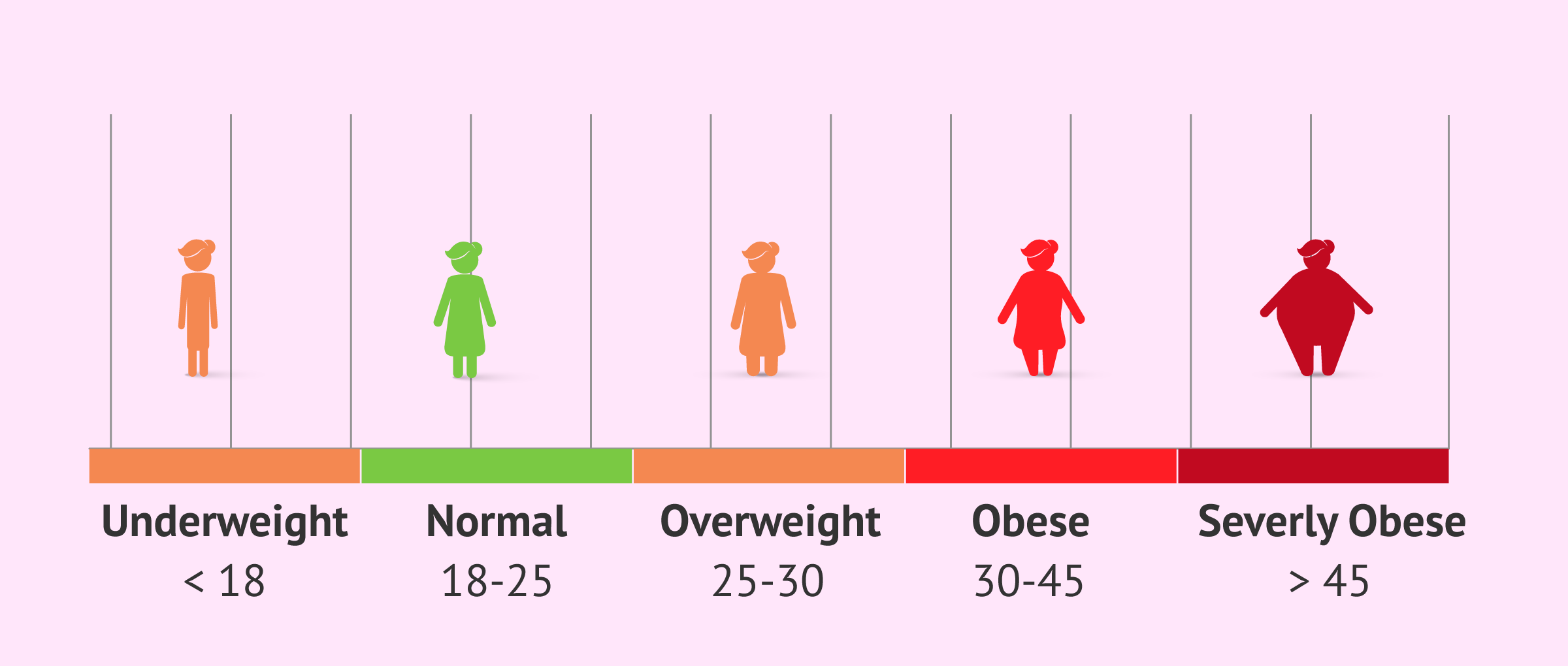
BMI calculation
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measure that relates a person's weight to their height and serves to know if we are within a healthy weight range.
To calculate the BMI, simply use the following mathematical formula: Weight (lbs) x 703/height (in²).
The World Health Organization (WHO) considers the nutritional status of a human being to be healthy when the BMI is between 18.50 and 24.99.
Below, we show the entire classification of nutritional status according to each person's BMI:
- BMI < 18
- Underweight
- BMI 18-25
- Normal
- BMI 25-30
- Overweight
- BMI 30-45
- Obesity
- BMI < 45
- Morbidly Obese
It is recommended that all women seeking pregnancy have an adequate BMI in order to avoid not only fertility problems but also obstetric complications that could put the future baby's health at risk.
Effects of overweight and obesity
Nowadays, Overweight and obesity have become one of the world's major health problems, as people's excess weight increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and diabetes.
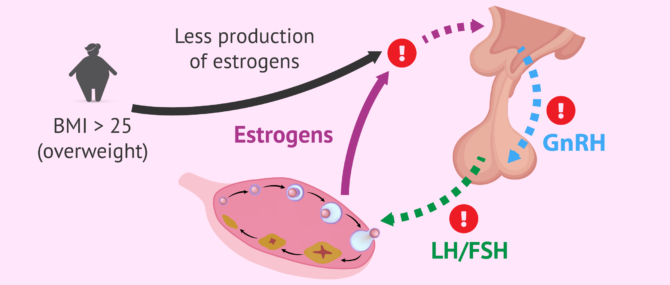
In addition, obesity also greatly affects the reproductive capacity of couples. On the one hand, it reduces the possibility of conceiving naturally and, on the other hand, it reduces the probability of success of an assisted reproduction treatment.
This is because body fat has an effect on estrogen production and blocking gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which in turn is responsible for regulating pituitary function and the release of FSH and LH hormones.
As a result of all this hormonal dysfunction, both the menstrual cycles of women and the sperm production of men are altered.
In the following sections, we will discuss in more depth the effects of overweight and obesity on infertility.
In women
The excess of oestrogens in overweight women affects the entire hypothalamus-hypophysis-ovarian reproductive axis and causes alterations such as the following:
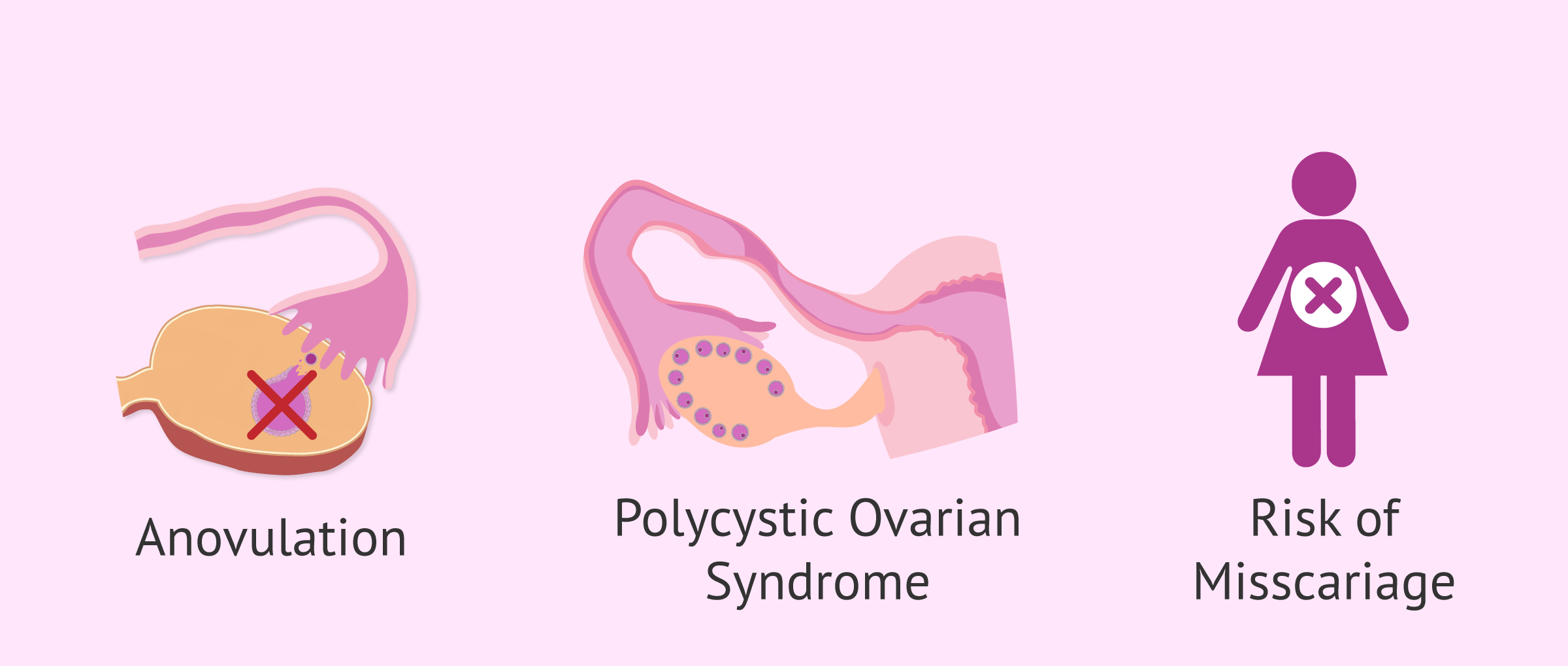
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Anovulation
- Hormonal changes that affect the development of the endometrium
- Mayor risks in reproductive surgeries
- Insulin resistance and association with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Risk of miscarriage
- Increased risk of pregnancy complications: hypertension, gestational diabetes, congenital malformations, increased birth weight, cesarean delivery, etc.
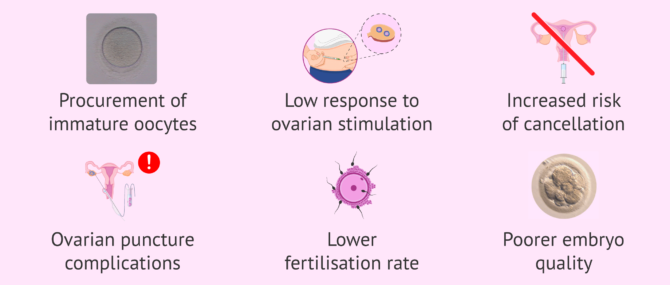
As for assisted reproduction treatments, obese or overweight women also have a lower rate of gestation due to a multitude of problems that may arise during the cycle:
- Resistance to gonadotropins, so they will need a higher hormonal dose in ovarian stimulation
- Follicular asynchrony and obtaining immature eggs
- Low response to stimulation
- Increased risk of cycle cancellation
- Increased risk of complications during follicular puncture
- Lower fertilization rate
- Worse embryo quality
In addition to all of this, it is important to bear in mind that BMI is an important factor to the fertility center. Some fertility centers may not treat women with a BMI of over 30 due to the lower success rates of the treatments.
In men
Obesity is also a cause of male infertility, since it causes alterations in semen and other dysfunctions in the reproductive system. These are discussed below:
- Low testosterone levels
- Erectile dysfunction
- Elevated scrotal temperature
- Alterations in spermatogenesis
- Increased risk of oligozoospermia, asthenozoospermia and teratozoospermia
- Increased rate of sperm DNA fragmentation
All of these abnormalities lead to a higher rate of fertilization failure and implantation failure, as well as an increased risk of miscarriage.
If you want to read more about the effect of being overweight on male fertility, we recommend you enter the following article:
Effects of being underweight
Drastic weight loss or being underweight with a BMI of <18 can also influence the fertility of men and women.This weight loss may be due to dietary restrictions, such as anorexia, or increased energy demands on the body, for example, due to illness or intense physical exercise.Low weight also affects hormone production and metabolism. Therefore, it is common for the following alterations to appear in a woman's menstrual cycle:
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Amenorrhea
- Endometrial alterations that prevent implantation
As for men, low weight also implies sperm alterations, such as reduced concentration and reduced sperm motility.
Recommendations for getting pregnant
Couples who have an altered BMI and are in search of gestation are advised to consult a nutrition expert in order to achieve optimal weight and a healthy pregnancy.
Obese patients should also visit the endocrinologist for stricter follow-up.
In general, a moderate loss of 5-10% of initial weight, through dietary education and physical exercise over six months, may be sufficient to restore reproductive function and achieve a natural pregnancy.
Next, we are going to give some essential advice and recommendations to achieve an adequate BMI and a correct distribution of body fat:
- Complete lifestyle changes
- Having a healthy and balanced diet based on the intake of vegetables, fruits, fish, legumes, etc.
- Taking folic acid supplements
- Moderate excercising
- Avoiding exposure to toxic agents and the consumption of substances such as alcohol, tobacco, caffeine, etc.
In short, all sterility problems resulting from excessive thinness or overweight can be reversed by simply modifying lifestyle and eating habits.
By regaining normal weight, it is possible to stabilize hormonal imbalances again and thus restore male and female fertility.
In assisted reproduction treatments, weight loss also helps women respond better to ovarian stimulation and ovulation induction drugs.
Besides, maintaining a healthy weight not only reduces infertility and the risk of complications during pregnancy but also contributes to overall health and improves self-esteem.
FAQs from users
How does one's lifestyle affect fertility?
Whether you're thinking about getting pregnant or you've already been trying, it's never too soon or too late to evaluate your lifestyle choices. Starting healthy habits or getting rid of the bad ones can improve your overall health. And some lifestyle changes can improve fertility for both you and your partner. For example, quit smoking, reduce alcohol use, eliminate street drugs, practice safe sex, avoid (male) overheating, limit caffeine intake, and exercise regularly.
Is the man's BMI also taken into account for IVF and AI?
There is very limited information about the effects of obesity and overweight in the male and the results of fertility treatments.
Most studies conclude that there is no relationship between high male BMI and semen quality.
Read more
What is the maximum BMI to be accepted for IVF treatment?
Obesity has been shown to decrease the spontaneous fertility of a couple by alteration of the male factor, that is to say, of the seminal quality and also by alteration of the ovarian function.
In addition, gestation rates after assisted reproduction treatments are also reduced when this factor (obesity) is present.
It is probably the female factor that is most intensely affected by a high BMI, since alterations are induced in the ovarian cycle leading to ovulatory dysfunctions and, in addition, a greater number of spontaneous miscarriages.
Although there is no standardised criterion, it is considered that a BMI in women equal to or greater than 30 may interfere with getting pregnant.
Is it common to gain weight after AI or IVF?
Patients who undergo ovarian stimulation usually retain more fluid, as well as increase the volume of their ovaries.
In artificial insemination treatments there is usually no weight gain.
However, in vitro fertilization there is. Although the response is variable, given that the medications and doses can be different, in ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization there is usually an average weight increase of 1 kilo. This increase is transitory and usually decreases at the end of the cycle (as soon as menstruation stops if the treatment has not worked).
Read more
Does BMI affect fertility?
The body mass index is an indicator that links the weight with the height of an individual, determining the body surface area. This equation makes it possible to diagnose weight problems and to measure the risk of pathologies associated with its imbalance.
Since the endocrine system is regulated by hormones and these hormones are involved in metabolic processes, an imbalance in BMI could affect hormonal regulation and alter ovulation.
What consequences can anorexia have for a woman seeking pregnancy?
The problems of excessive thinness in women can cause alterations in their menstrual cycle. Ovulation can become irregular and even disappear, especially when there is a situation of anorexia nervosa.
The decrease in sex hormones can also affect the development of the endometrium, which makes it difficult to implant the embryo and, therefore, reduces the chances of pregnancy.
What risks do children of obese mothers have?
Babies born to obese women are at increased risk for birth defects, such as neural tube defects, cardiovascular abnormalities, and macrosomia (a large baby at birth). They also have an increased risk of complications at birth, perinatal death, and a predisposition to childhood obesity.
Can obesity cause male infertility?
Of course. Different scientists have proven that men with a body mass index over 30 have a poorer seminal quality and, therefore, have greater difficulties in achieving a pregnancy naturally.
The reason for this is that overweight men tend to have low levels of androgens, such as testosterone. As a consequence of this decrease in male sex hormones, spermatogenesis, i.e. sperm production, is affected.
Therefore, men with a high BMI may have oligozoospermia, a semen disorder characterized by a low sperm concentration.
Is it necessary to have a body mass index within the normal range for artificial insemination?
BMI does have a negative influence, although per se, it does not prevent artificial insemination. It will ultimately depend on how this degree of overweight or obesity influences the ovarian cycle and whether or not this can be corrected with medication despite maintaining a high BMI.
Read more
Recommended reading
Ad well as weight, there are other factors related to lifestyle that can cause infertility. You can get more information on this topic here: To what extent do lifestyle factors affect reproductive health?
We have mentioned that increased body weight can also mean a great risk of obstetric complications in pregnancy. For more in depth reading on this subject please visit the following link: What are considered pregnancy complications?
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
Bellver J, Busso C, Pellicer A, Remohí J, Simón C. Obesity and assisted reproductive technology outcomes. Reprod Biomed Online 2006; 12: 562-568 (View)
ESHRE Capri Workshop Group. Nutrition and reproduction in women. Hum Reprod Update 2006; 12: 193-207 (View)
Ferrando M, Bellver J. Impacto de la obesidad sobre la reproducción humana natural y asistida. Rev Esp Obes 2008; 6:302-16 (View)
Nguyen RHN, Wilcox AJ, Skjaerven R, Baird D. Men´s body mass index and infertility. Hum Reprod 2007; 22: 2488-2493 (View)
FAQs from users: 'How does one's lifestyle affect fertility?', 'Is the man's BMI also taken into account for IVF and AI?', 'What is the maximum BMI to be accepted for IVF treatment?', 'Is it common to gain weight after AI or IVF?', 'Does BMI affect fertility?', 'What consequences can anorexia have for a woman seeking pregnancy?', 'What risks do children of obese mothers have?', 'Can obesity cause male infertility?' and 'Is it necessary to have a body mass index within the normal range for artificial insemination?'.
Authors and contributors



More information about Michelle Lorraine Embleton









Hey there! I am really pretty overweight, with a BMI of 36. My doctors have told me to lose weight to increase my chances of becoming a mom and having a better pregnancy. I understand why and the need to do it, but how?! I don´t seem to find the motivation to do it.
Hi hodgekins
It is understandable that you are finding it hard to “lose weight” so maybe getting into a different mindset will help you. Instead of focusing on losing weight and your BMI you could think about making lifestyle changes to healthy habits. These could be simple changes such as decreasing processed foods and eating more fresh food, fruit and vegetables; moving around more and walking instead of driving; find an activity that you enjoy such as dance or sport and do it regularly. Cut back on alcohol.
The combination of small changes can mean that you will slowly drop the pounds while buidling a healthy body and lifestyle, which not only improves your fertility but also your life in general.
I hope this helps.
Best wishes